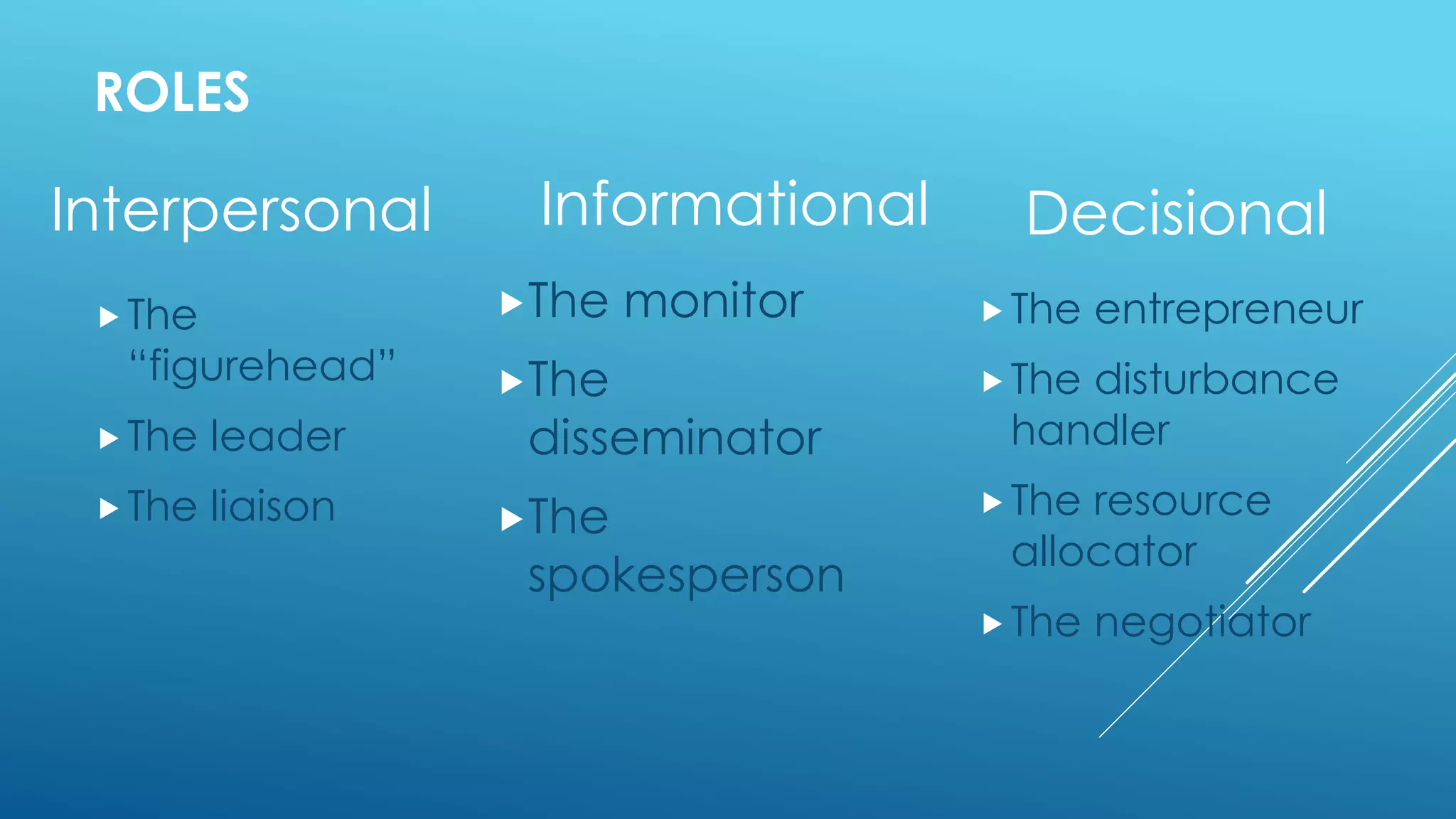
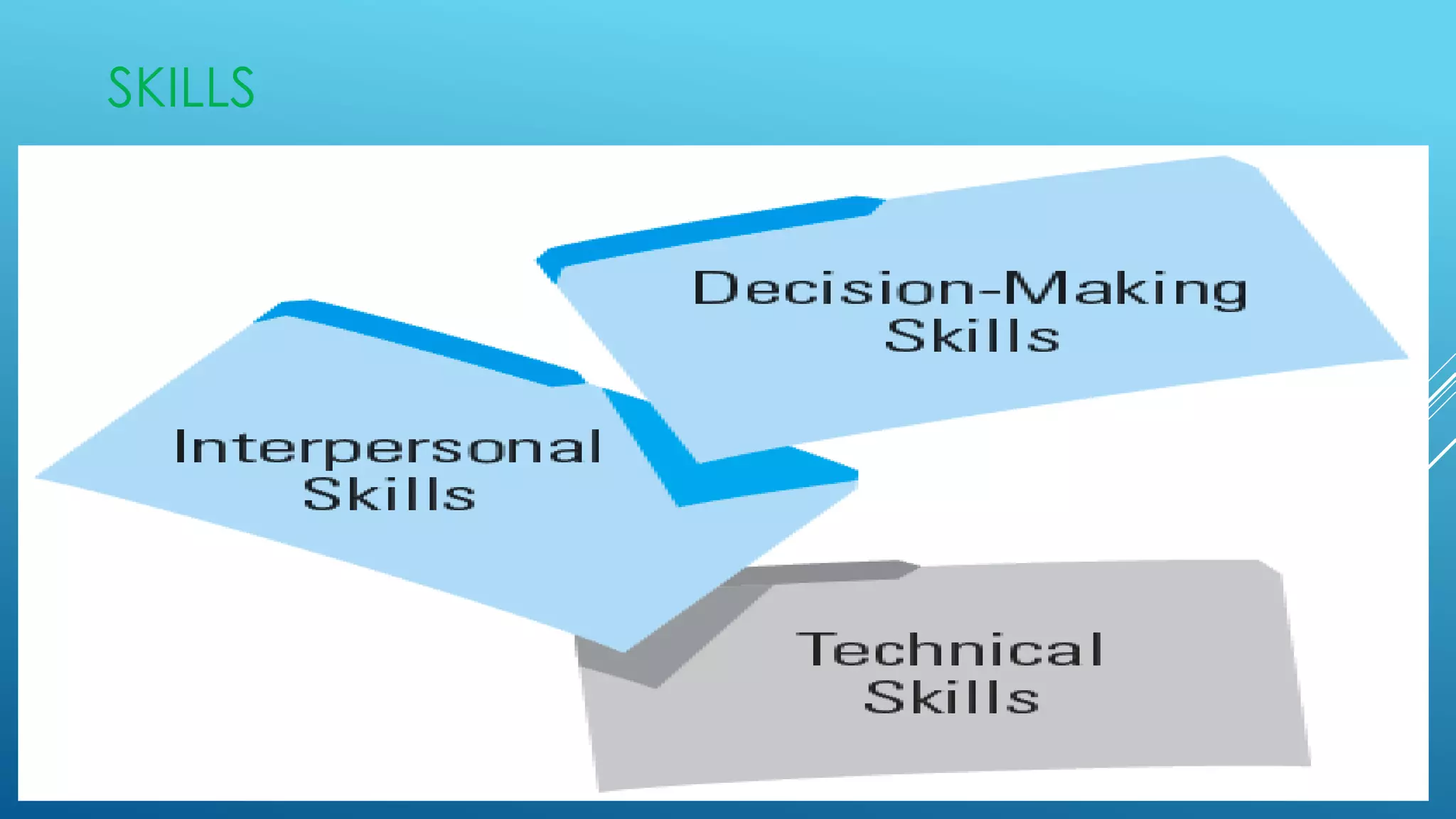
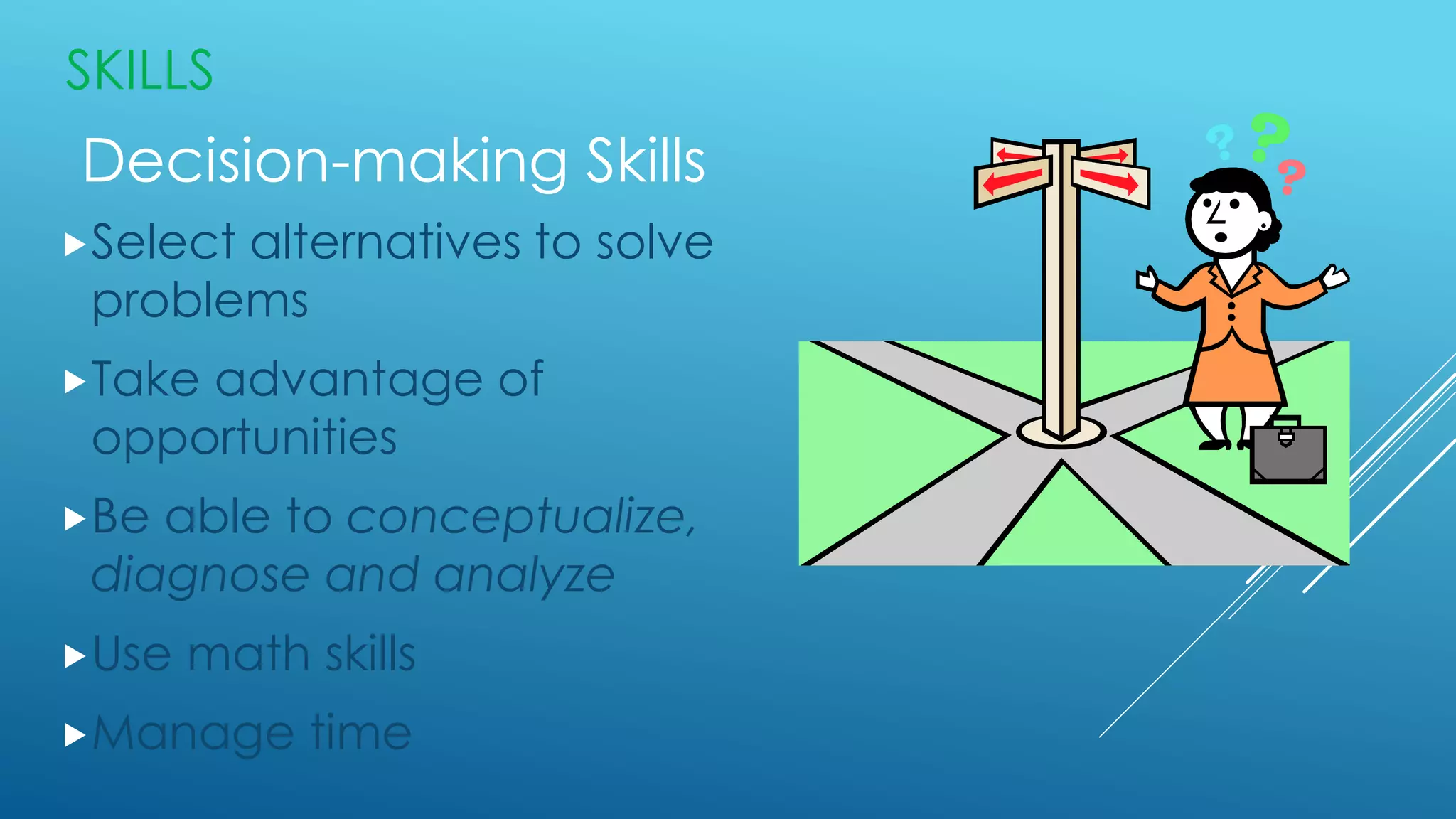
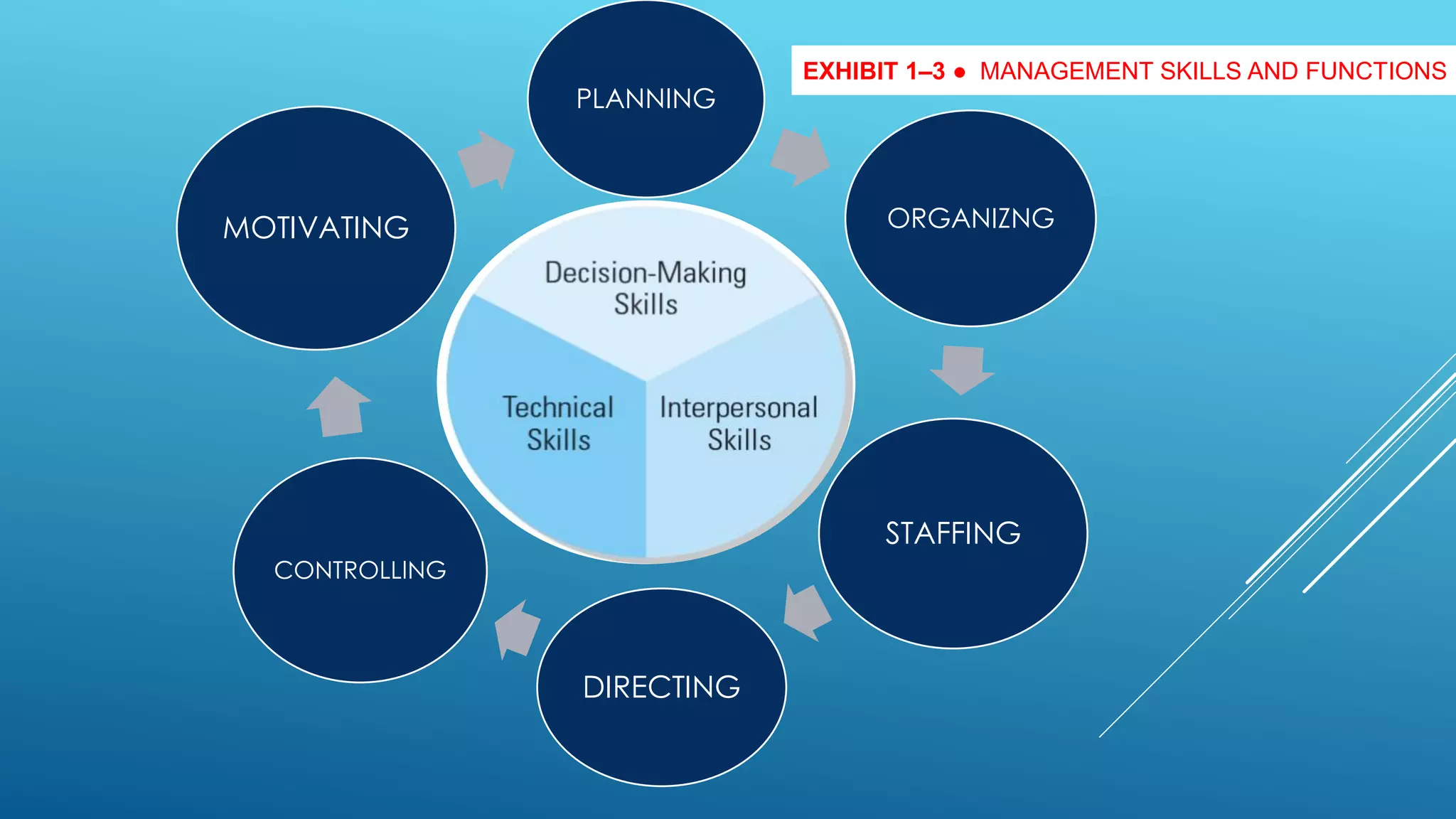
The document discusses the functions, roles, and skills of managers. It describes managers as achieving objectives through efficiently and effectively using resources. The core functions of managers are planning, organizing, staffing, directing, and controlling. Managers fulfill interpersonal, informational, and decisional roles. They require technical, interpersonal, and decision-making skills. Managers use human, financial, physical, and information resources. They can operate at the top, middle, or first-line levels of management within an organization.