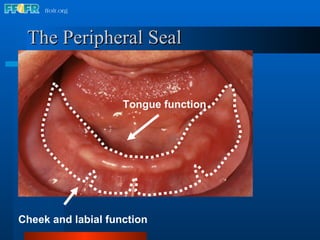
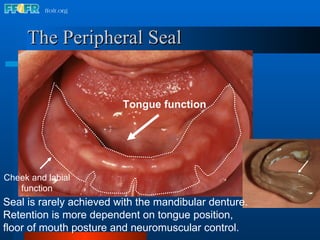
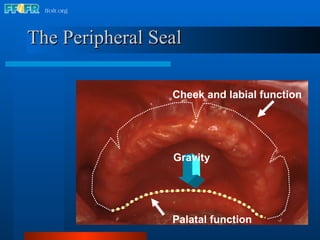
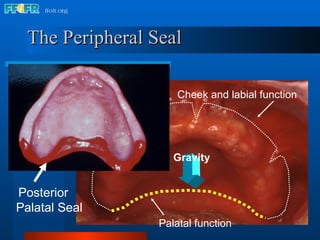
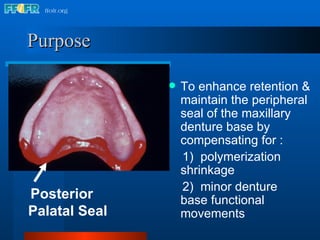
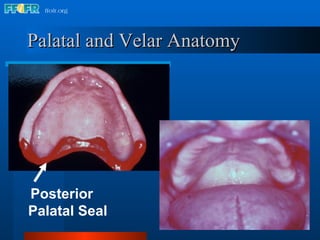
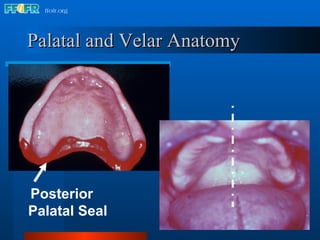
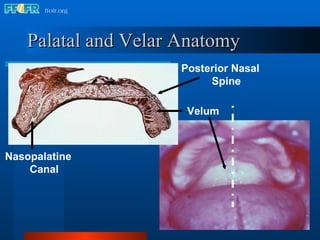
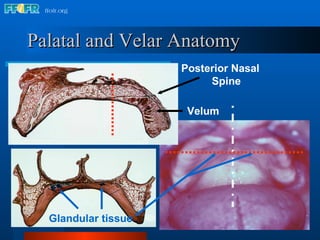
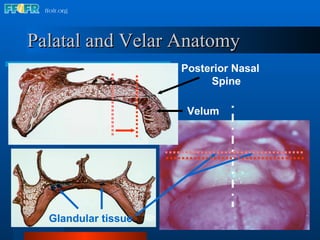
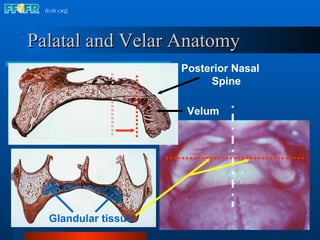
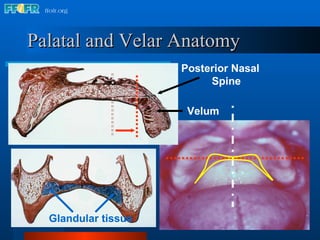
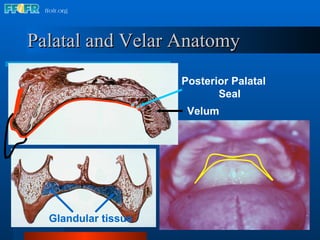
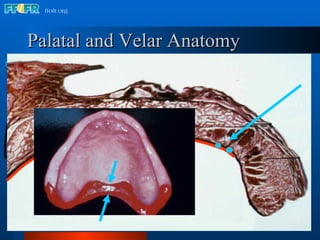
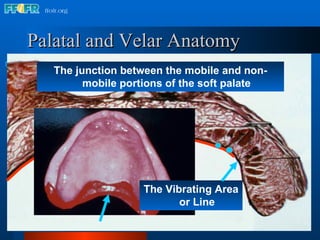
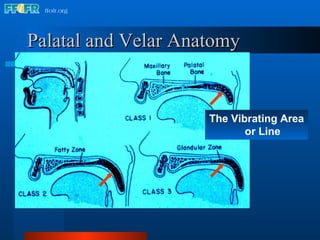
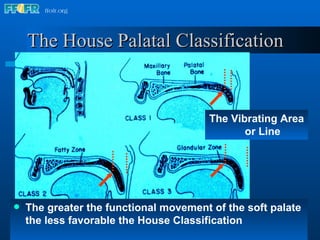
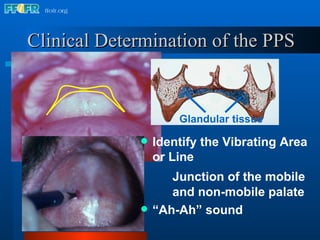
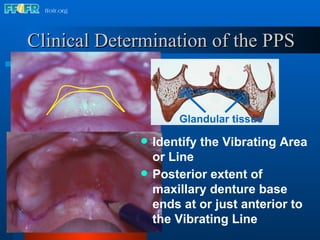
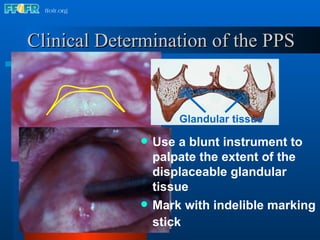
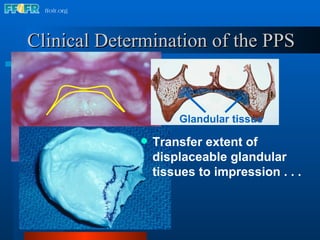
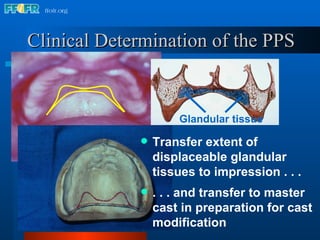
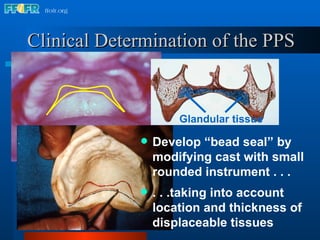
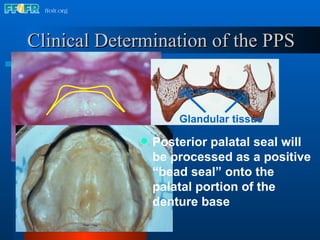
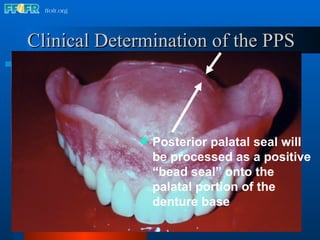
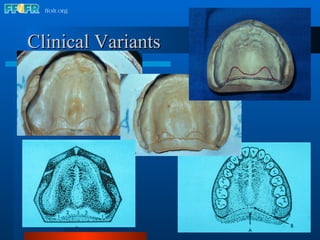
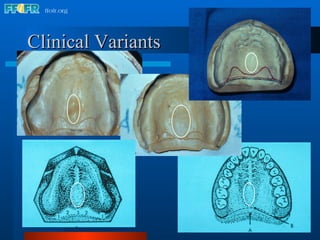
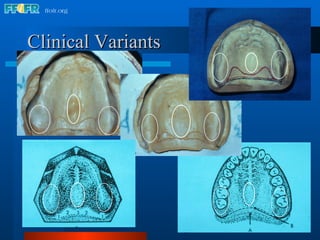
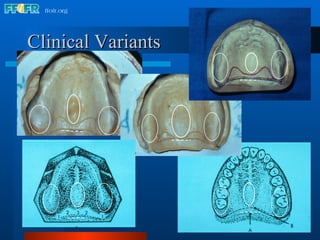
The document discusses the posterior palatal seal, which enhances retention and maintains the peripheral seal of a maxillary denture base. It compensates for polymerization shrinkage and minor denture base movements. The posterior palatal seal is determined by identifying the vibrating area or line between the mobile and non-mobile portions of the soft palate. Glandular tissues are palpated and their extent is marked and transferred to the master cast to modify it with a small rounded instrument, developing a "bead seal" processed onto the denture base.