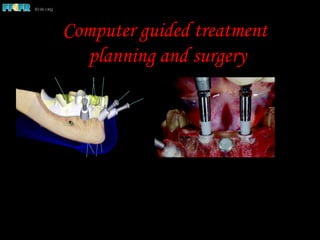
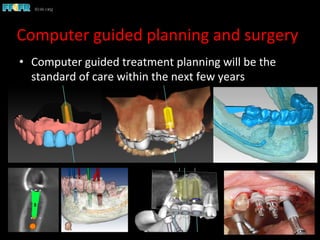
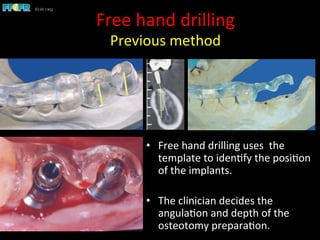
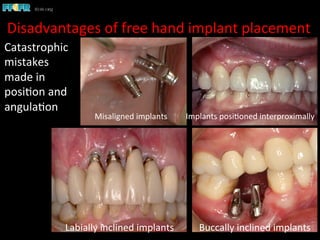
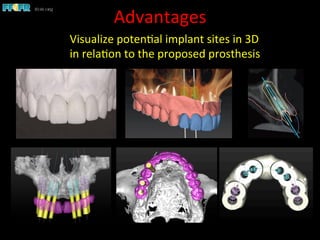
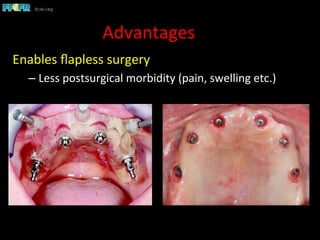
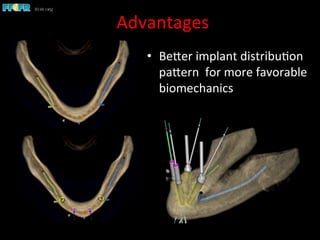
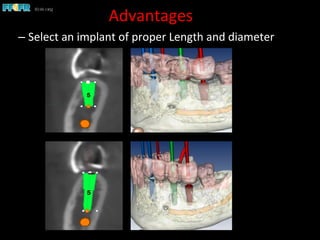
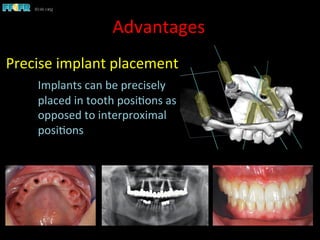
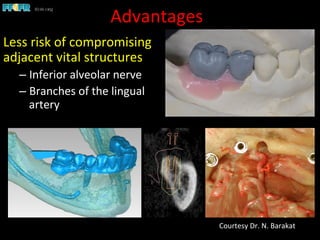
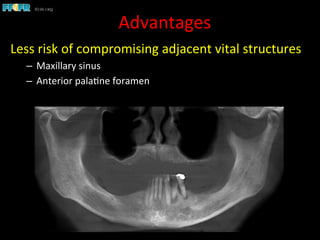
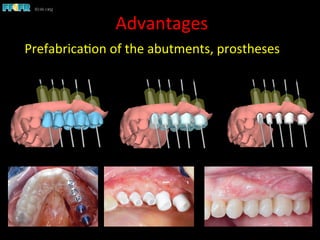
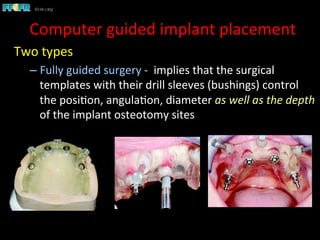
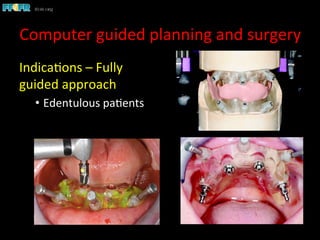
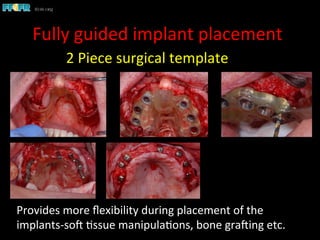
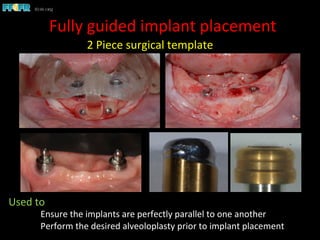
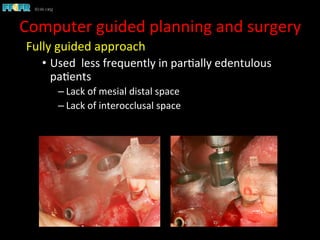
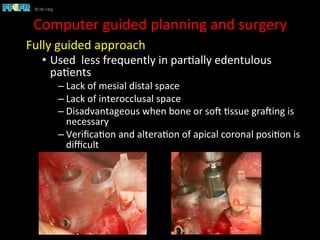
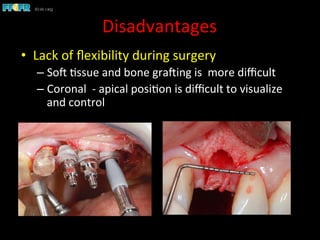
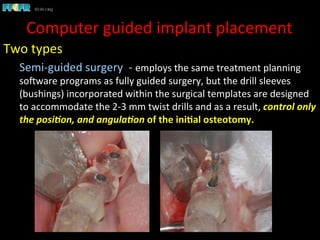
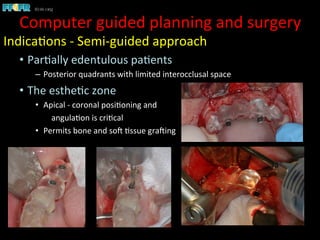
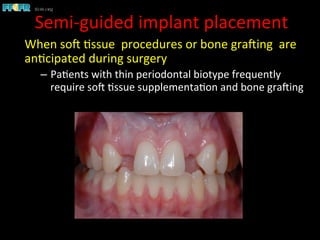
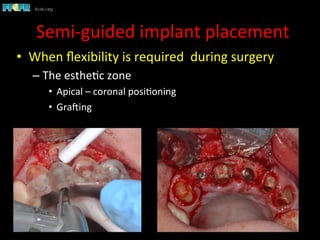
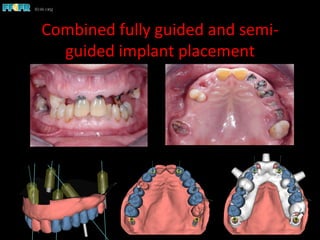
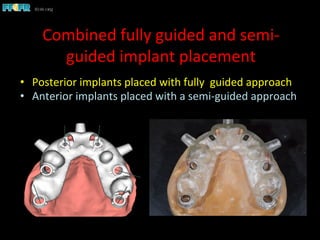
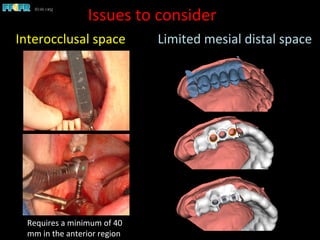
This document discusses computer guided treatment planning and implant placement. It describes how computer guided planning allows visualization of potential implant sites in 3D and more precise placement compared to free-hand drilling. Fully guided surgery uses surgical templates to control position, angle, depth and diameter of osteotomies, while semi-guided surgery controls initial position and angle only, allowing more flexibility. Fully guided is used for edentulous patients, while semi-guided is preferred for partially edentulous patients where soft tissue manipulation or bone grafting may be needed.