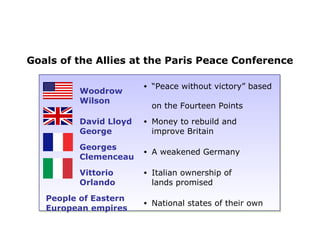
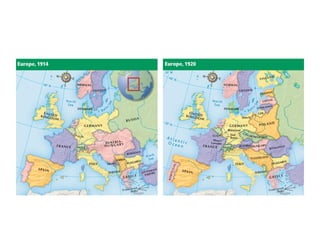
The document summarizes the key factors that influenced the peace treaties ending World War I and the reactions to the treaties. The major powers - Britain, France, US - met at the Paris Peace Conference in 1919 to determine the fate of the defeated Central Powers and colonies. The treaties punished Germany severely and redrew borders in Europe, creating new countries but denying independence to colonies. This led to resentment from Germany and other affected countries and colonies, which some argue sowed the seeds for World War II.