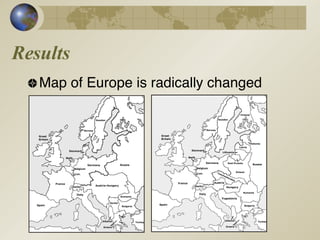
World War I ended with Germany agreeing to an armistice in November 1918. The Paris Peace Conference then established the Treaty of Versailles in 1919, imposing harsh terms on Germany. It forced Germany to accept war guilt, pay large reparations, lose territory, and face military restrictions. While establishing the League of Nations, the treaty dissatisfied Germany and other nations, sowing seeds for future conflict.