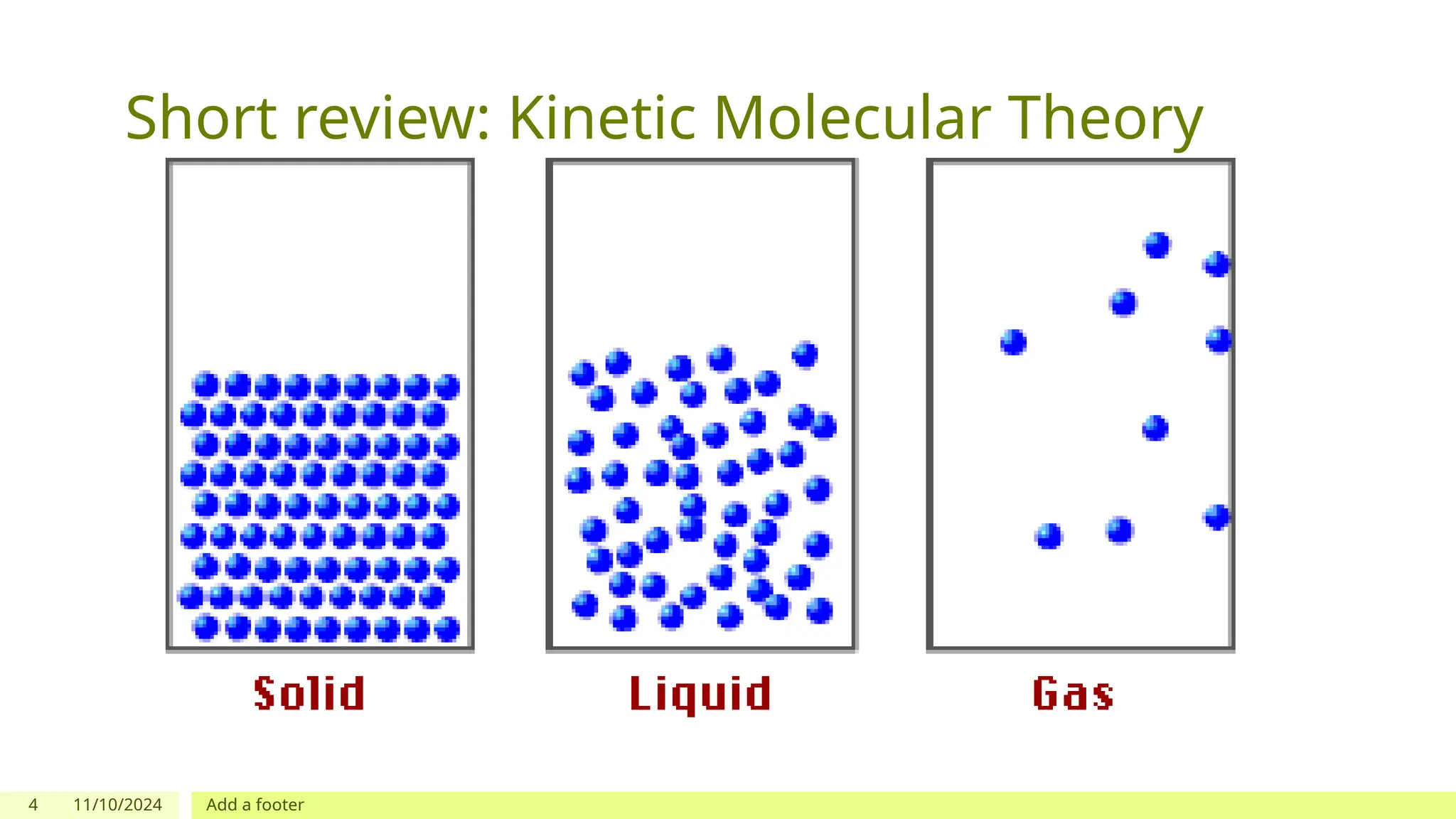
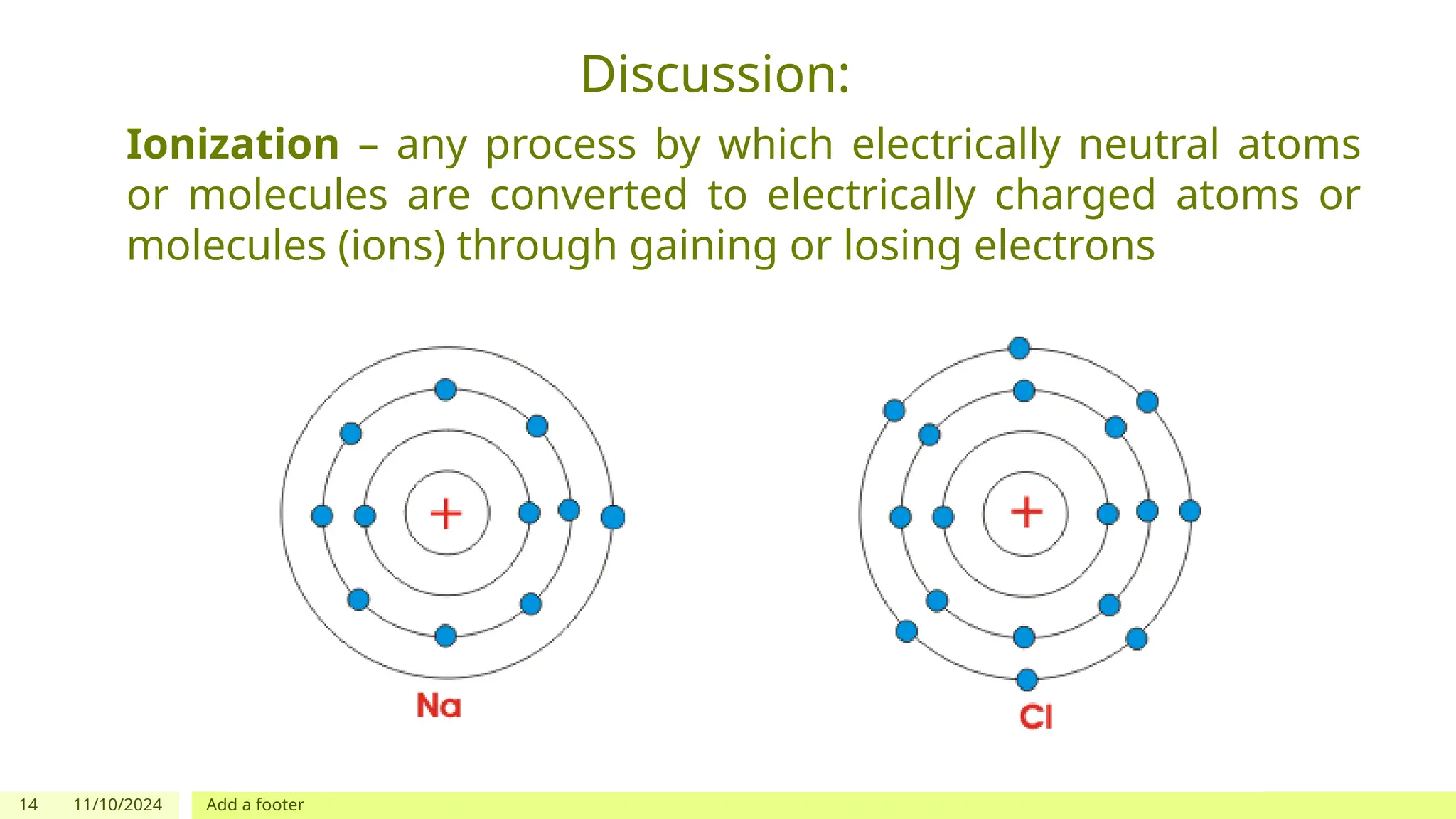
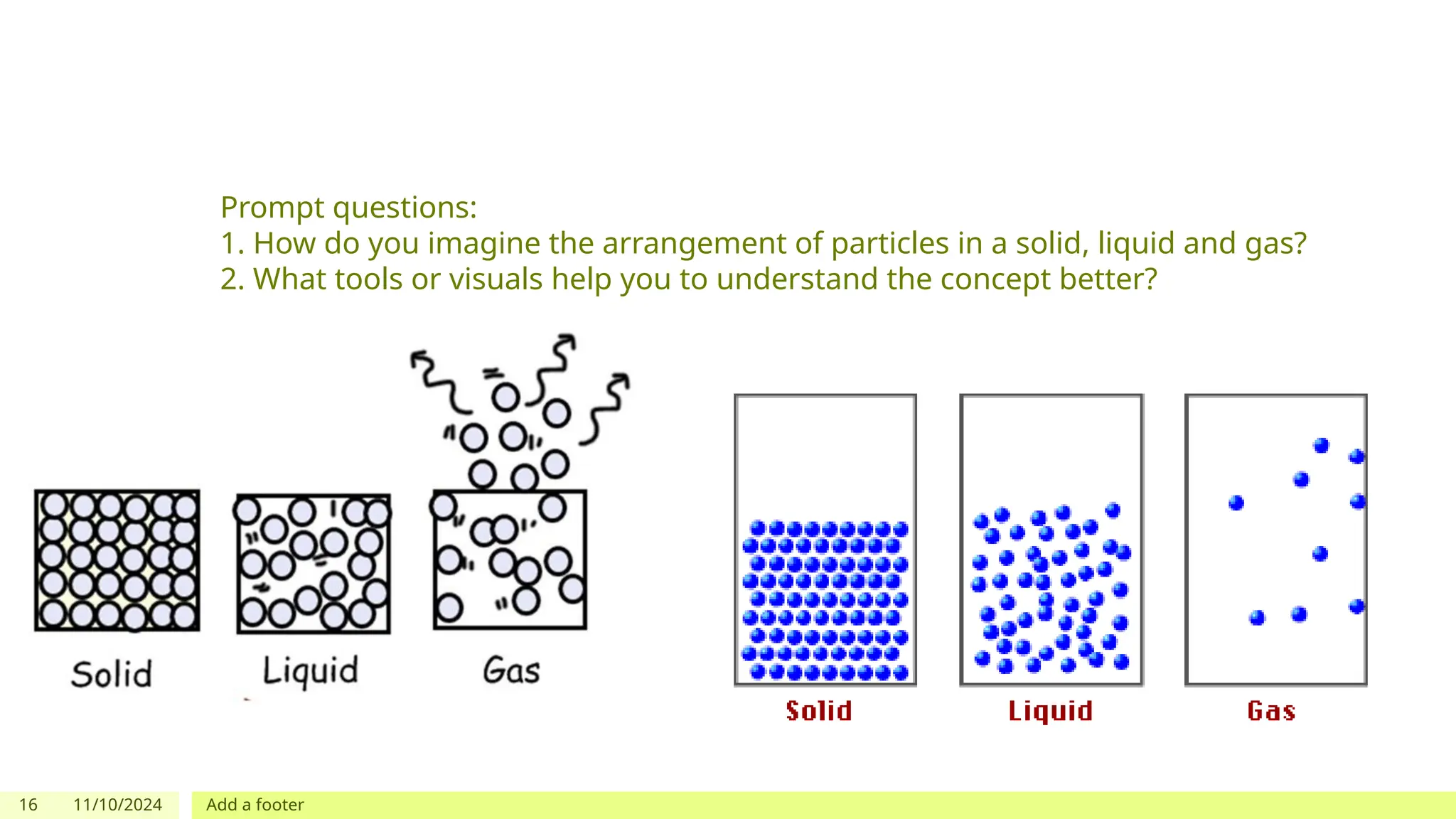
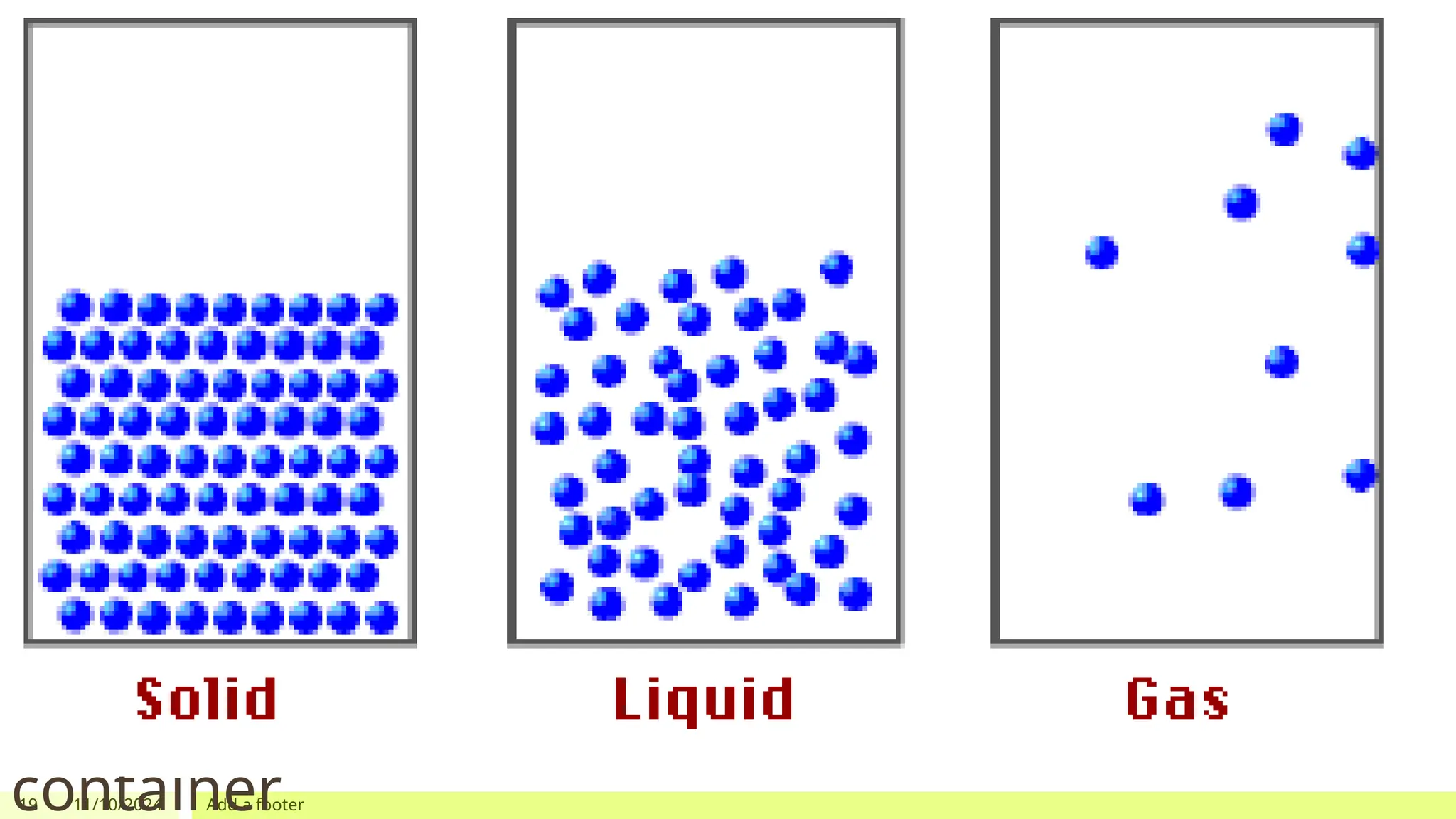
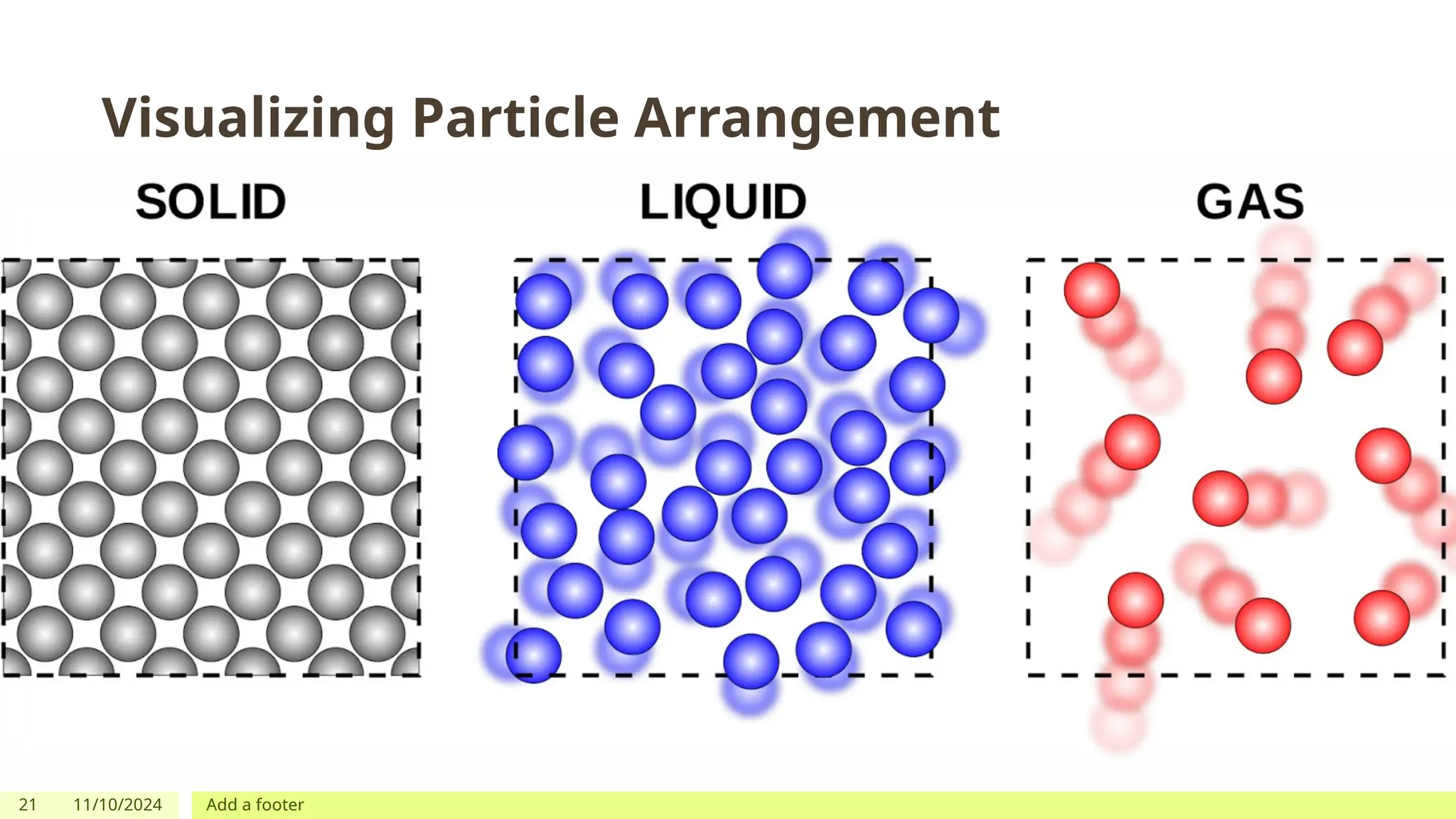
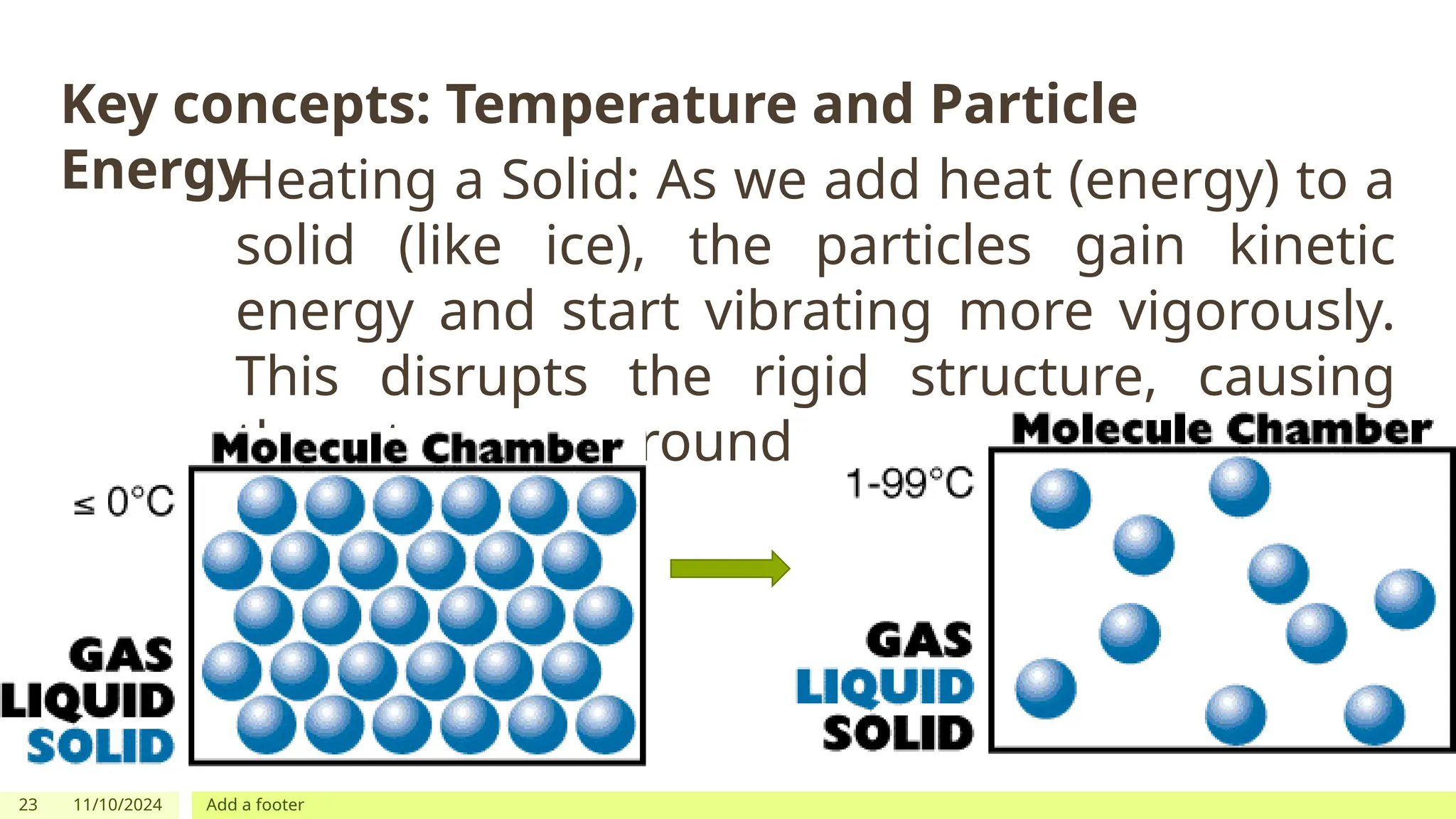
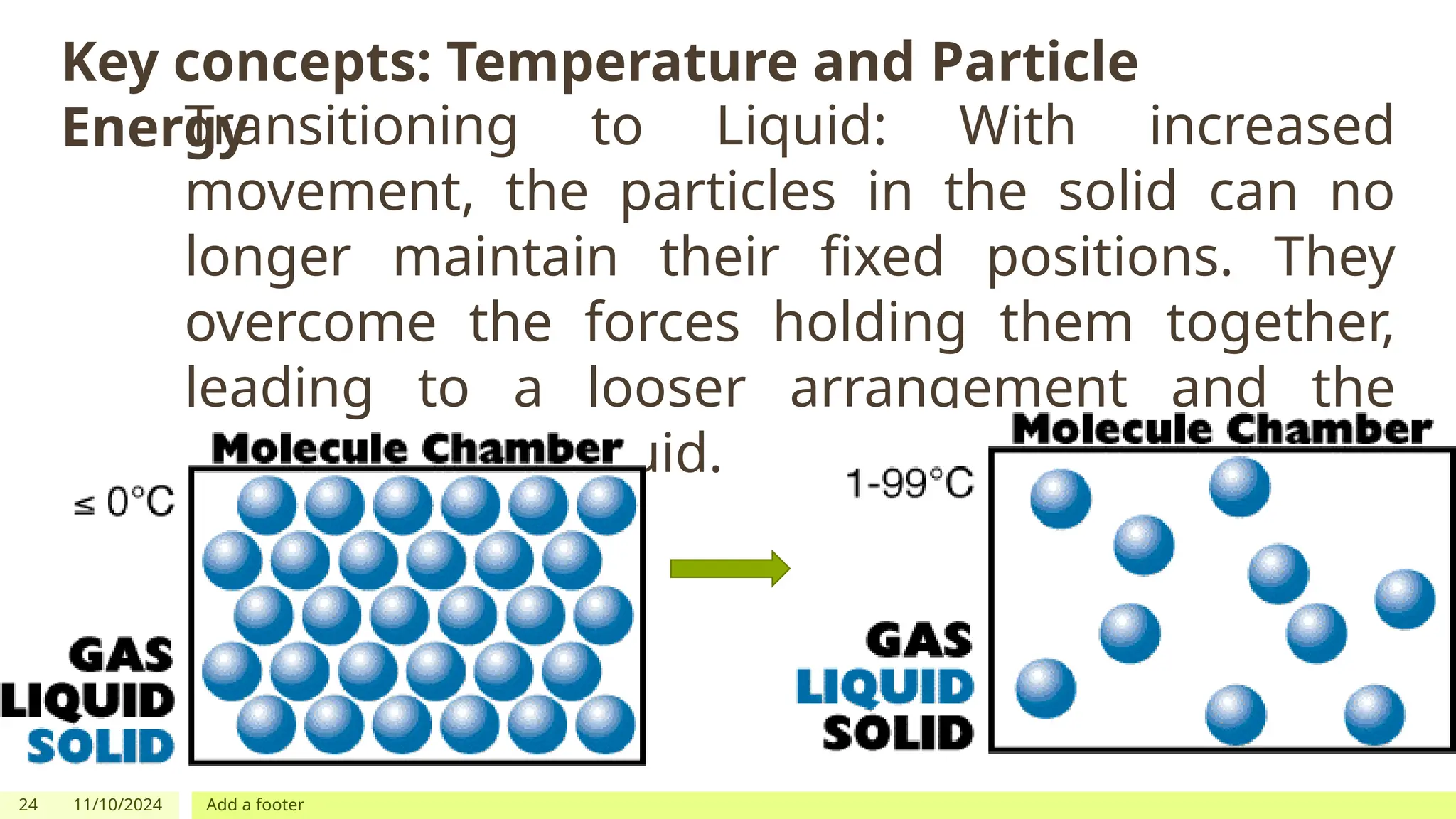
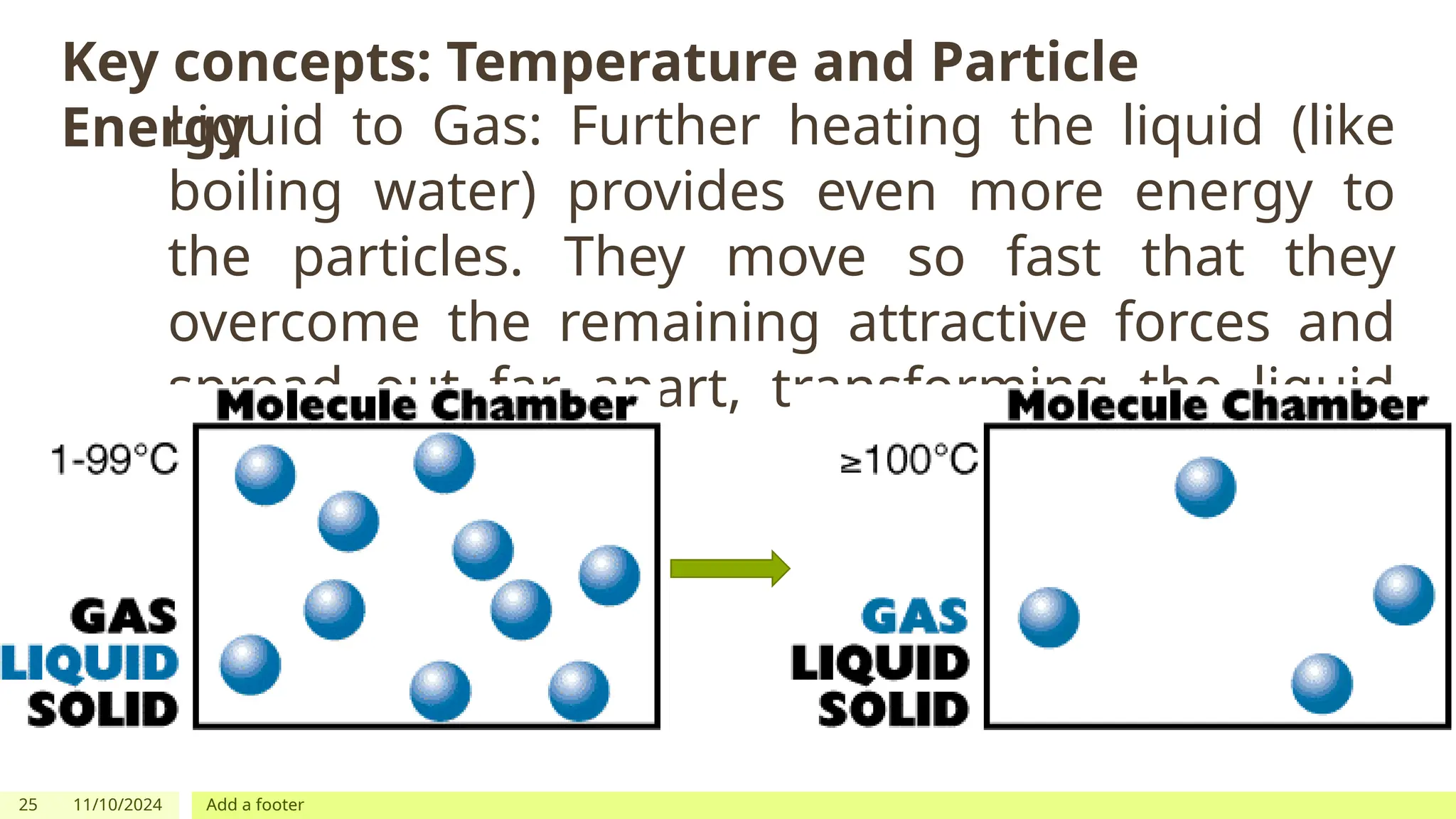
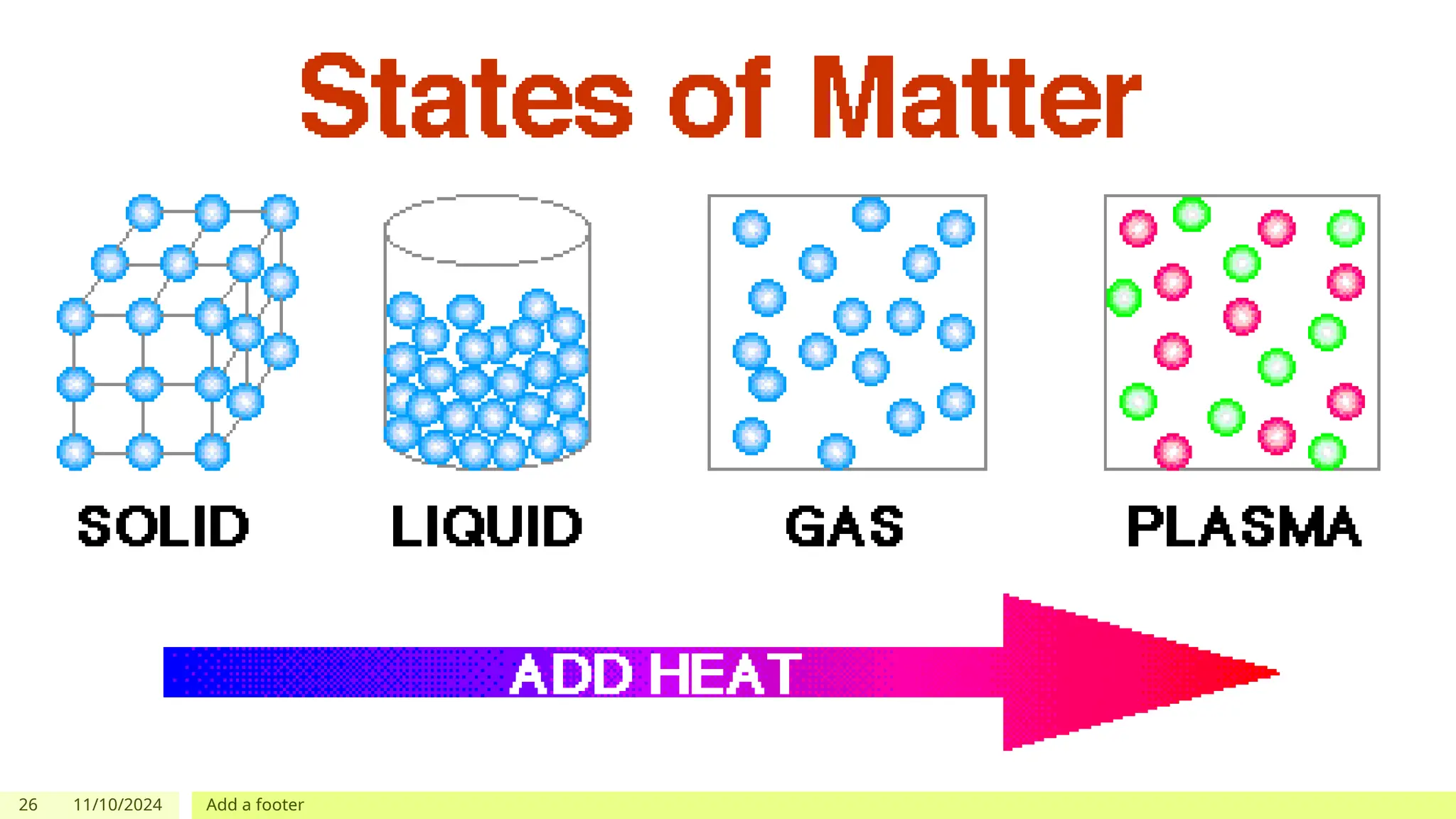
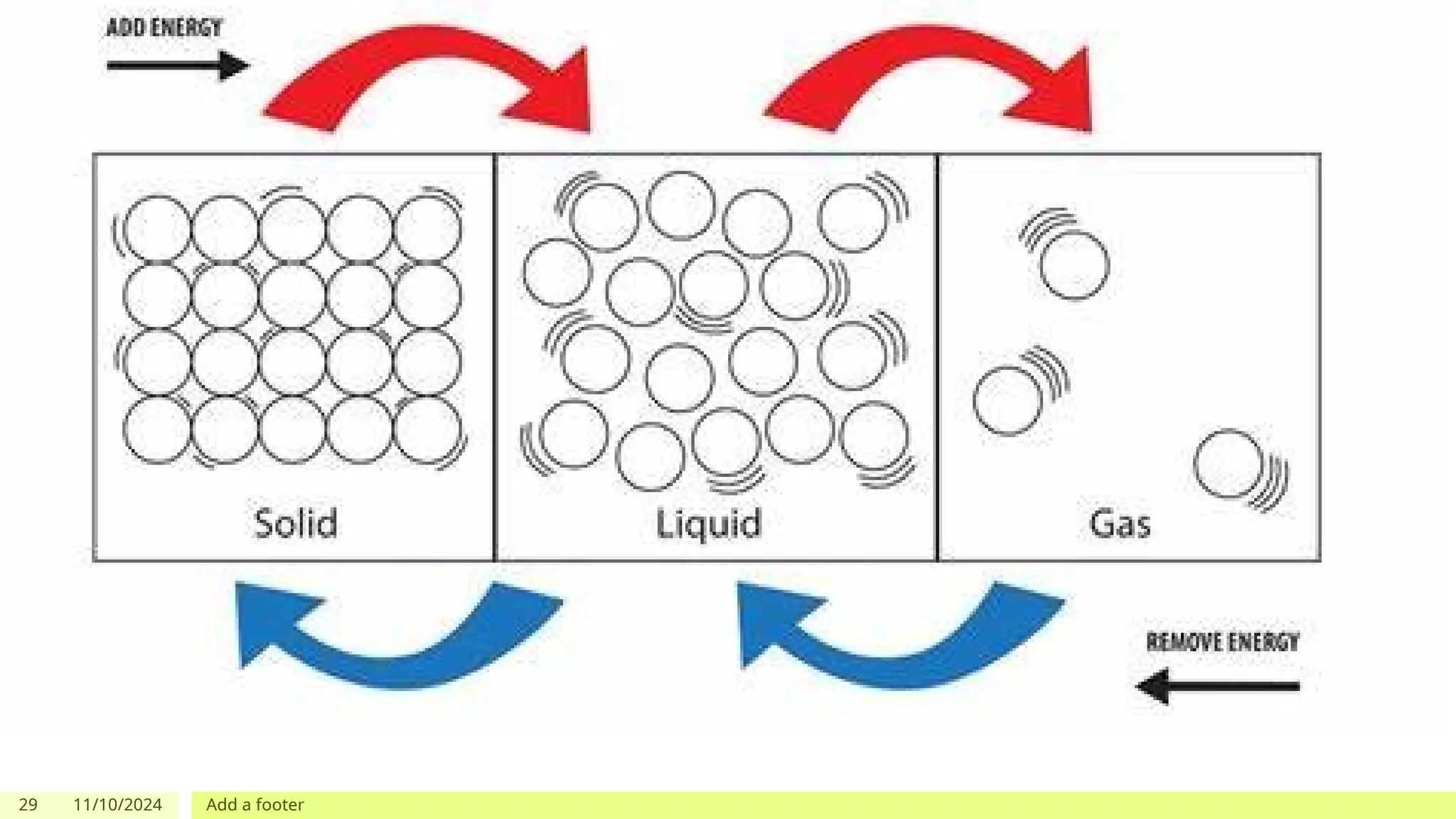
The document outlines learning objectives focused on understanding the states of matter and the changes between them, including solid, liquid, gas, and their respective behaviors at different temperatures. It introduces the kinetic molecular theory, discusses essential vocabulary, and provides demonstrations, discussions, and formative assessments related to changes of state such as melting, freezing, condensation, and evaporation. Key concepts include particle arrangement, energy changes during state transitions, and prompts for visualizing these processes.