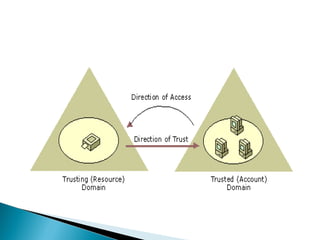
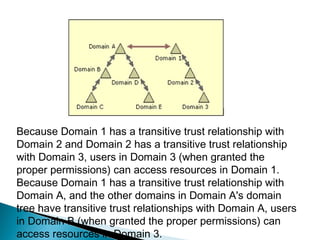
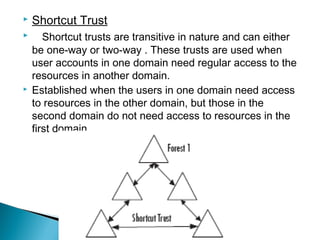
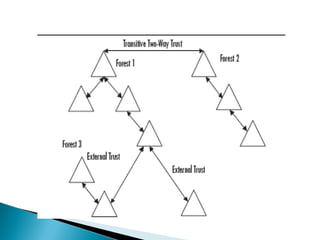
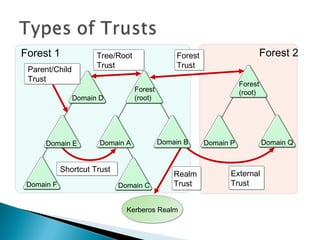
Trust relationships allow authentication and access to resources between domains. There are several types of trusts: transitive trusts allow authentication across linked domains; one-way trusts only flow in one direction; two-way trusts flow both ways; shortcut and realm trusts provide specific authentication flows; and external and forest trusts connect domains across different forests.