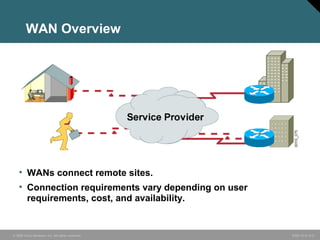
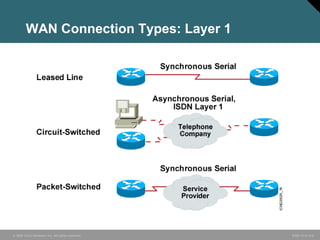
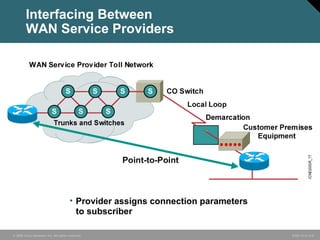
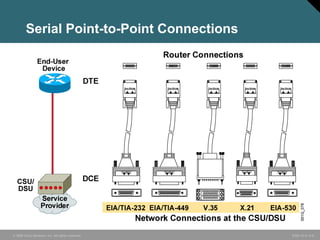
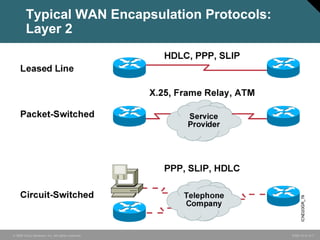
The document discusses wide area networks (WANs) and how they connect remote sites over long distances. It covers WAN connection types, components, and cabling used at layer 1. Layer 2 encapsulation protocols are explained, including HDLC, PPP, SLIP, X.25, Frame Relay and ATM. The summary restates that WANs connect distant sites, different connection options exist depending on needs, and common layer 2 protocols are used to encapsulate data for transmission over WAN links.