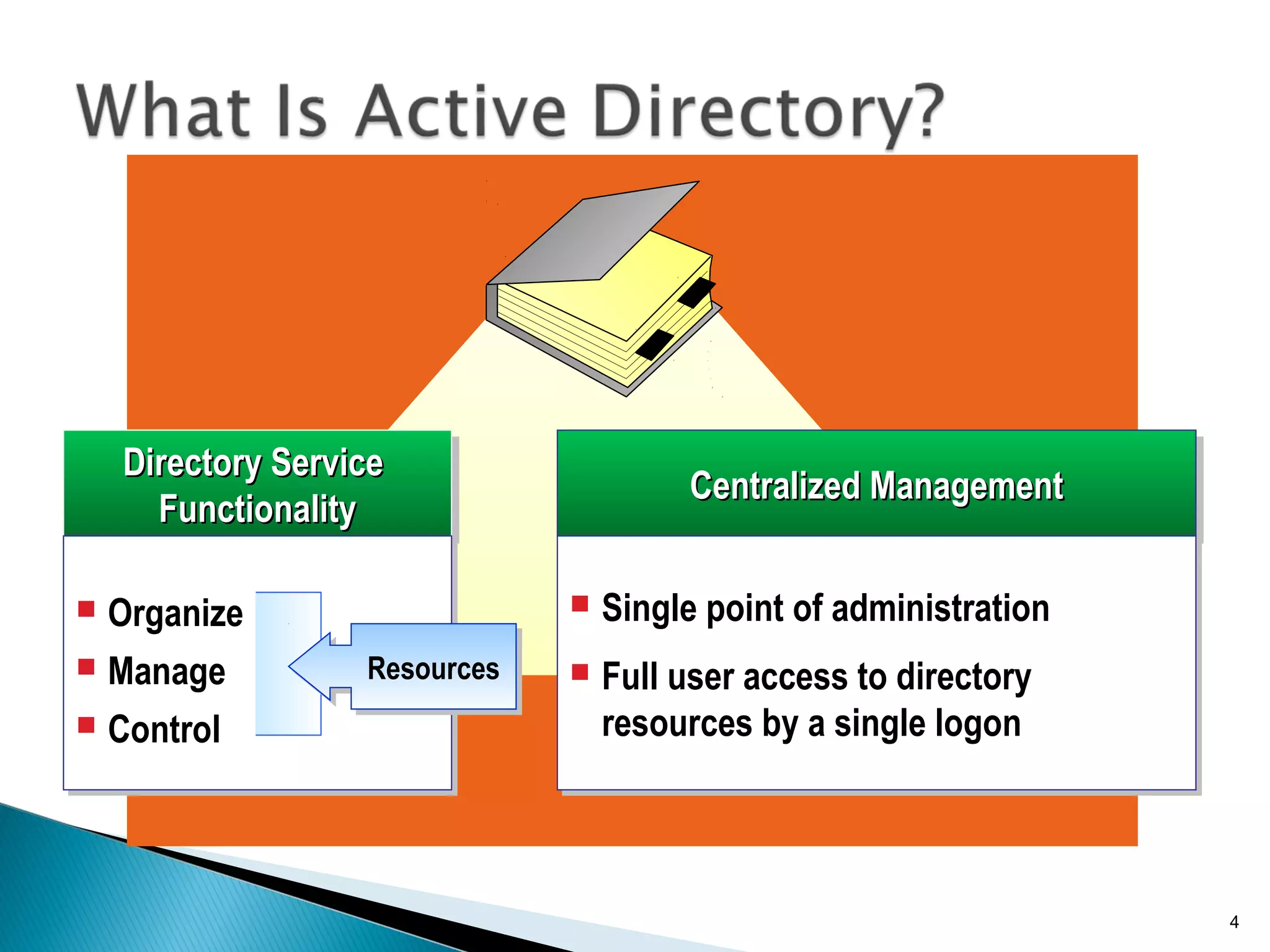
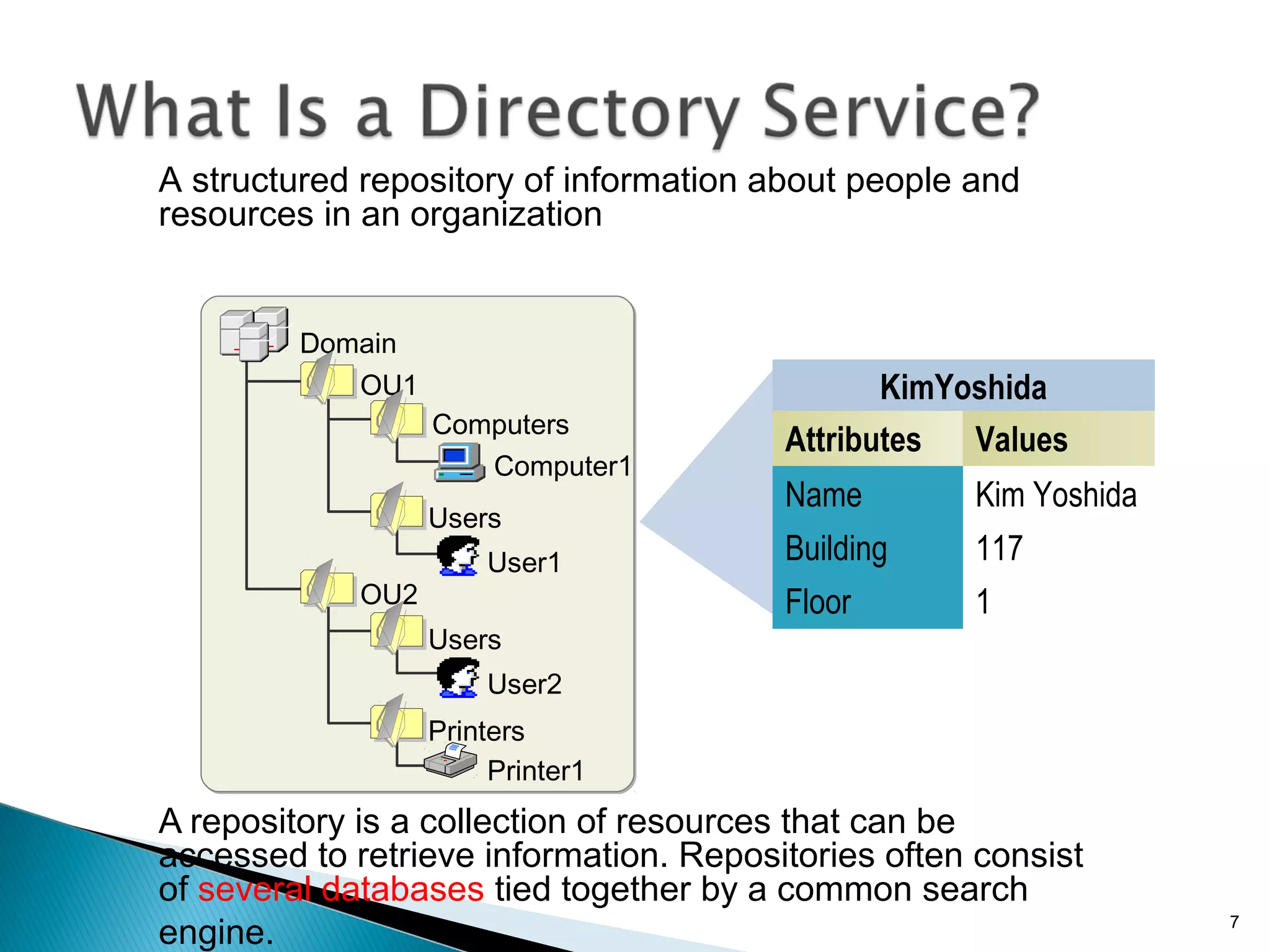
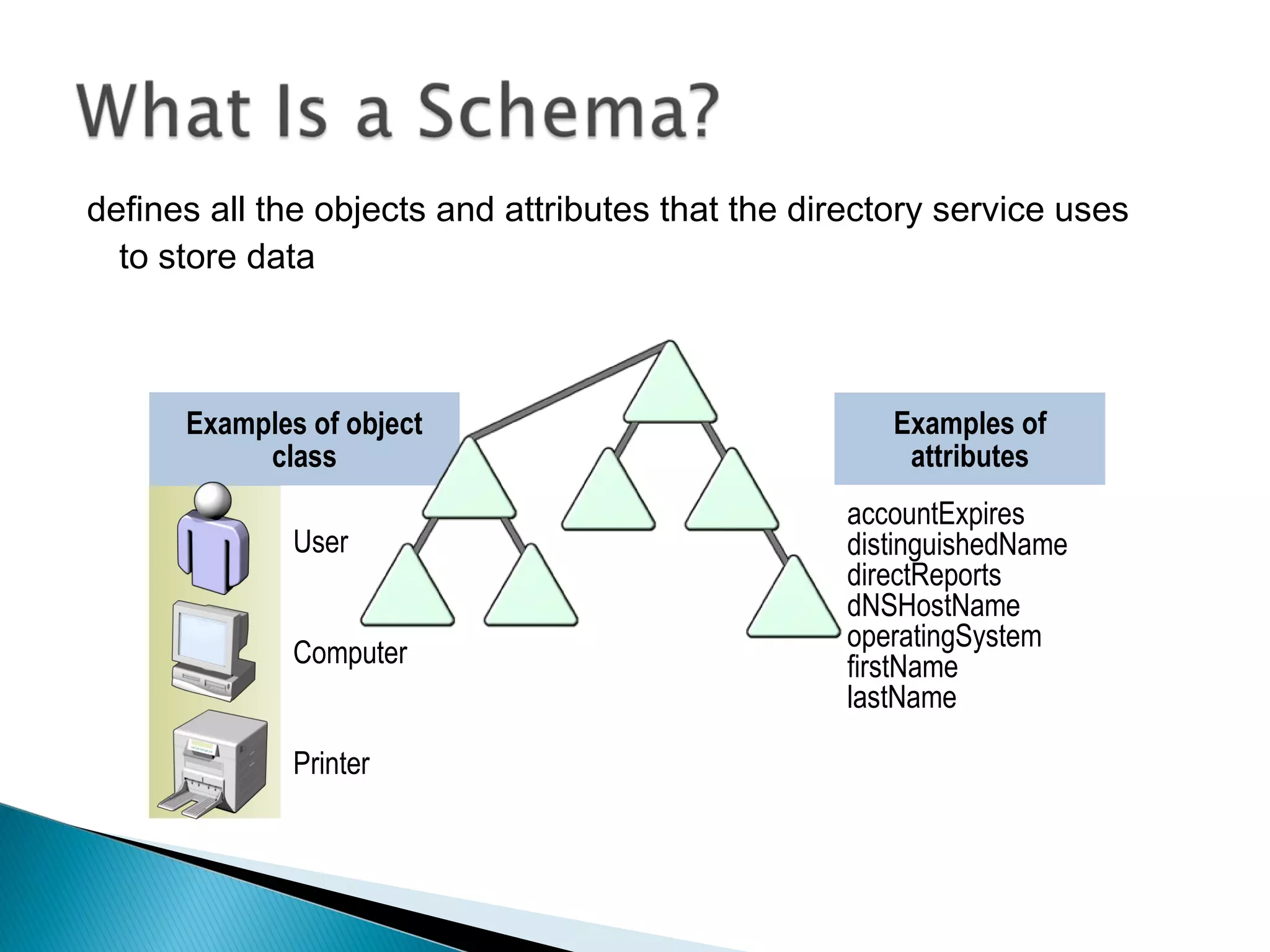
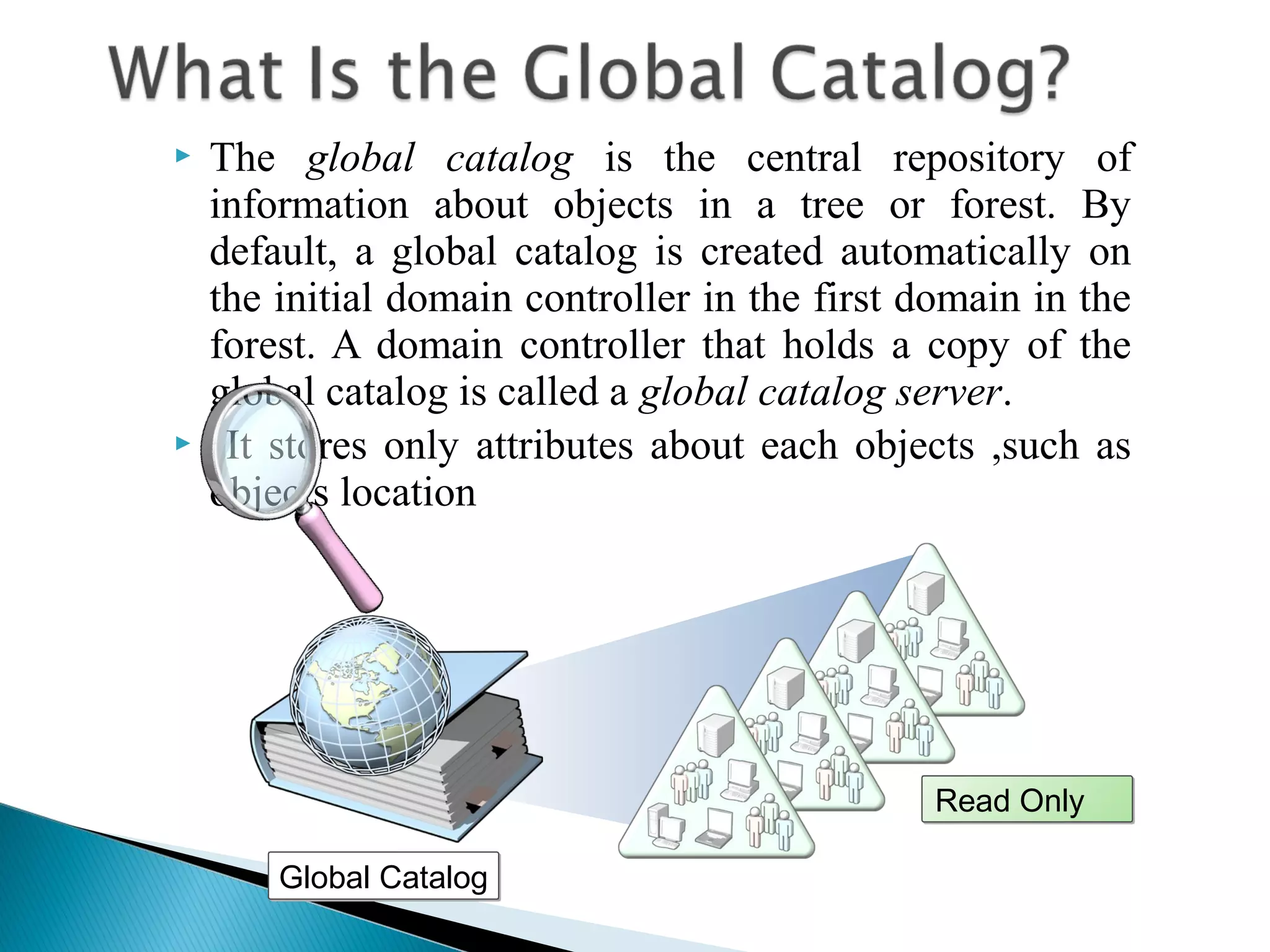
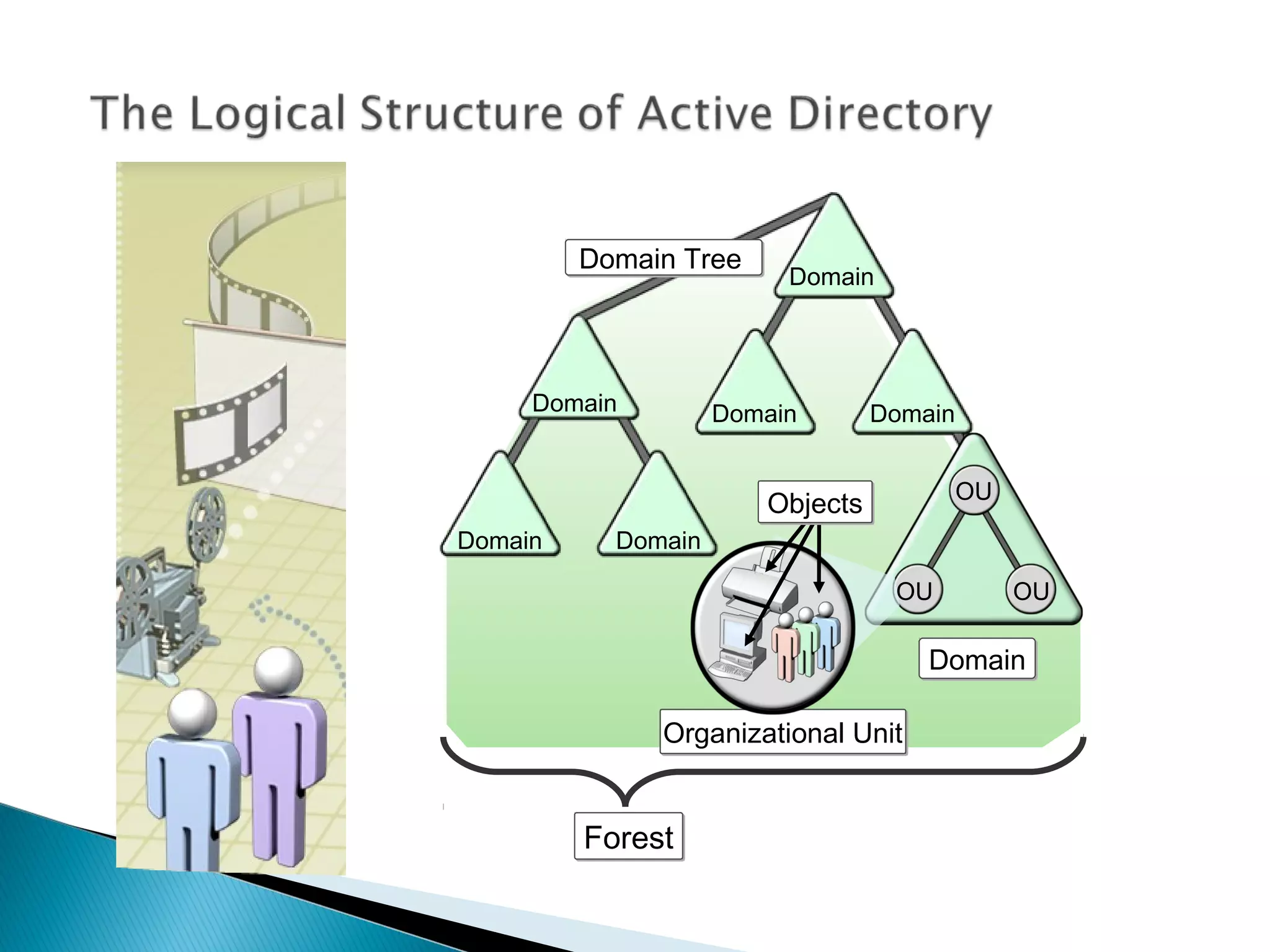
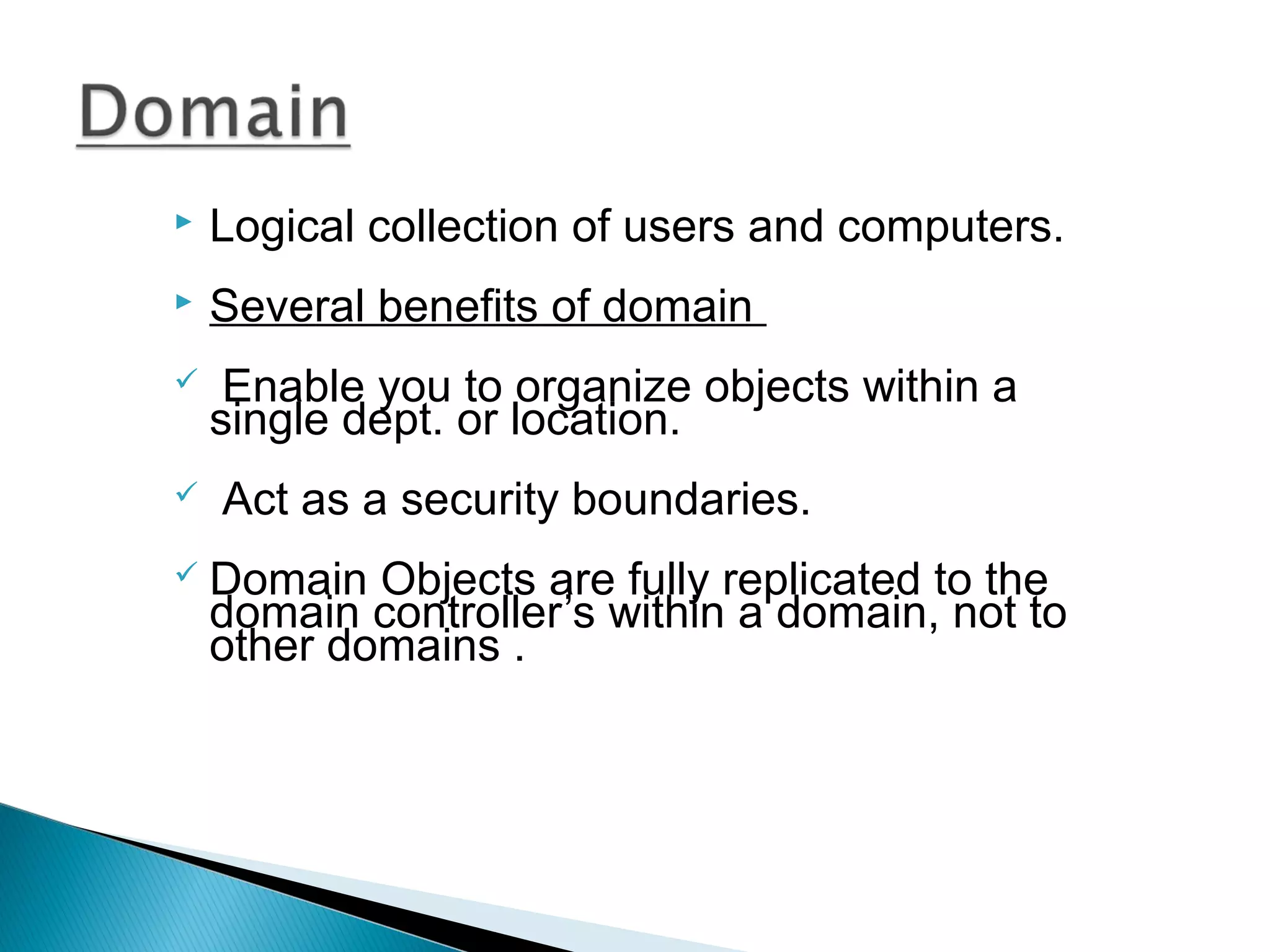
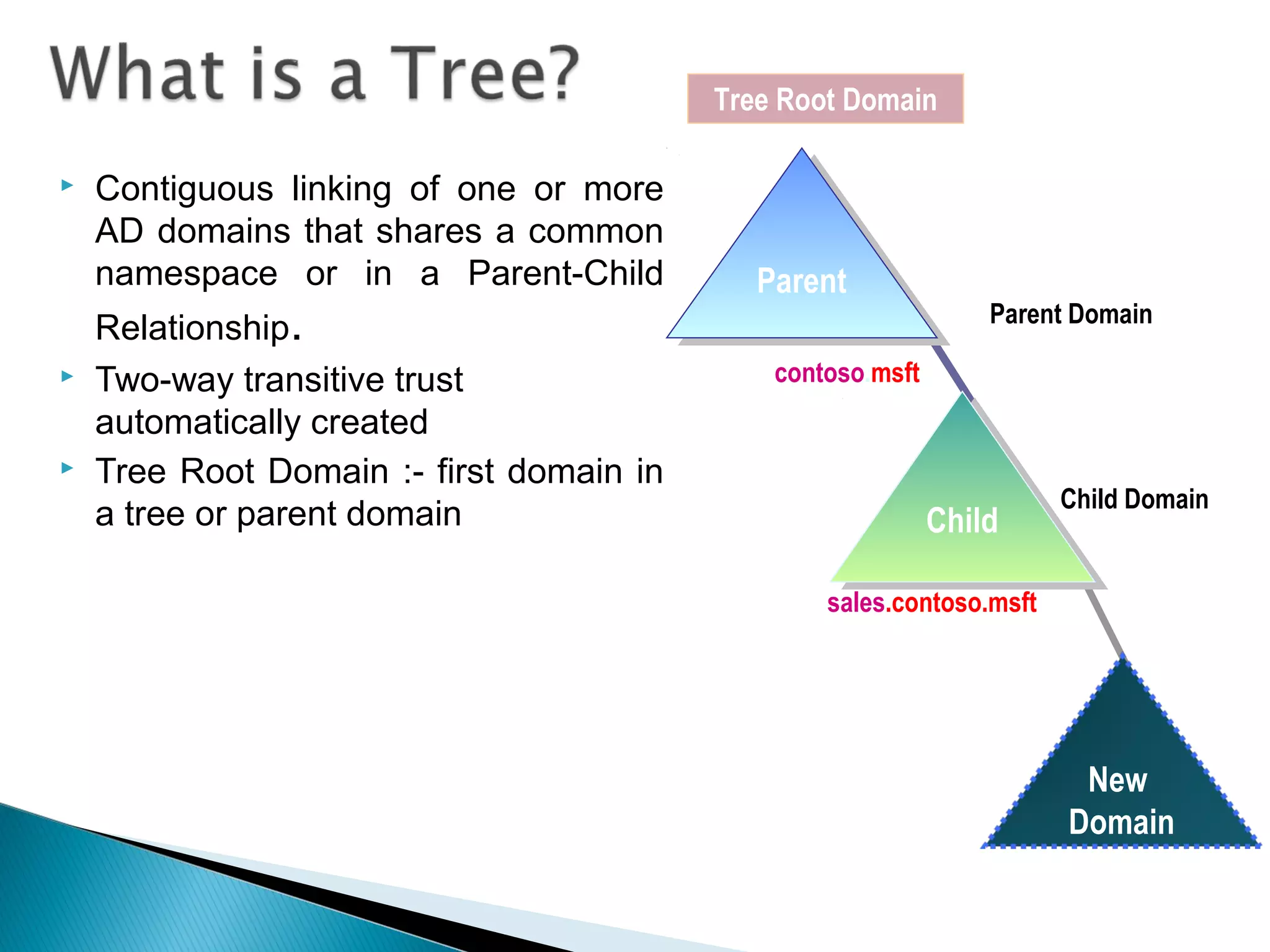
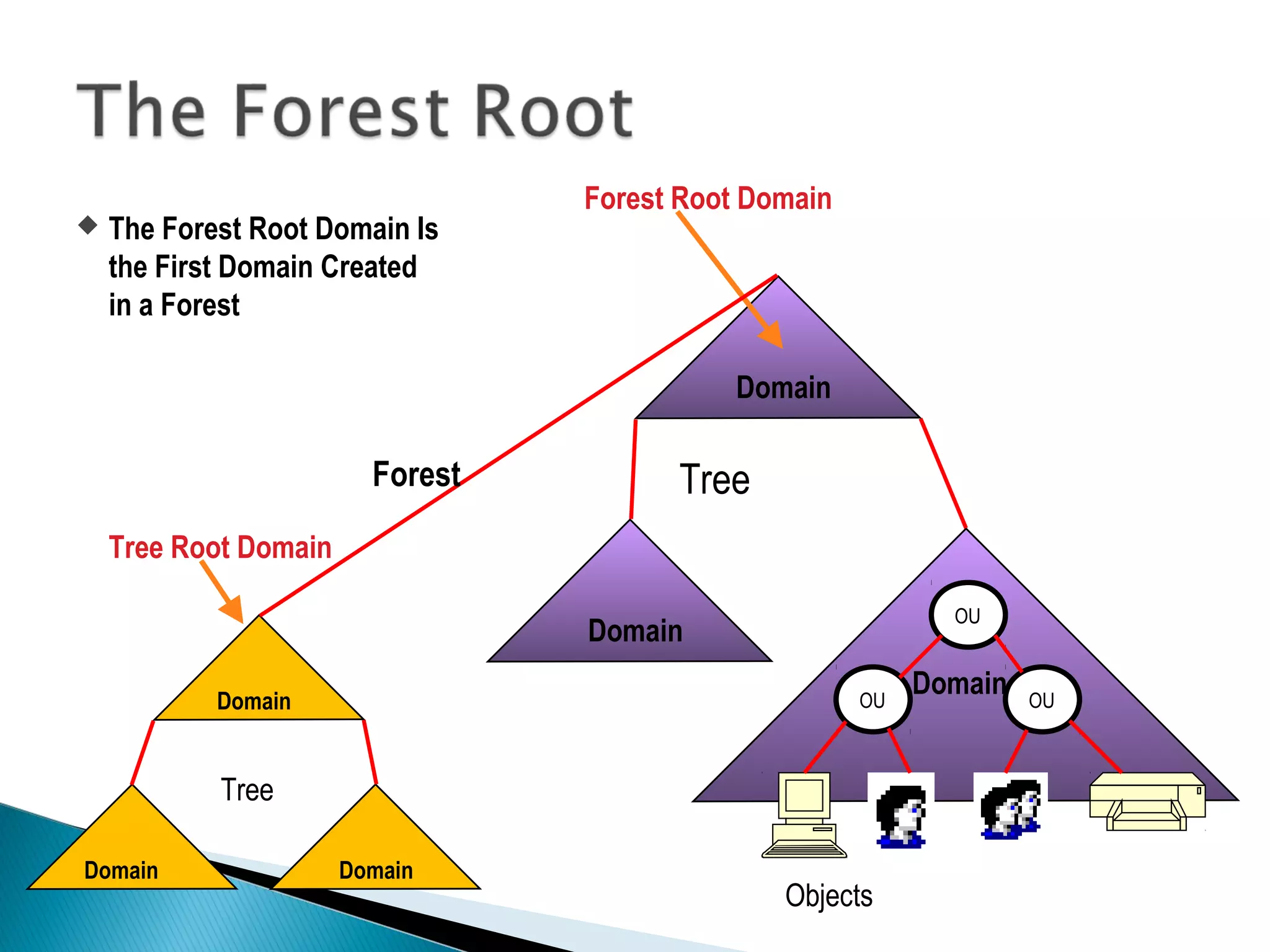
This document provides an overview of Active Directory, including its logical and physical structures. Logically, Active Directory uses domains, organizational units (OUs), trees, and forests to organize objects in a hierarchical manner. Physically, it leverages sites and domain controllers to replicate data across network locations. Key Active Directory components include objects like users and groups, attributes that describe these objects, and the schema that defines object classes and permissible attributes.