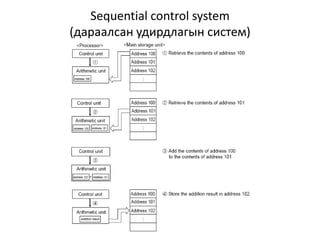
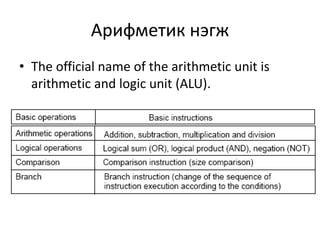
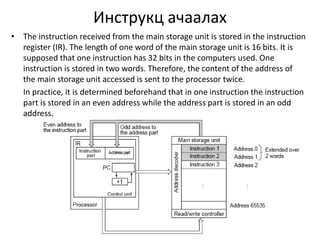
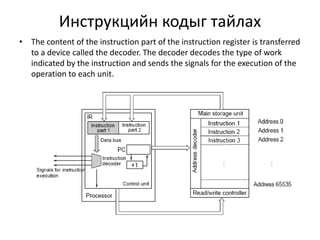
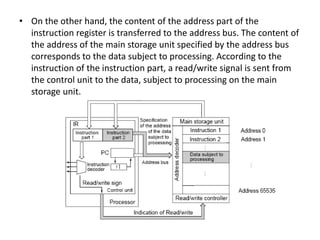
This document discusses the architecture of processors. It describes how a CPU is composed of a control unit and arithmetic unit. The control unit retrieves and decodes instructions from main storage and sends signals to other units for execution. Instructions are represented in binary machine language and contain an operation code and addresses. Instruction formats include zero-address, single-address, two-address, and three-address formats depending on how many operands are specified. The instruction decoding process involves storing the instruction in a register, decoding the operation code, and retrieving or storing data at specified addresses.