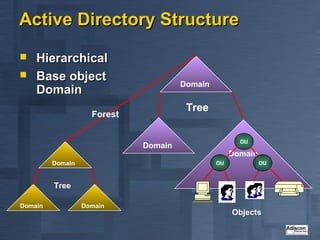
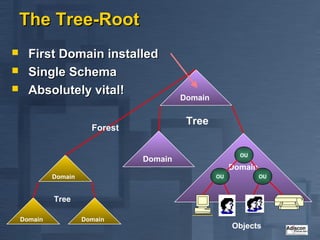
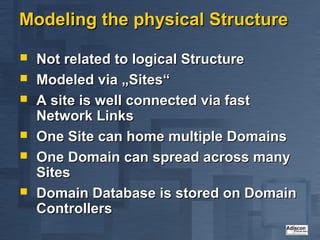
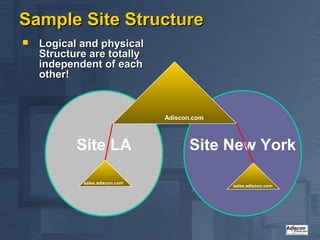
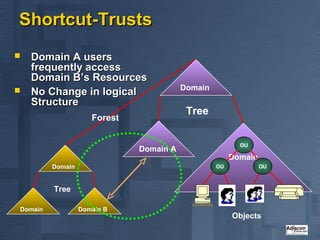
Active Directory is Microsoft's directory service that is the successor to LAN Manager domains. It aims to provide open standards, high scalability, simplified administration and compatibility with existing Windows NT systems and applications. Active Directory uses a hierarchical structure with domains, trees and forests. It contains objects like users, groups, computers and distribution lists. Changes are replicated between domain controllers to provide multi-master replication. Active Directory relies on DNS and requires at least two domain controllers. It is an important part of Microsoft's strategy with many applications now integrating with it.