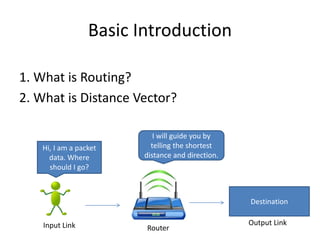
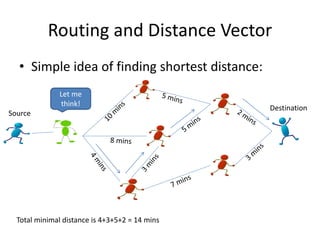
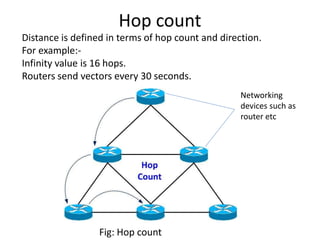
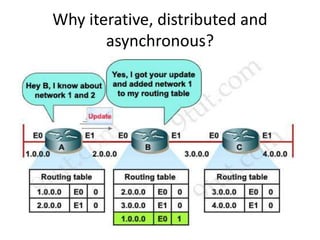
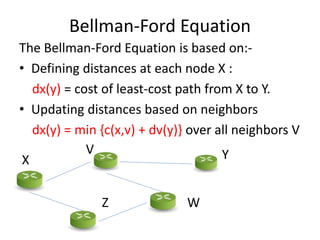
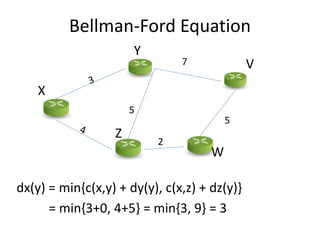
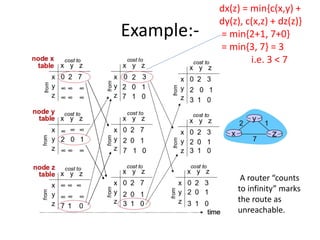
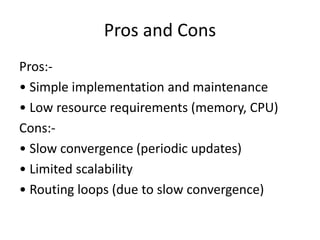
Distance vector routing is a distributed routing protocol that uses the Bellman-Ford algorithm to calculate the shortest paths between nodes. Each router periodically sends its routing table to its neighbors, containing the distance and next-hop information to reach all known destinations. Upon receiving updates from neighbors, routers recalculate path costs and propagate changes to ensure all routers converge on the shortest paths over time. While simple to implement, distance vector routing suffers from slow convergence and potential routing loops during network changes.