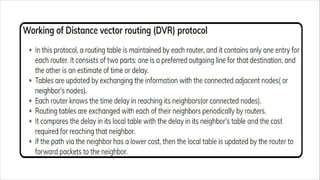
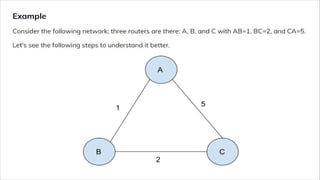
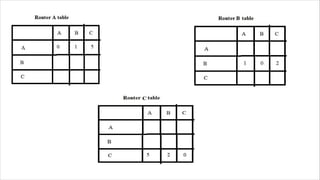
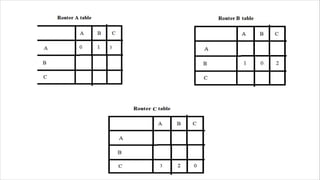
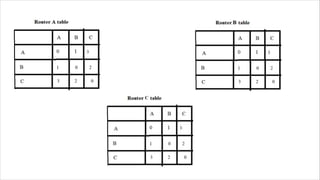
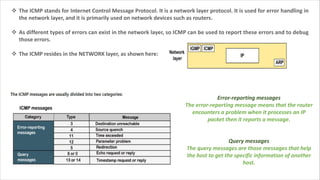
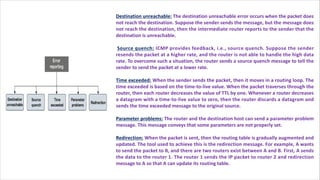
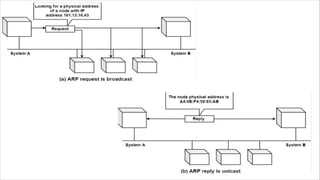
Routing is the process of selecting the best path to send data from a source to a destination. Routers perform routing by using routing protocols and algorithms to determine the optimal path. Distance vector routing uses hop count as the metric to calculate the best path, while link state routing uses the least cost path based on metrics like bandwidth and delay. Key differences are that distance vector routing shares distance vectors with neighbors periodically, while link state routing shares complete topology information and triggers updates when links change state.