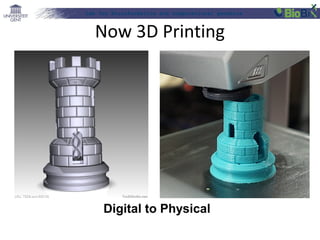
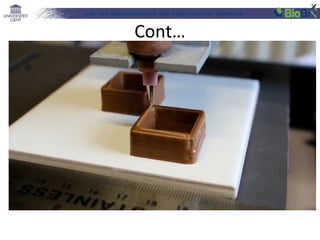
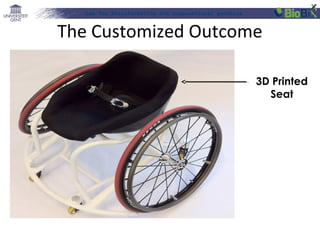
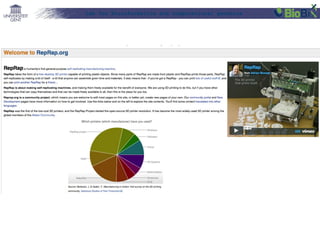
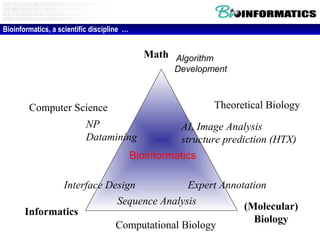
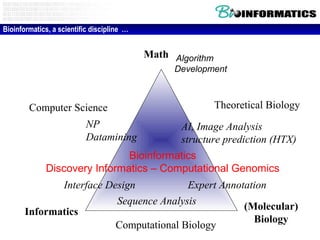
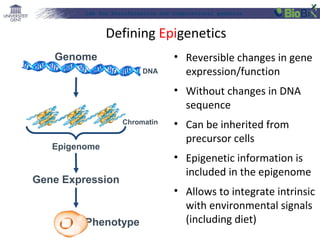
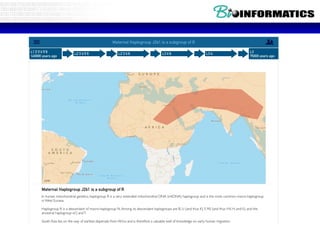
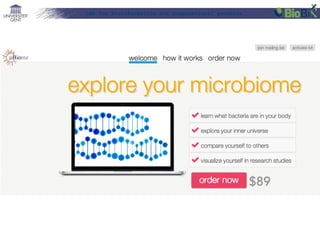
The document discusses a lab for bioinformatics and computational genomics at Ghent University. The lab has 10 "genome hackers" who are mostly engineers and 42 scientists, technicians, geneticists and clinicians. The lab focuses on bioinformatics, epigenetics, personal genomics and 3D printing. Bioinformatics is defined as the application of information technology to biological information, facilitated by computers. The document then discusses various topics related to genetics, genomics and personalized medicine.

![Lab for Bioinformatics and computational genomics
13 maart 2015
• ^ Biobix: Who ? Where ?
• Bioinformatics
• Epigenetics
• Personal Genomics
• 3D printing
^[now][transl comput]ational⎮ [epi]genomic$](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20150313puursvpublic-150313172537-conversion-gate01/85/2015-03-13_puurs_v_public-2-320.jpg)
![Lab for Bioinformatics and computational genomics
13 maart 2015
• ^ Biobix: Who ? Where ?
• Bioinformatics
• Epigenetics
• Personal Genomics
• 3D printing
^[now][transl comput]ational⎮ [epi]genomic$](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20150313puursvpublic-150313172537-conversion-gate01/85/2015-03-13_puurs_v_public-3-320.jpg)

![Lab for Bioinformatics and computational genomics
13 maart 2015
• ^ Biobix: Who ? Where ?
• Bioinformatics
• Epigenetics
• Personal Genomics
• 3D printing
^[now][transl comput]ational⎮ [epi]genomic$](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20150313puursvpublic-150313172537-conversion-gate01/85/2015-03-13_puurs_v_public-5-320.jpg)
![Lab for Bioinformatics and computational genomics
13 maart 2015
• ^ Biobix: Who ? Where ?
• Bioinformatics
• Epigenetics
• Personal Genomics
• 3D printing
^[now][transl comput]ational⎮ [epi]genomic$](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20150313puursvpublic-150313172537-conversion-gate01/85/2015-03-13_puurs_v_public-6-320.jpg)

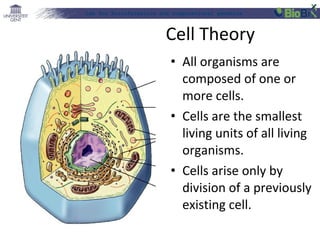
![Lab for Bioinformatics and computational genomics
13 maart 2015
• ^ Biobix: Who ? Where ?
• Bioinformatics
• Epigenetics
• Personal Genomics
• 3D printing
^[now][transl comput]ational⎮ [epi]genomic$](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20150313puursvpublic-150313172537-conversion-gate01/85/2015-03-13_puurs_v_public-12-320.jpg)
![Lab for Bioinformatics and computational genomics
13 maart 2015
• ^ Biobix: Who ? Where ?
• Bioinformatics
• Epigenetics
• Personal Genomics
• 3D printing
^[now][transl comput]ational⎮ [epi]genomic$](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20150313puursvpublic-150313172537-conversion-gate01/85/2015-03-13_puurs_v_public-13-320.jpg)
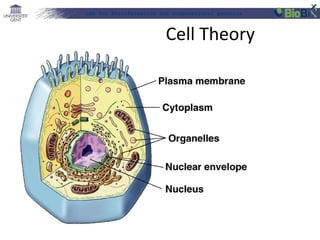
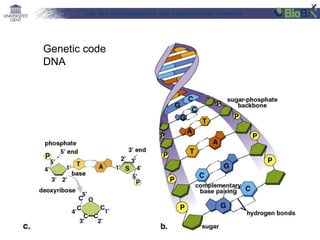
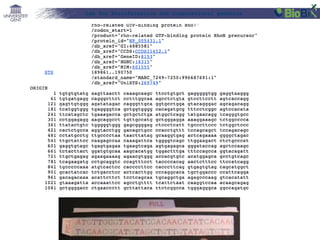




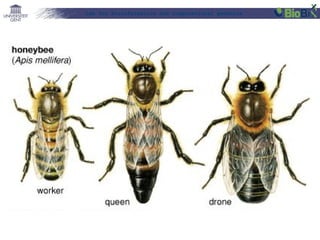


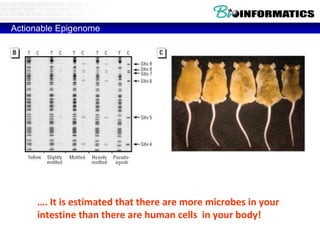

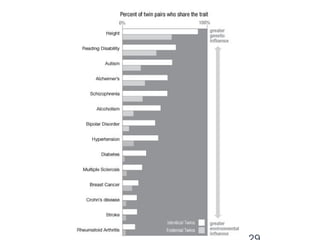
![Lab for Bioinformatics and computational genomics
13 maart 2015
• ^ Biobix: Who ? Where ?
• Bioinformatics
• Epigenetics
• Personal Genomics
• 3D printing
^[now][transl comput]ational⎮ [epi]genomic$](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20150313puursvpublic-150313172537-conversion-gate01/85/2015-03-13_puurs_v_public-30-320.jpg)
![Lab for Bioinformatics and computational genomics
13 maart 2015
• ^ Biobix: Who ? Where ?
• Bioinformatics
• Epigenetics
• Personal Genomics
• 3D printing
^[now][transl comput]ational⎮ [epi]genomic$](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20150313puursvpublic-150313172537-conversion-gate01/85/2015-03-13_puurs_v_public-31-320.jpg)




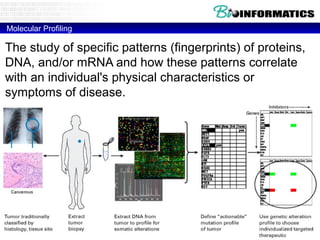
![Lab for Bioinformatics and computational genomics
Overview
• Who ? Where ?
• > Genetics
• Technology: Next Gen
Sequencing
• … Personal Genomics
• Manifesto
• The App
^[now][transl comput]ational⎮ [epi]genomic$](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20150313puursvpublic-150313172537-conversion-gate01/85/2015-03-13_puurs_v_public-38-320.jpg)




















![Lab for Bioinformatics and computational genomics
13 maart 2015
• ^ Biobix: Who ? Where ?
• Bioinformatics
• Epigenetics
• Personal Genomics
• 3D printing
^[now][transl comput]ational⎮ [epi]genomic$](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20150313puursvpublic-150313172537-conversion-gate01/85/2015-03-13_puurs_v_public-67-320.jpg)
![Lab for Bioinformatics and computational genomics
13 maart 2015
• ^ Biobix: Who ? Where ?
• Bioinformatics
• Epigenetics
• Personal Genomics
• 3D printing
^[now][transl comput]ational⎮ [epi]genomic$](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20150313puursvpublic-150313172537-conversion-gate01/85/2015-03-13_puurs_v_public-68-320.jpg)