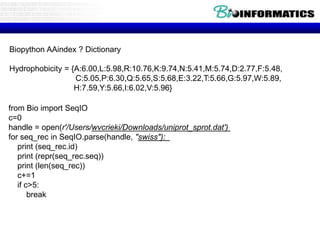
The document discusses various topics related to analyzing protein sequences using Python and Biopython. It provides examples of using Biopython to parse sequence data from UniProt, calculate lengths and translations of sequences. It also discusses analyzing properties of sequences like molecular weight, isoelectric point, transmembrane regions, and comparing sequences to find conserved motifs. Finally, it introduces hydropathy indices and tools for predicting properties like transmembrane helices from primary sequences.




![Control Structures
if condition:
statements
[elif condition:
statements] ...
else:
statements
while condition:
statements
for var in sequence:
statements
break
continue](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/p62018biopython2b-181119220707/85/P6-2018-biopython2b-5-320.jpg)
![Lists
• Flexible arrays, not Lisp-like linked
lists
• a = [99, "bottles of beer", ["on", "the",
"wall"]]
• Same operators as for strings
• a+b, a*3, a[0], a[-1], a[1:], len(a)
• Item and slice assignment
• a[0] = 98
• a[1:2] = ["bottles", "of", "beer"]
-> [98, "bottles", "of", "beer", ["on", "the", "wall"]]
• del a[-1] # -> [98, "bottles", "of", "beer"]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/p62018biopython2b-181119220707/85/P6-2018-biopython2b-6-320.jpg)
![Dictionaries
• Hash tables, "associative arrays"
• d = {"duck": "eend", "water": "water"}
• Lookup:
• d["duck"] -> "eend"
• d["back"] # raises KeyError exception
• Delete, insert, overwrite:
• del d["water"] # {"duck": "eend", "back": "rug"}
• d["back"] = "rug" # {"duck": "eend", "back":
"rug"}
• d["duck"] = "duik" # {"duck": "duik", "back":
"rug"}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/p62018biopython2b-181119220707/85/P6-2018-biopython2b-7-320.jpg)