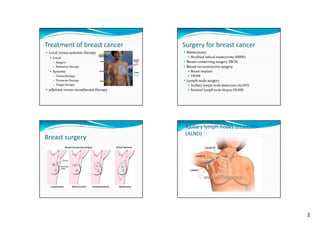
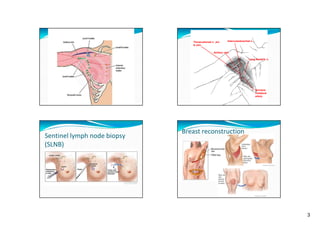
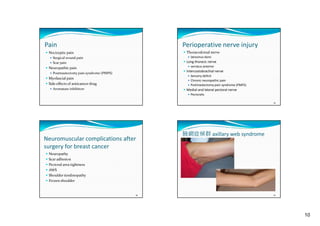
This document summarizes treatment for breast cancer, including surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy. It discusses different types of breast surgery including mastectomy, breast-conserving surgery, lymph node surgery, and breast reconstruction. It also covers common side effects of chemotherapy and hormone therapy. Physical therapy exercises for breast cancer recovery are proposed in four phases focusing on range of motion, strength, flexibility, and endurance.