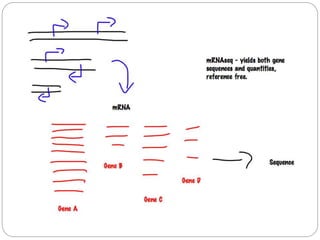
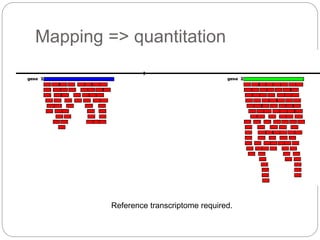
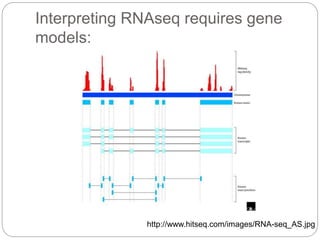
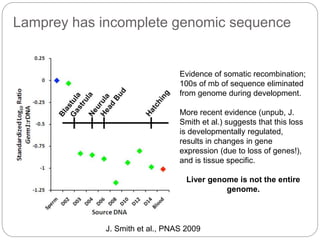
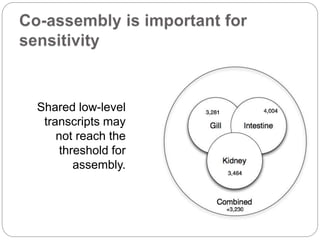
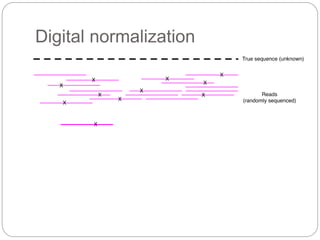
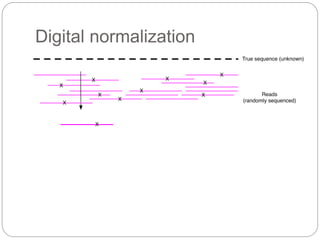
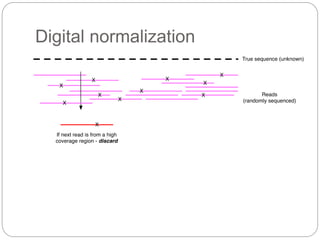
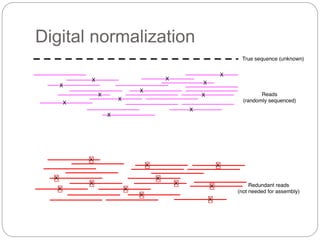
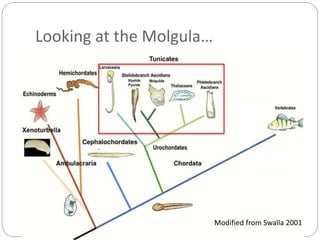
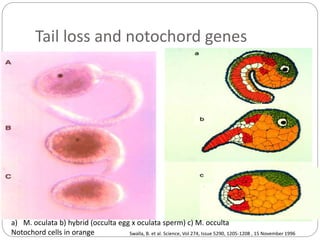
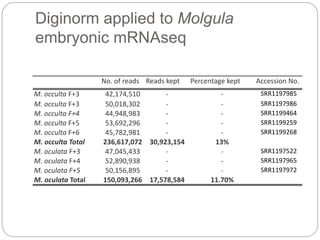
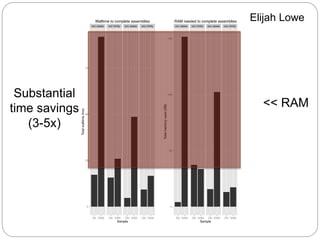
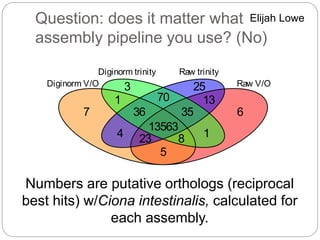
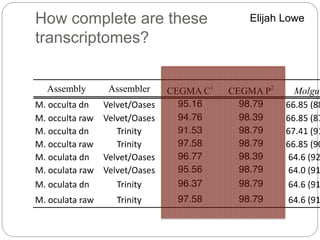
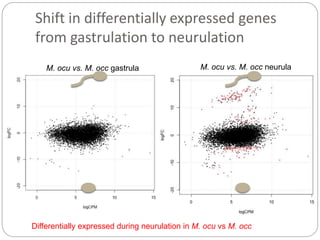
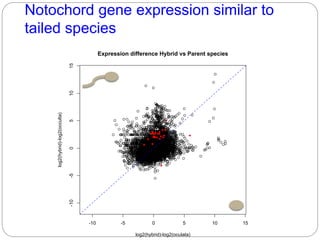
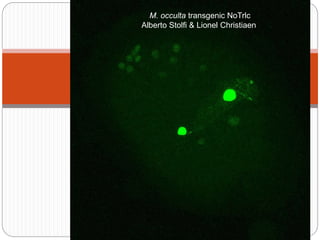
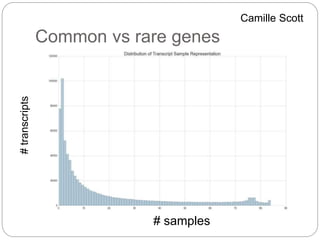
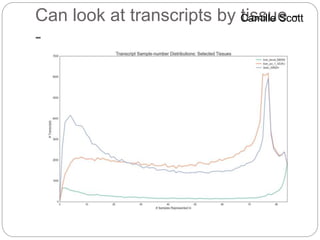
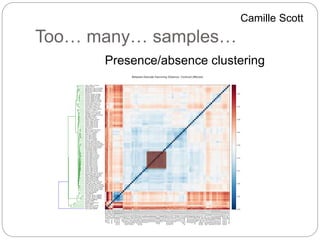
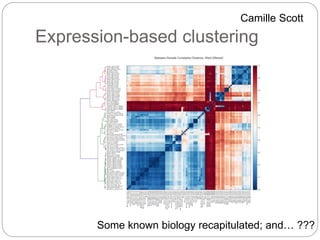
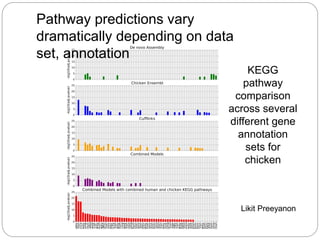
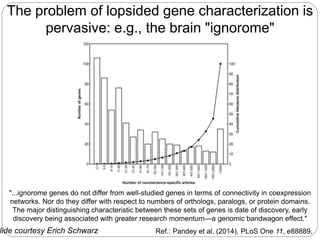
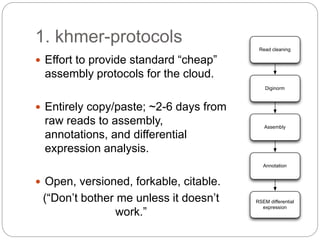
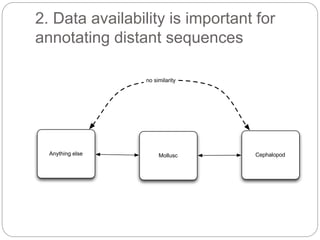
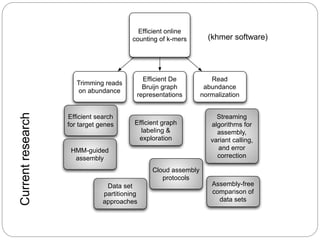
This document discusses challenges and opportunities in applying mRNA sequencing (mRNAseq) to non-model organisms. It describes using digital normalization to cope with large amounts of lamprey mRNAseq data that would otherwise be too computationally intensive to assemble. Digital normalization was applied successfully to Molgula ascidian mRNAseq data, enabling transcriptome analysis. The lamprey transcriptome was assembled from over 5 billion reads from 50 tissues, producing over 600,000 transcripts. Next steps include addressing contamination issues and using the more complete transcriptome to enable various evolutionary and biological studies of lamprey. The document advocates making protocols and data openly available to help characterize genes in non-model organisms.