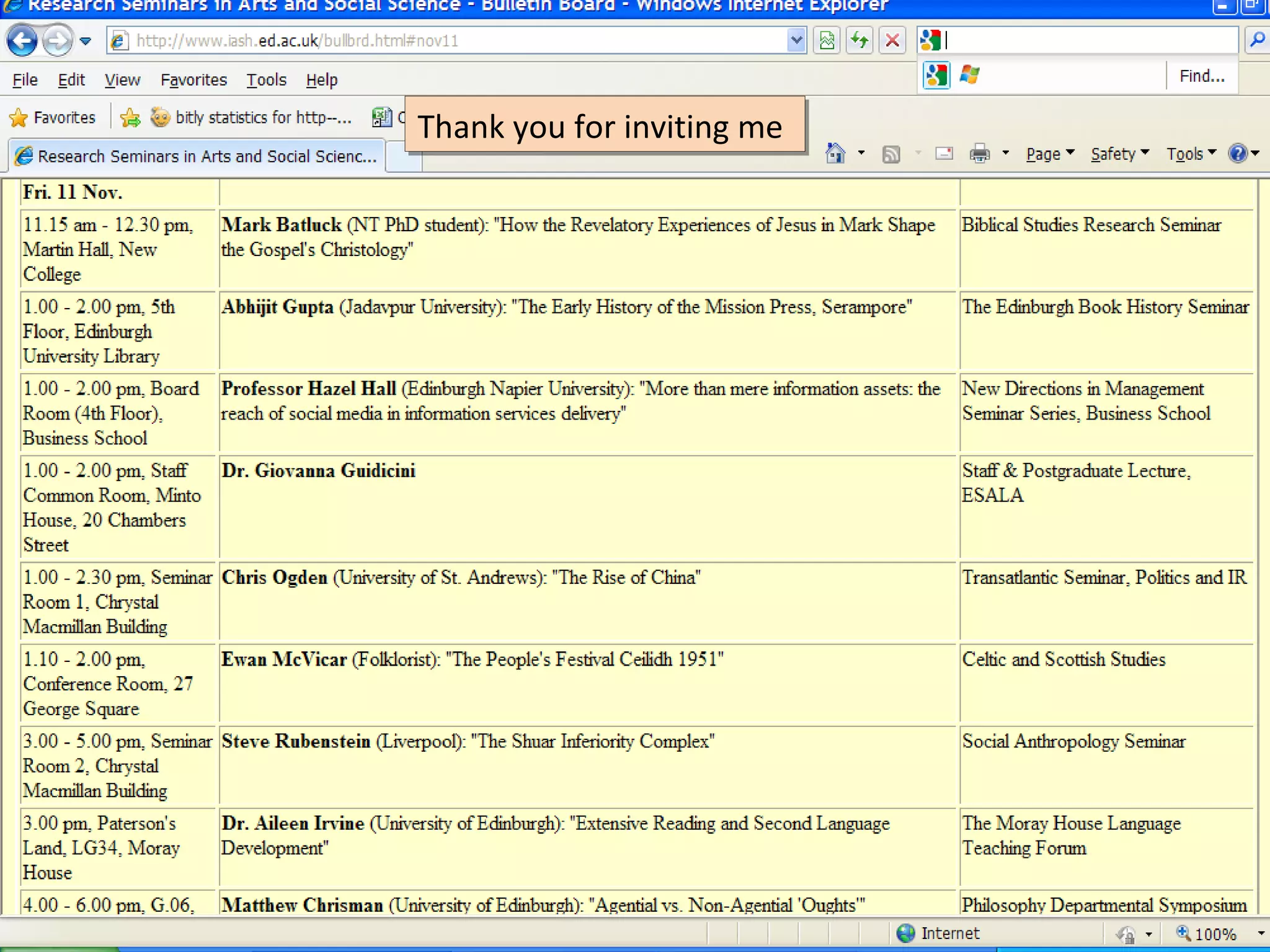
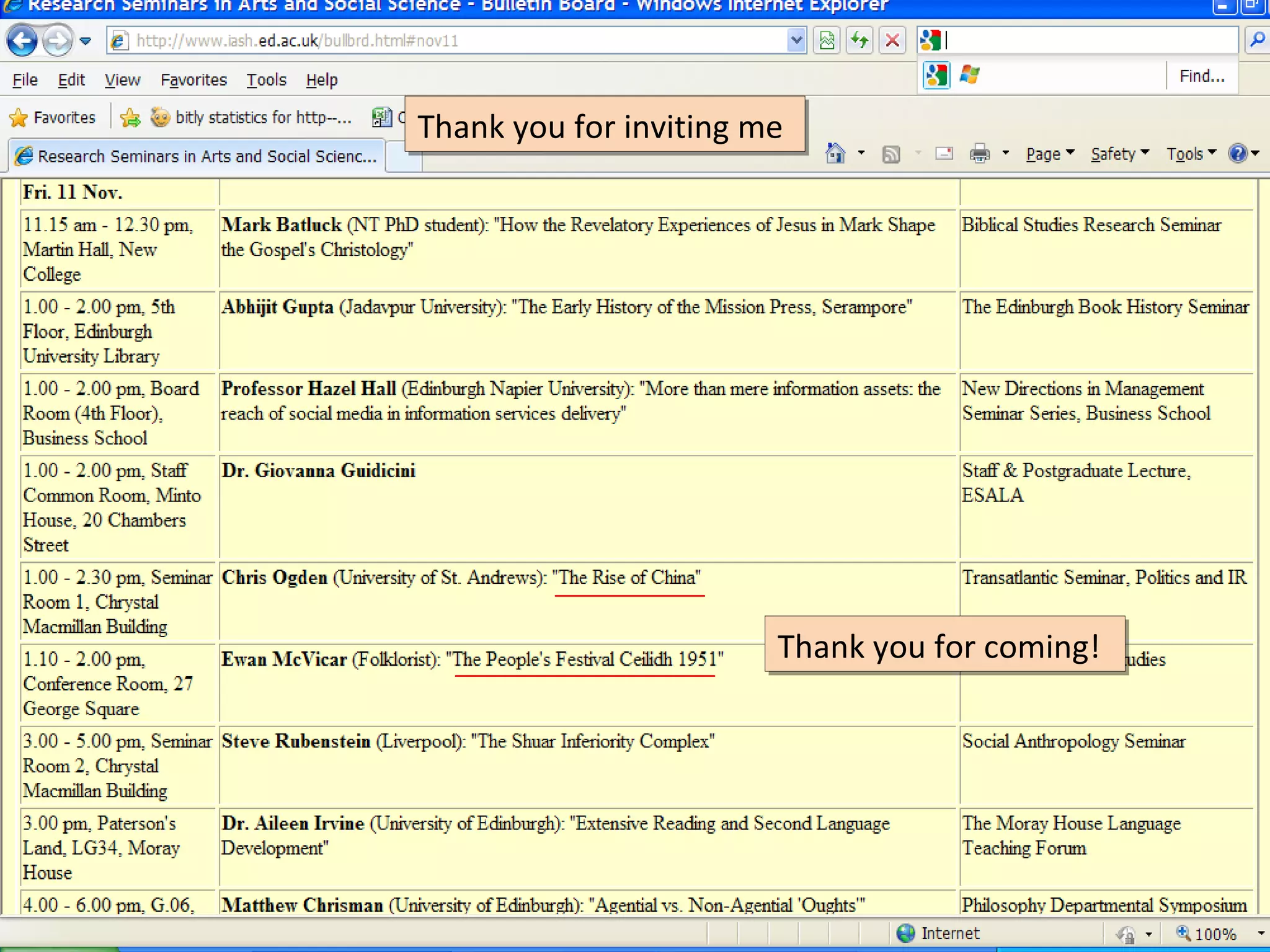
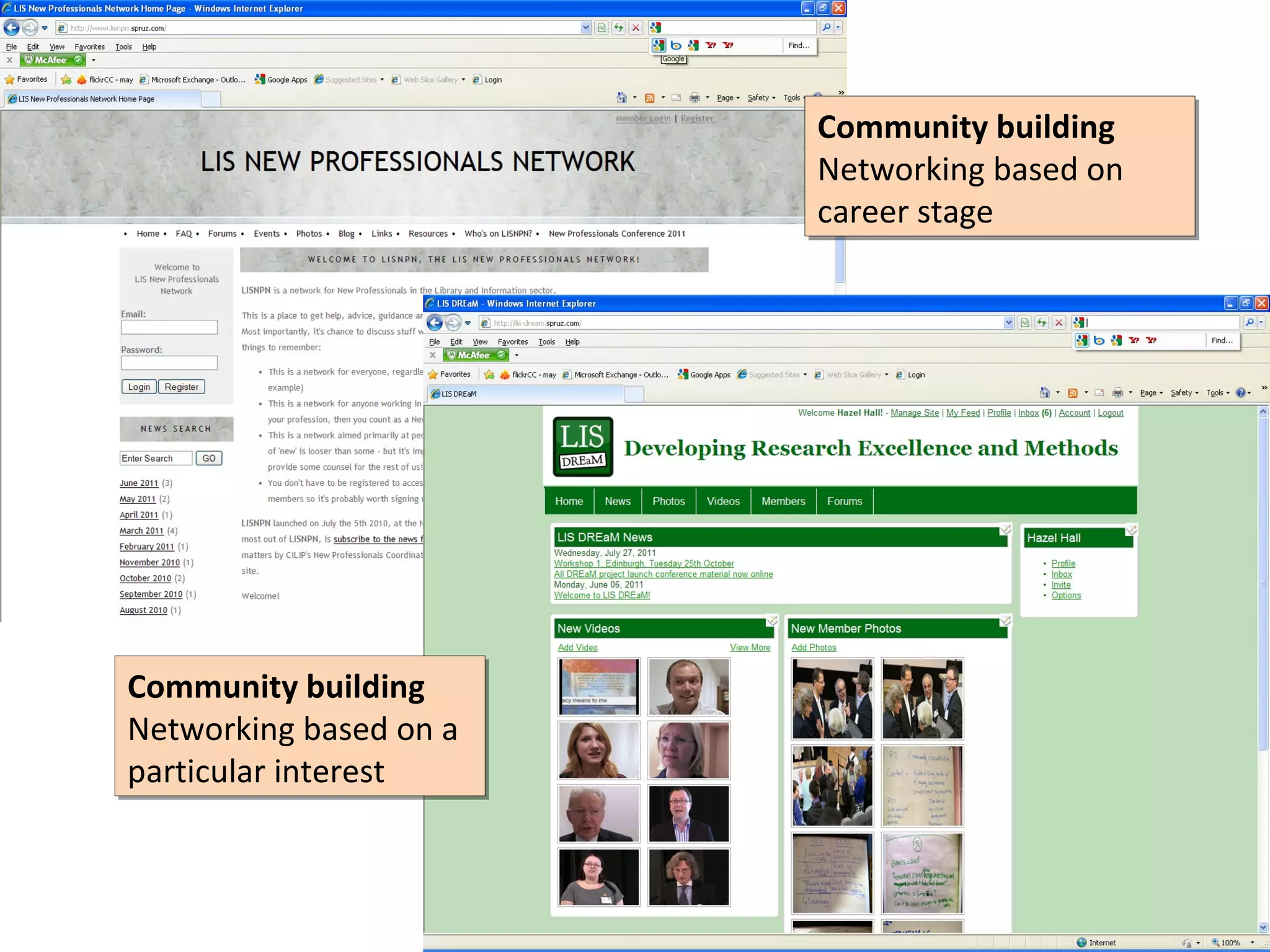
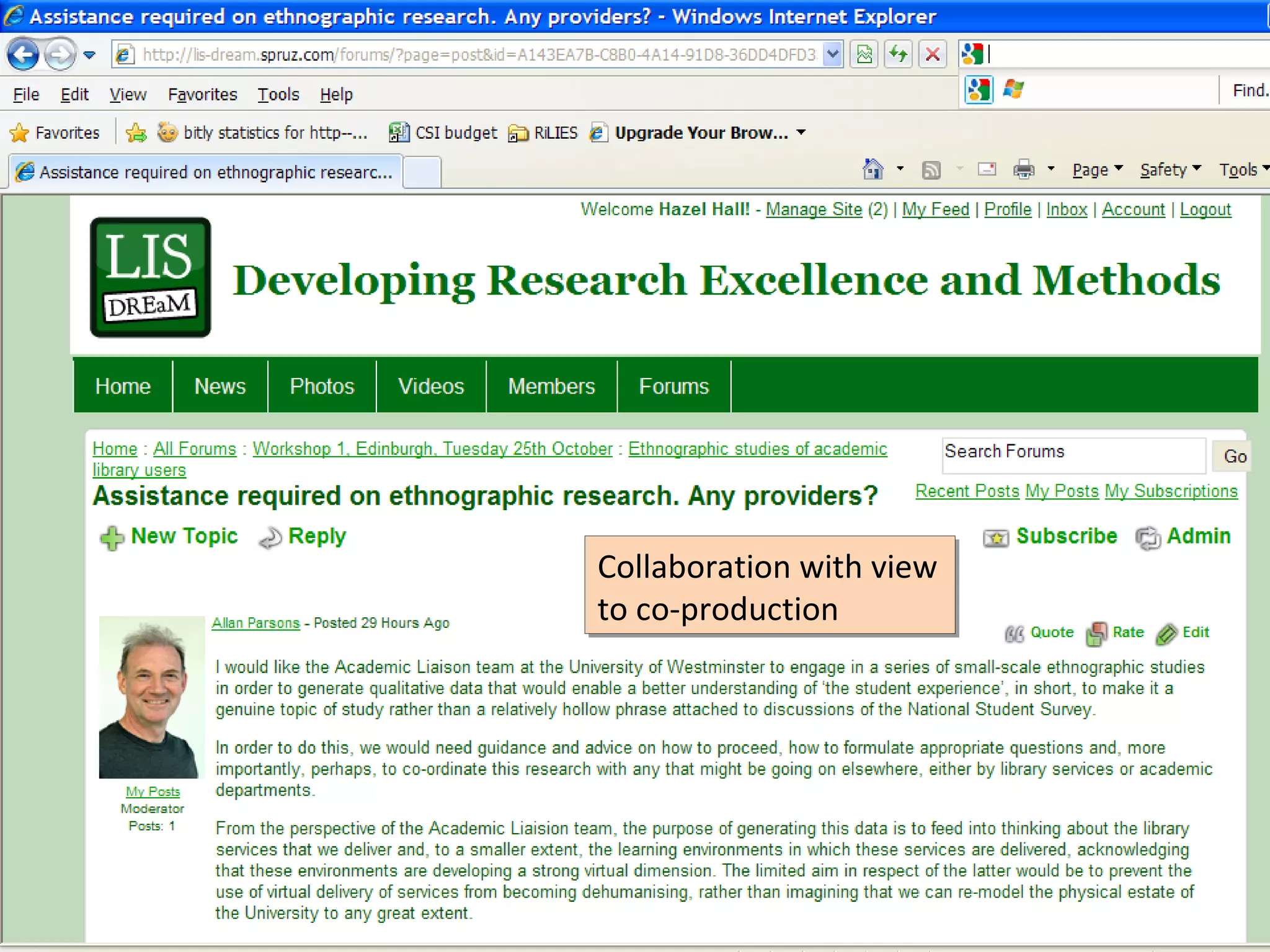
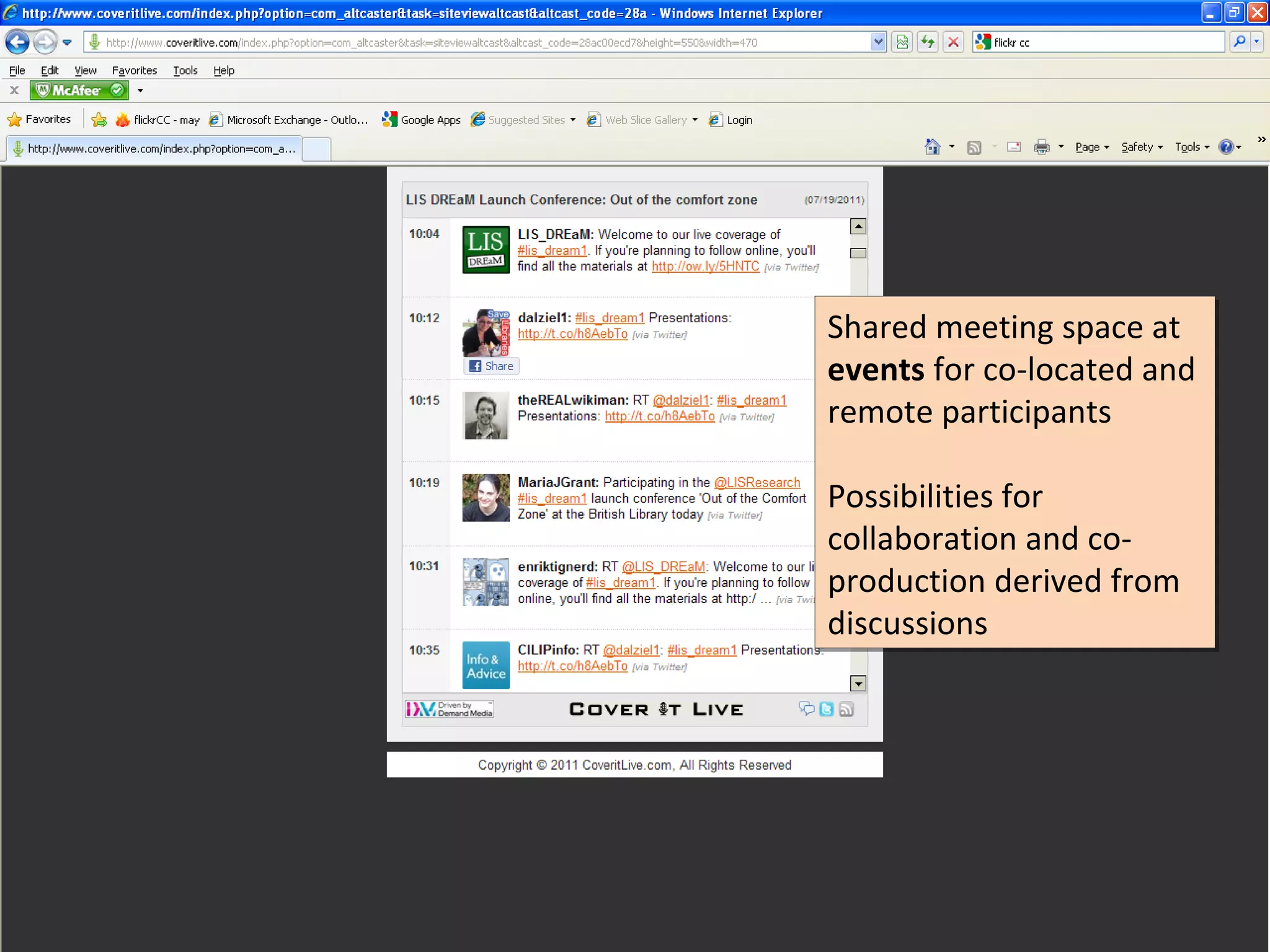
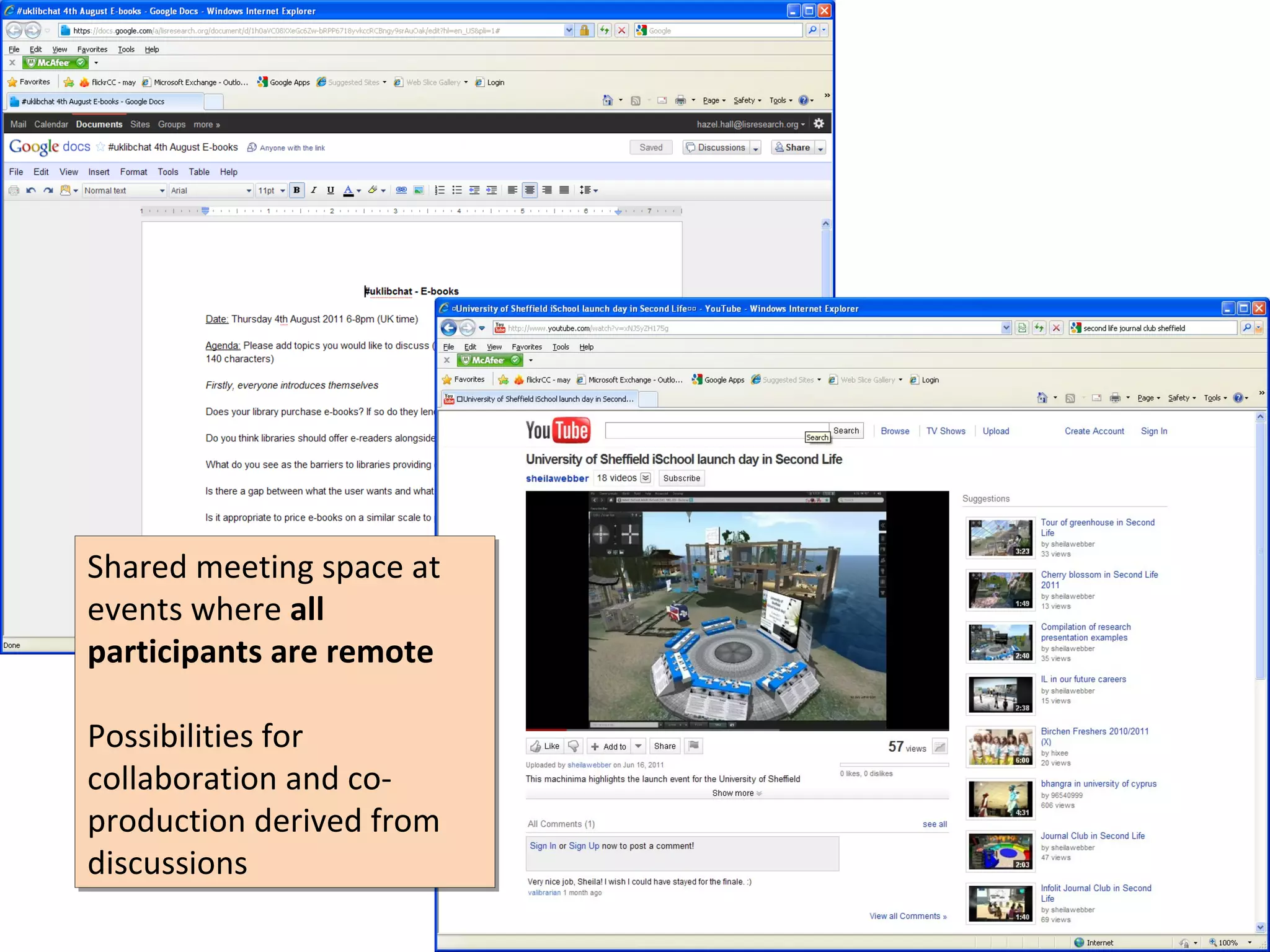
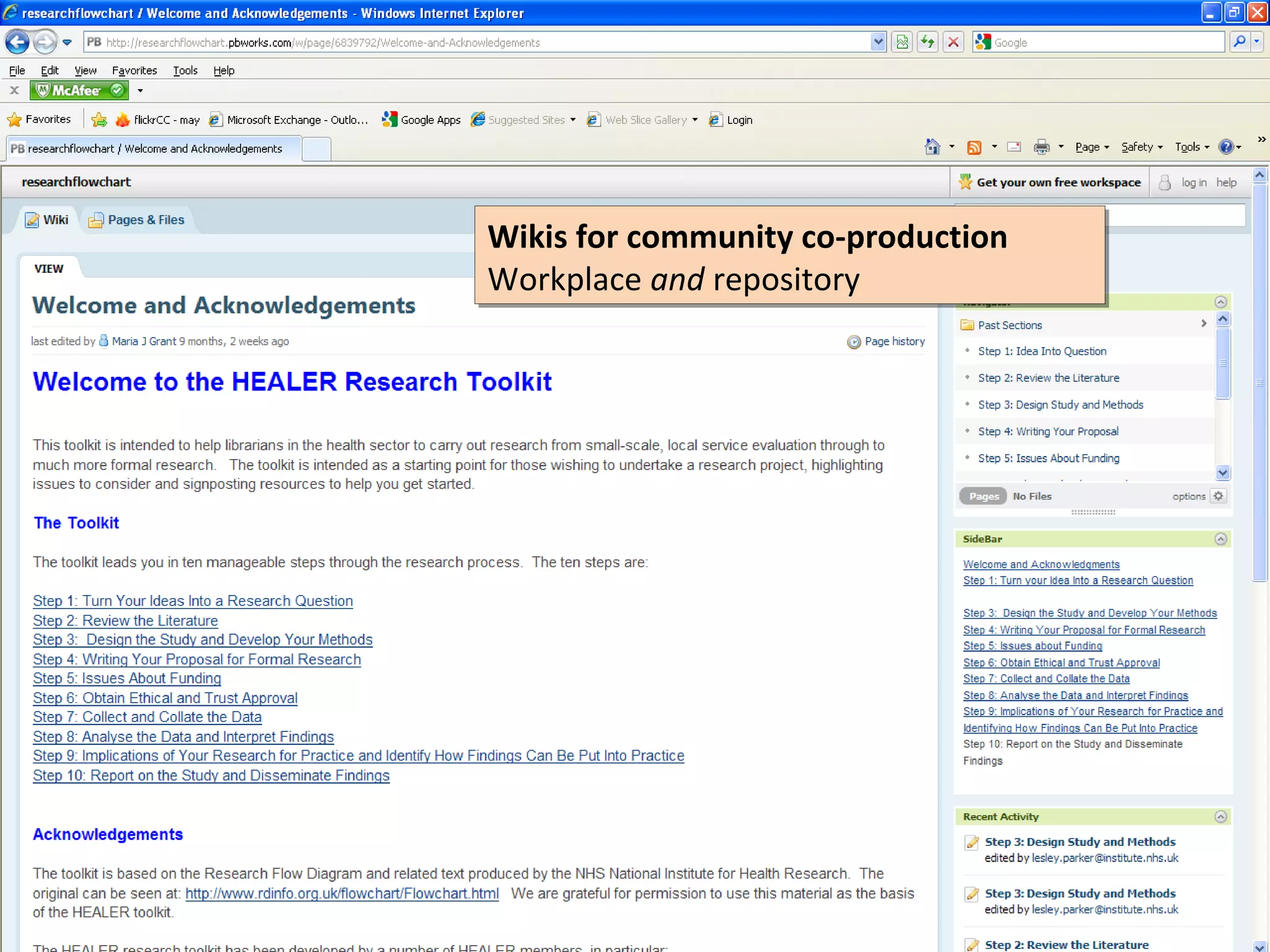
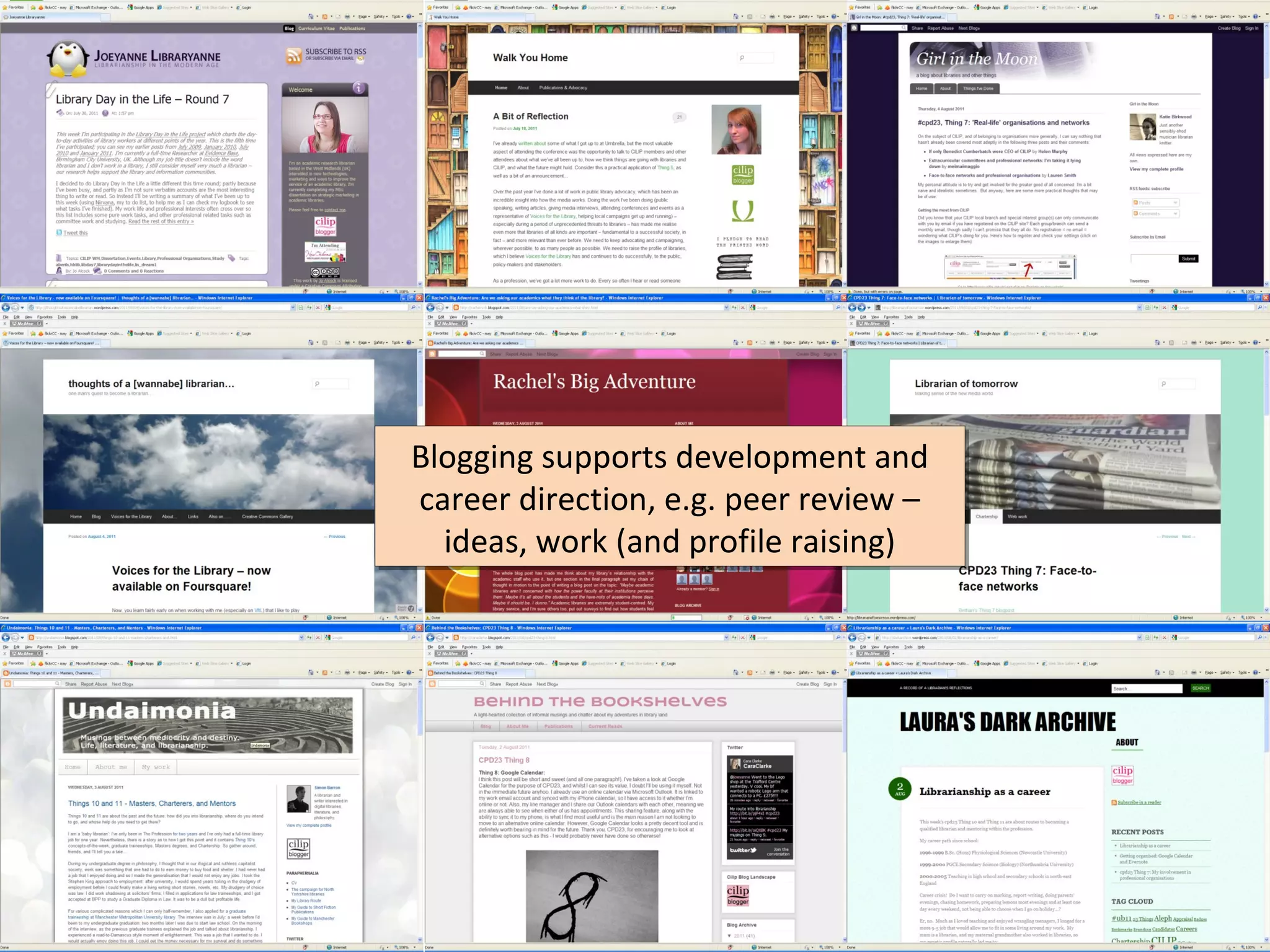
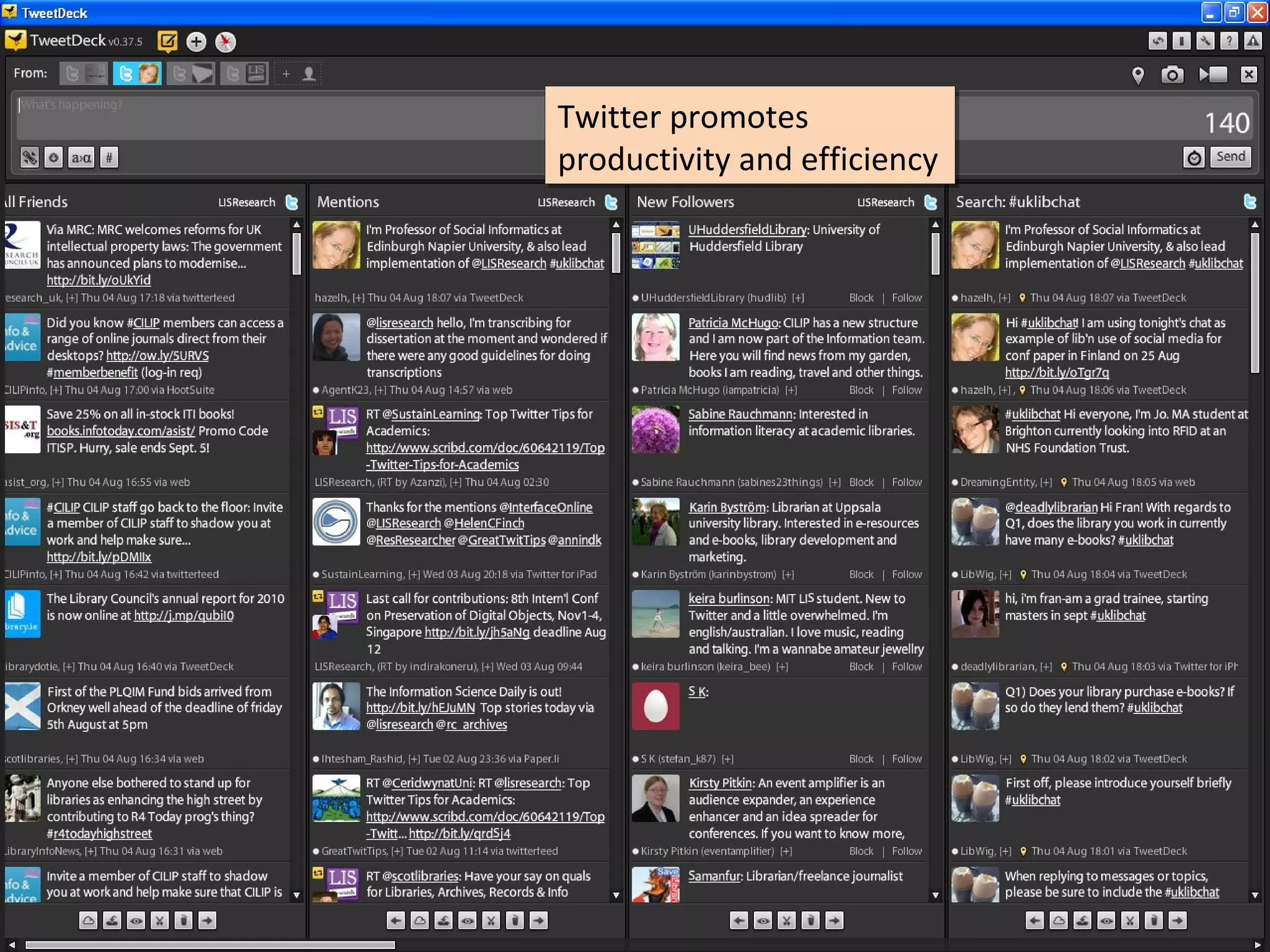
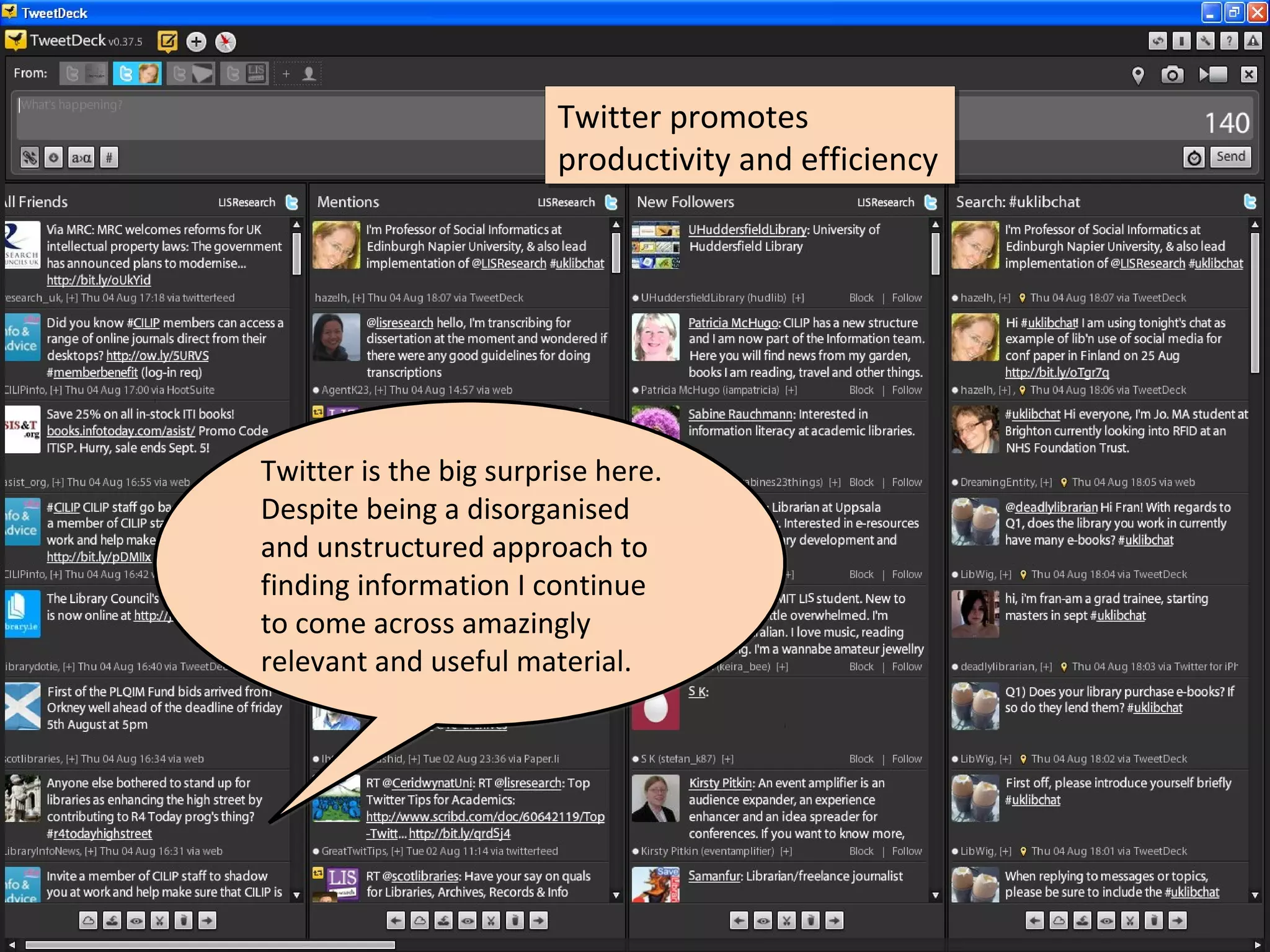
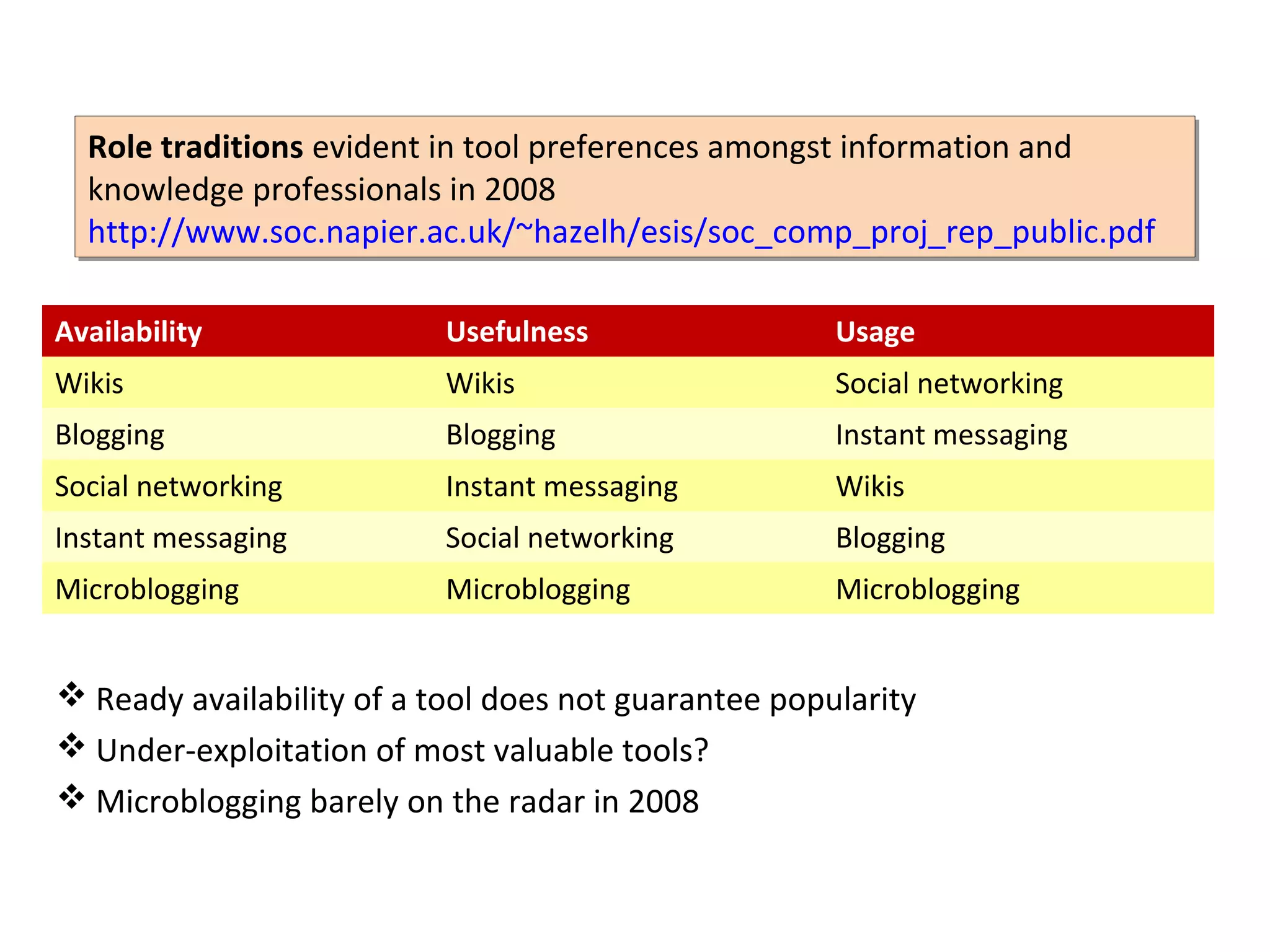
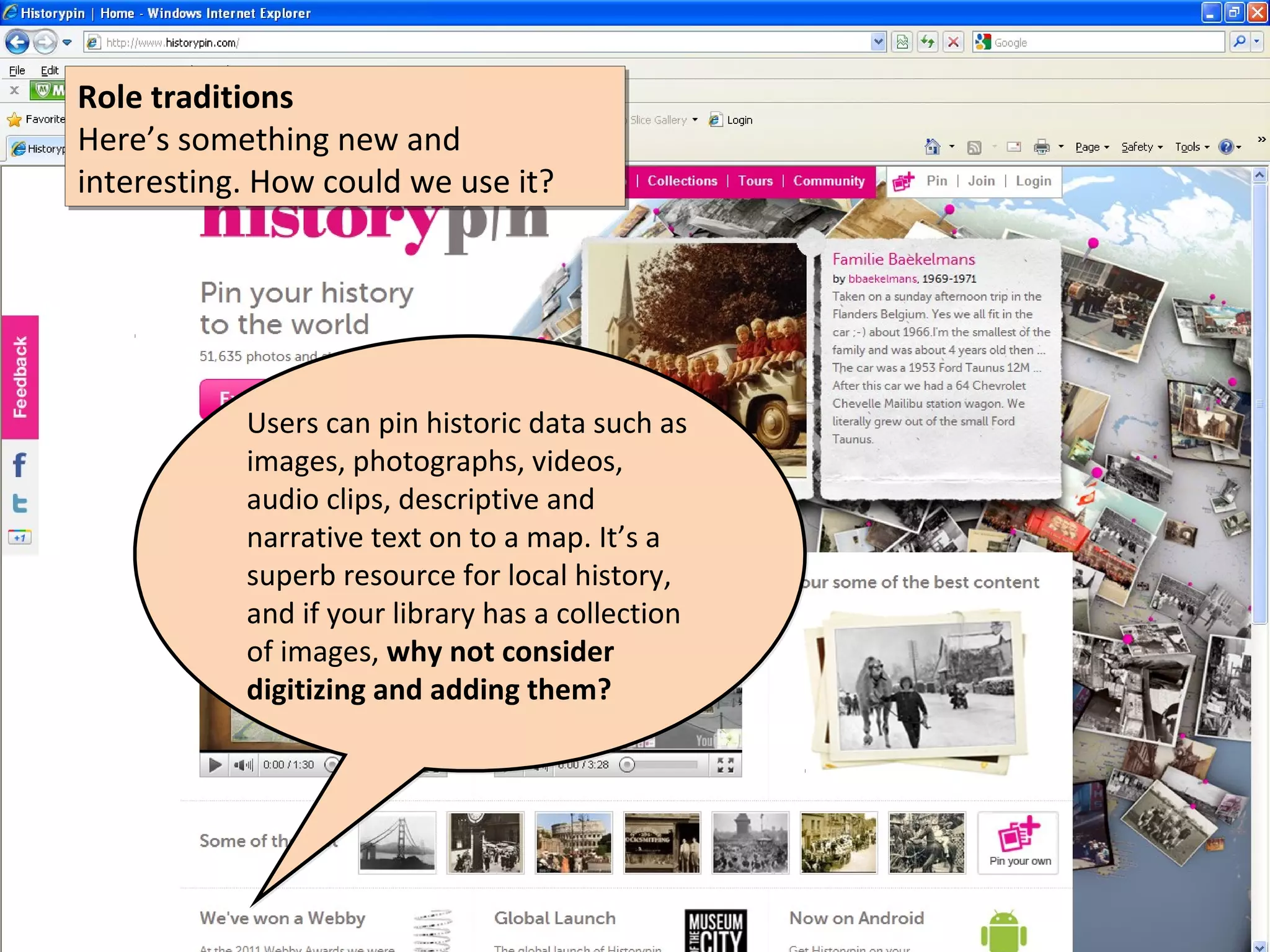
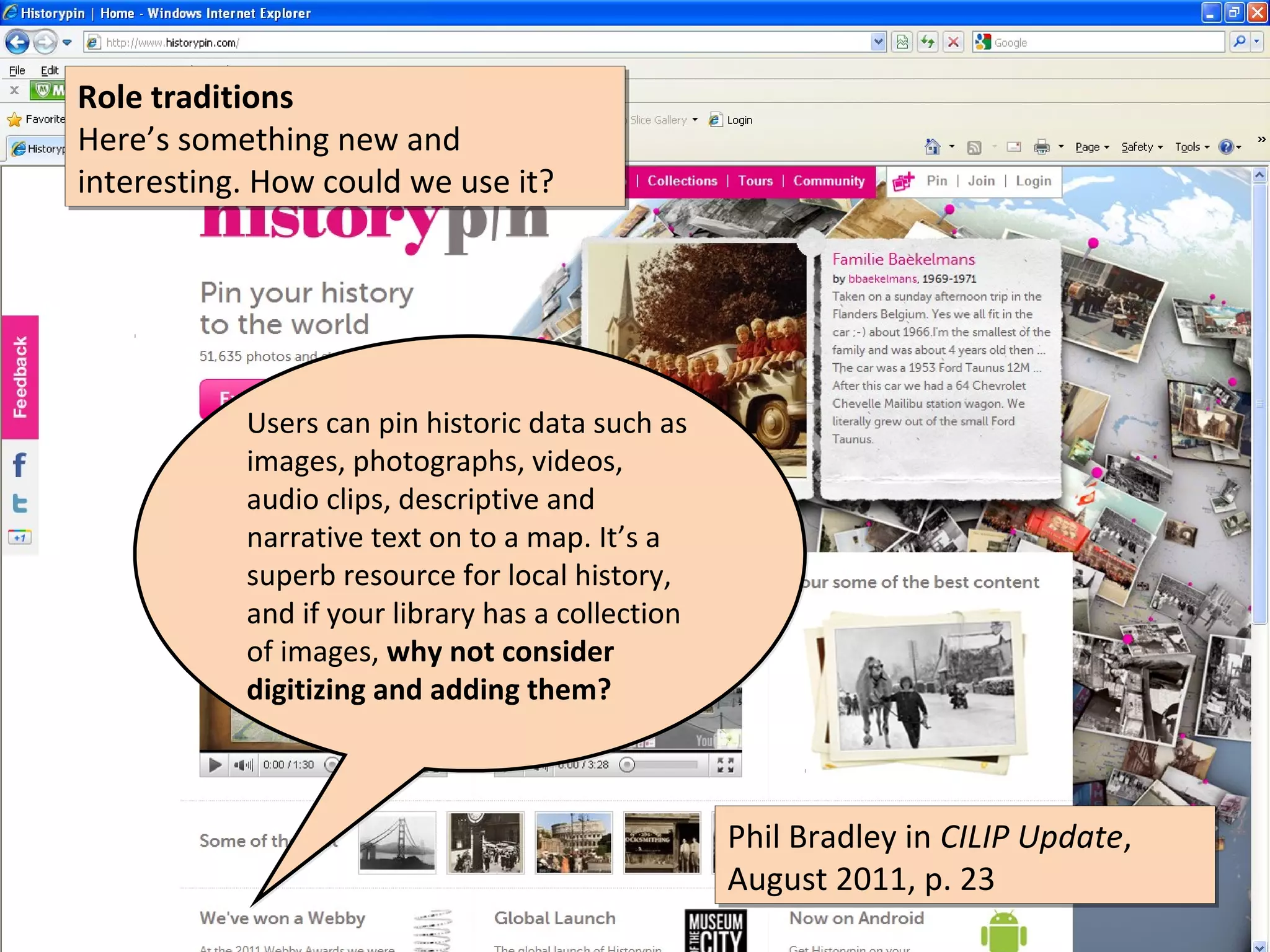
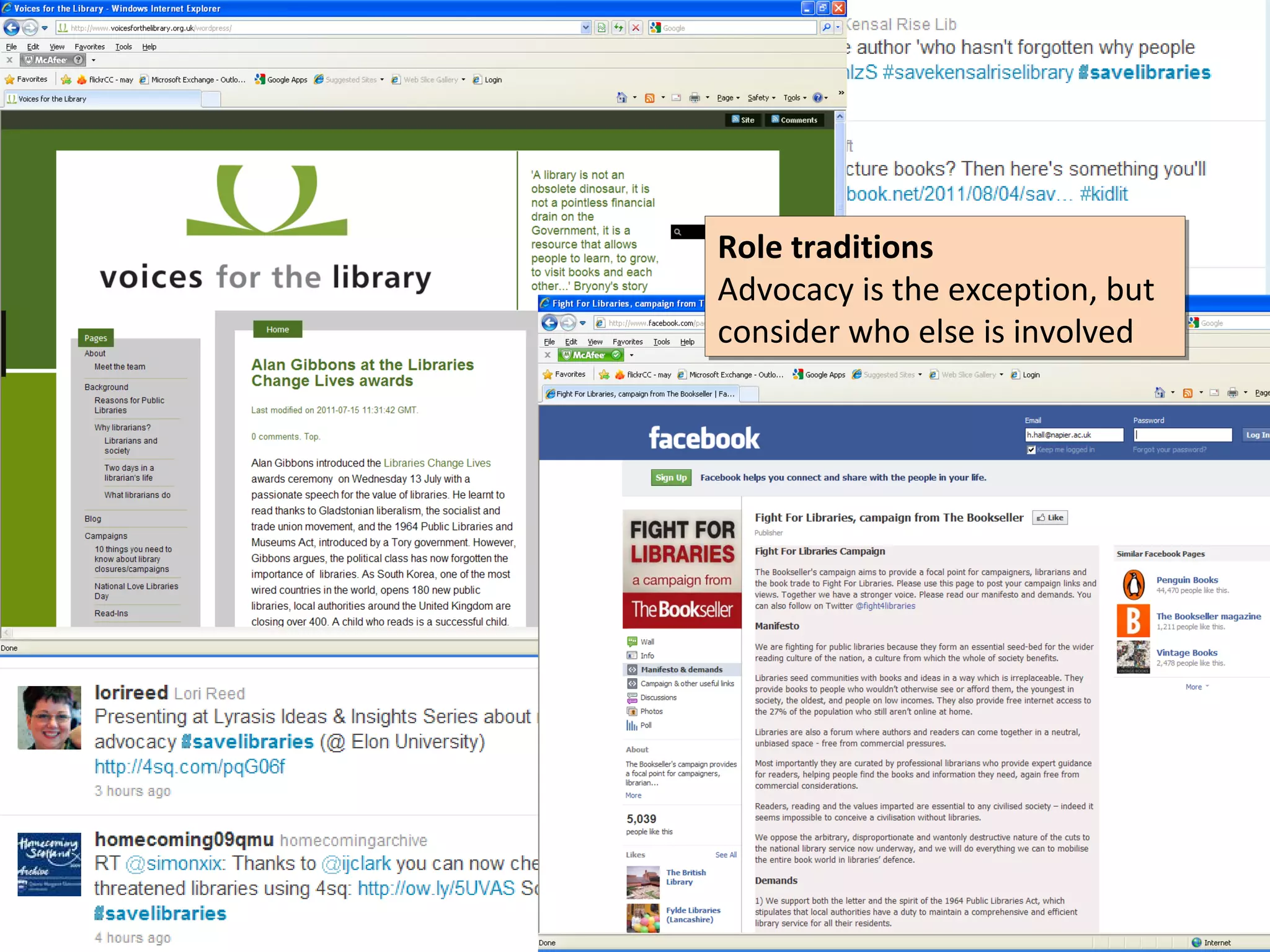
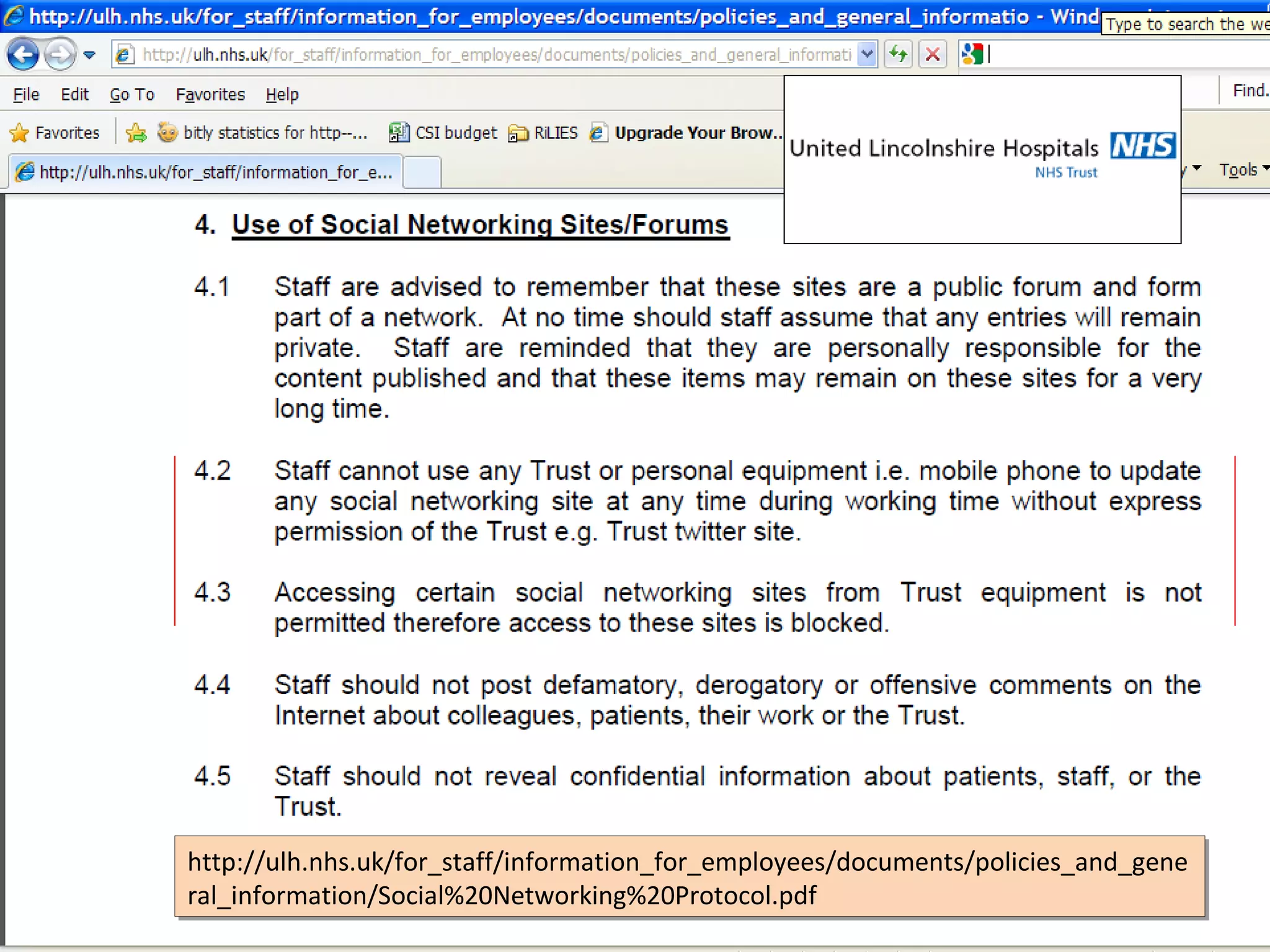
The document discusses the impact of social media on information services delivery, highlighting that its deployment often replicates traditional models and suggests possibilities for enhanced service through personal professional use. It emphasizes the importance of treating social media as integrated assets rather than just additional tools and notes the limitations posed by uncertainty around tools and established role traditions. Ultimately, the document advocates for a shift in perspectives to view users as active collaborators in service delivery.