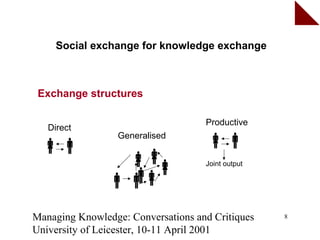
This document outlines a presentation on social exchange theory and its application in motivating knowledge sharing, emphasizing its significance in research and corporate environments. It discusses the theoretical framework of exchange theory, the role of actors and resources, and explores both hard and soft rewards as well as exchange conditions for effective knowledge sharing. The document concludes with considerations for future research directions in understanding knowledge sharing dynamics.