1. The document examines the relationship between brain anatomical networks and intelligence by analyzing structural, functional, and effective connectivity patterns.
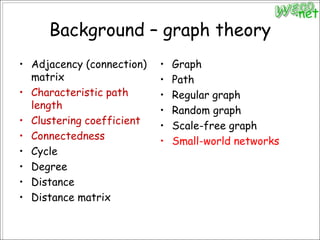
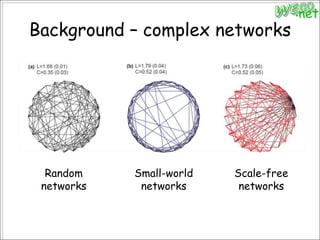
2. It reviews concepts from graph theory and complex networks that are relevant for studying brain networks, including small-world networks and scale-free networks.
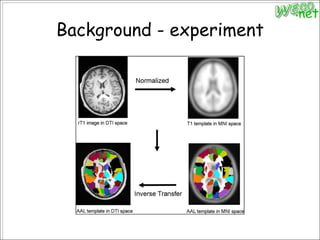
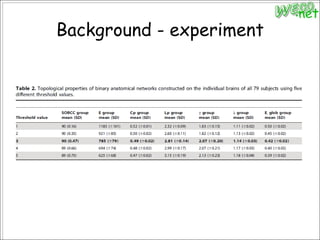
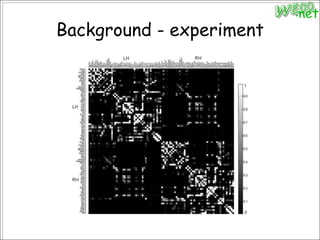
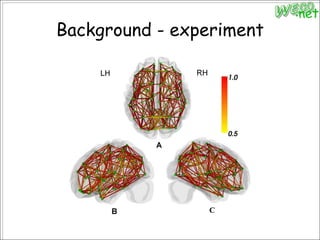
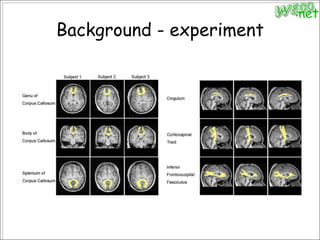
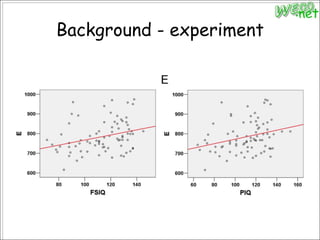
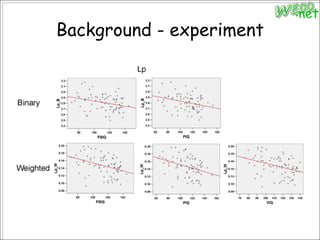
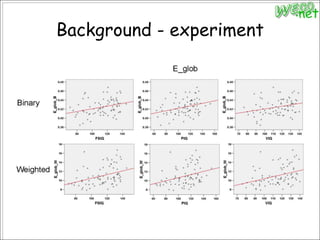
3. An experiment analyzed diffusion tensor images and other data from 79 subjects to construct and analyze anatomical brain networks and investigate their relationships with general and high intelligence.