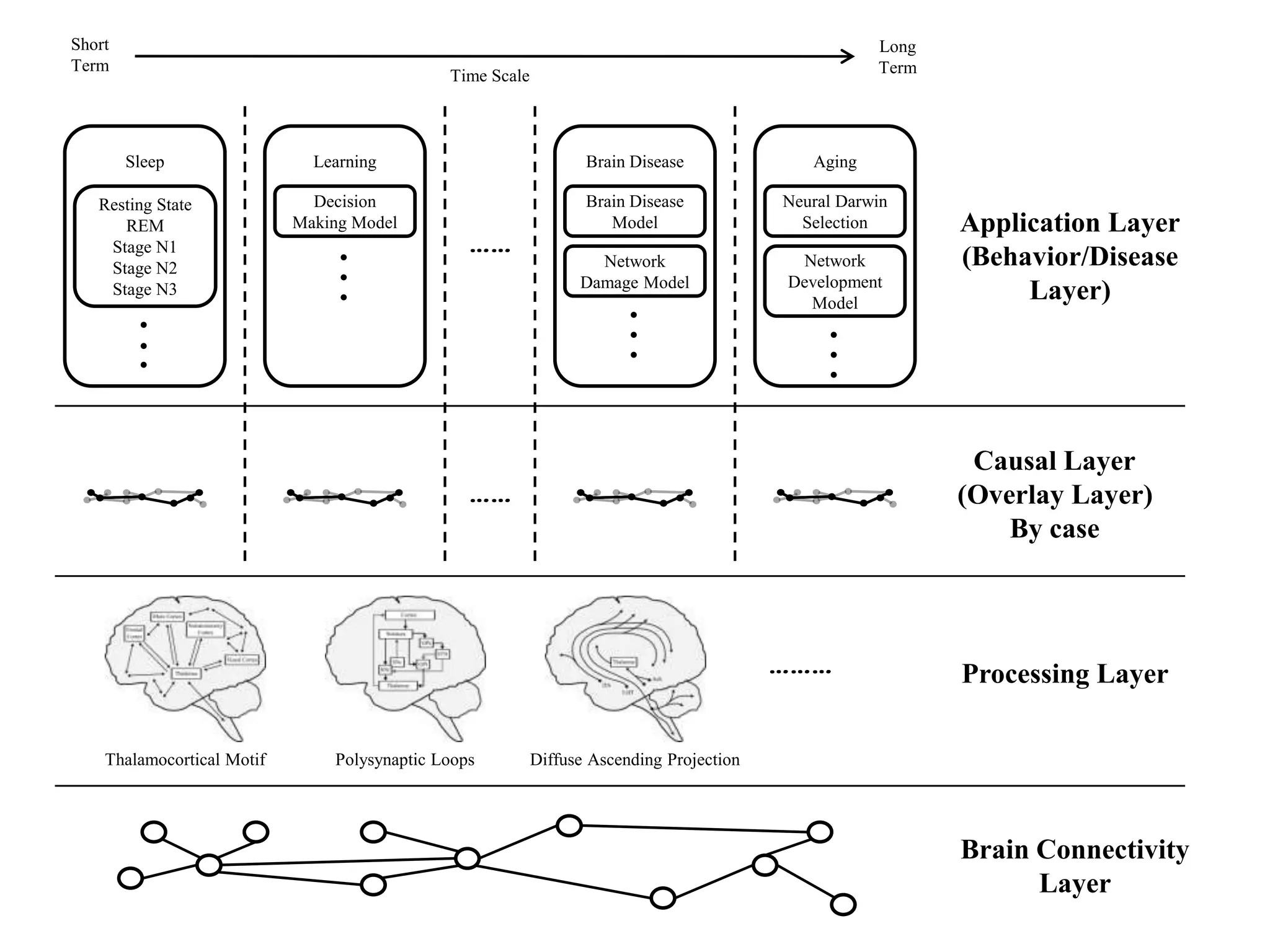
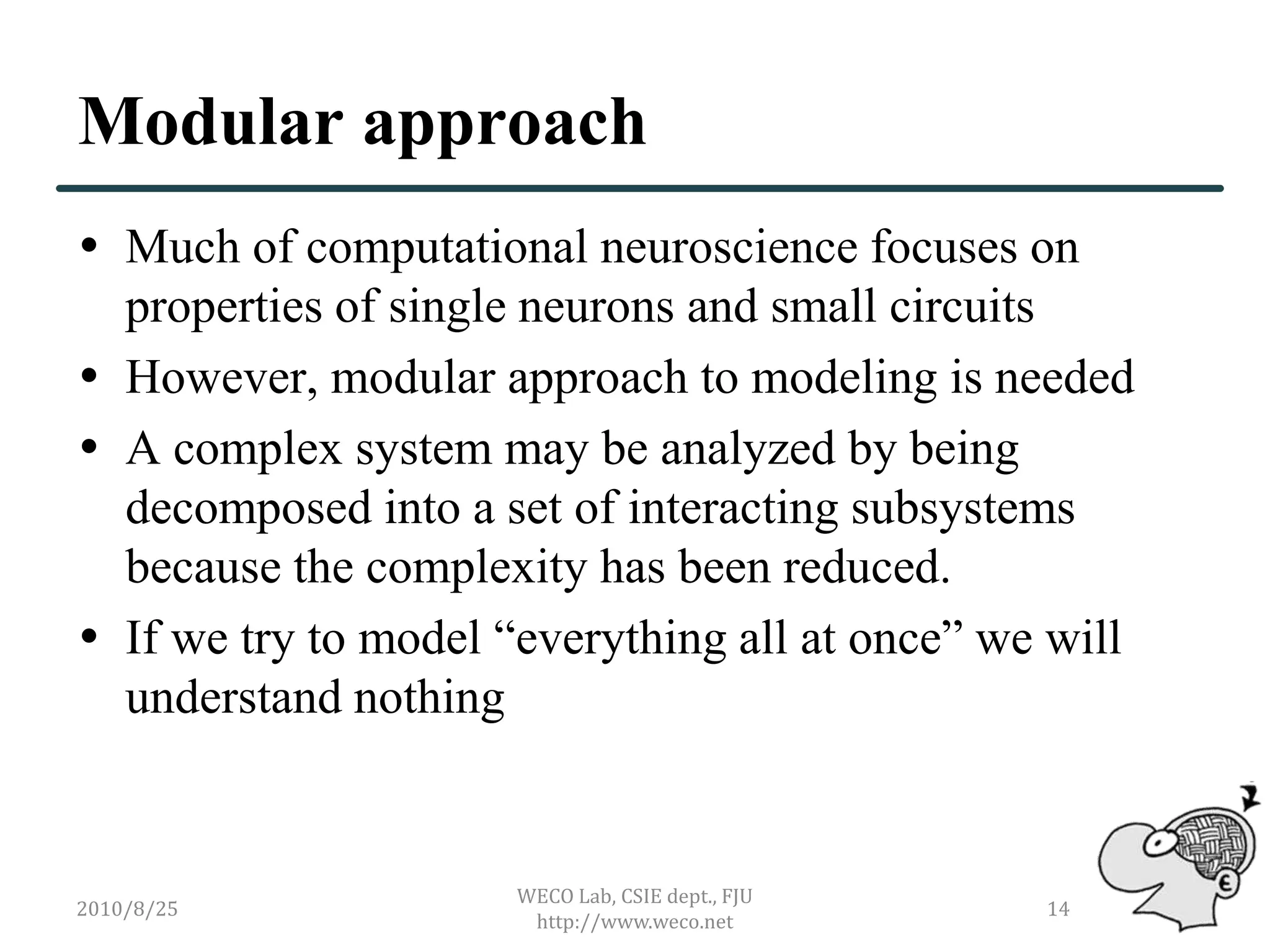
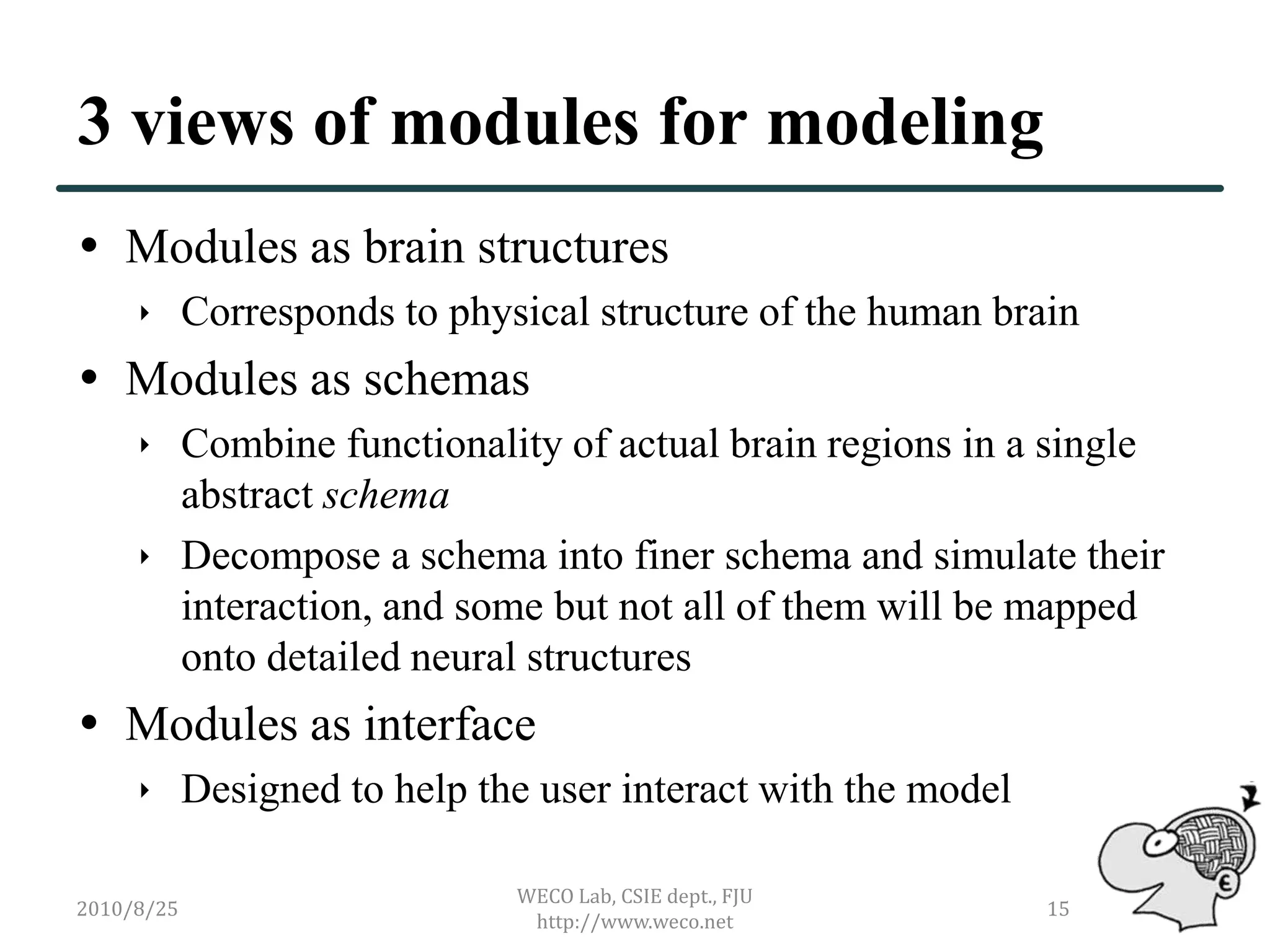
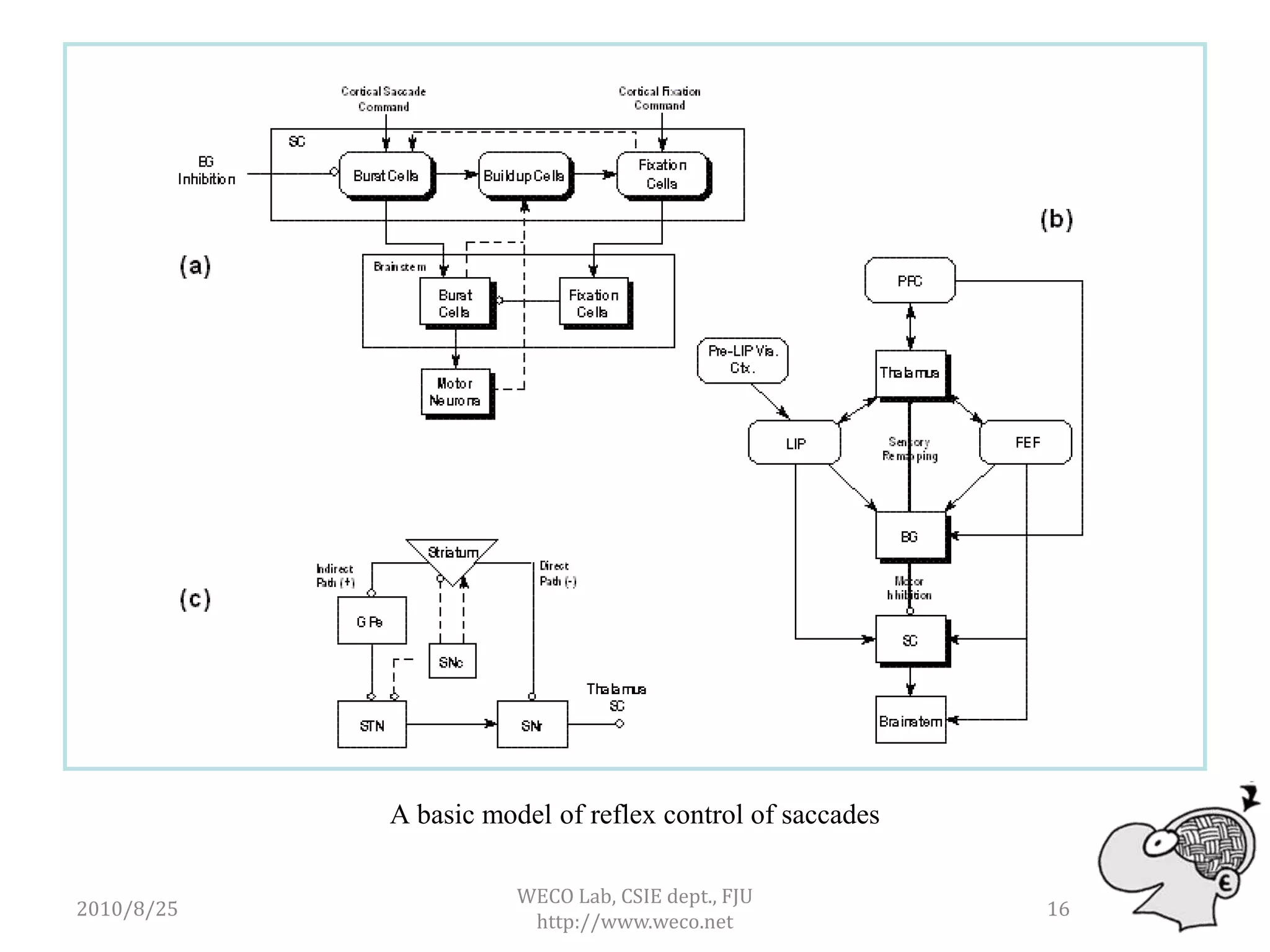
The document outlines the development of a brain simulator, discussing its connection to brain informatics, the current status of brain simulators, and the proposed architecture and approaches. It emphasizes the need for a modular modeling approach to simplify complex brain functions and interactions. The next steps focus on creating a comprehensive, extendable framework for brain simulation, integrating neuroanatomy and cognitive psychology.






![Reference
[1] Wen-Hsien Tseng, Song-Yun Lu, Hsing Mei, “On the development of a
brain simulator”, 2nd ICCCI (2010).
[2] Michael A Arbib (2007), Scholarpedia,
2(3):1869.doi:10.4249/scholarpedia.1869revision #59679
[3] Thomas M. Morse (2007), Scholarpedia,
2(4):3036.doi:10.4249/scholarpedia.3036revision #39060
WECO Lab, CSIE dept., FJU
2010/8/25 22
http://www.weco.net](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20100806onthedevelopmentofabrainsimulatorwecolab-100825040029-phpapp01/75/On-the-Development-of-a-Brain-Simulator-22-2048.jpg)