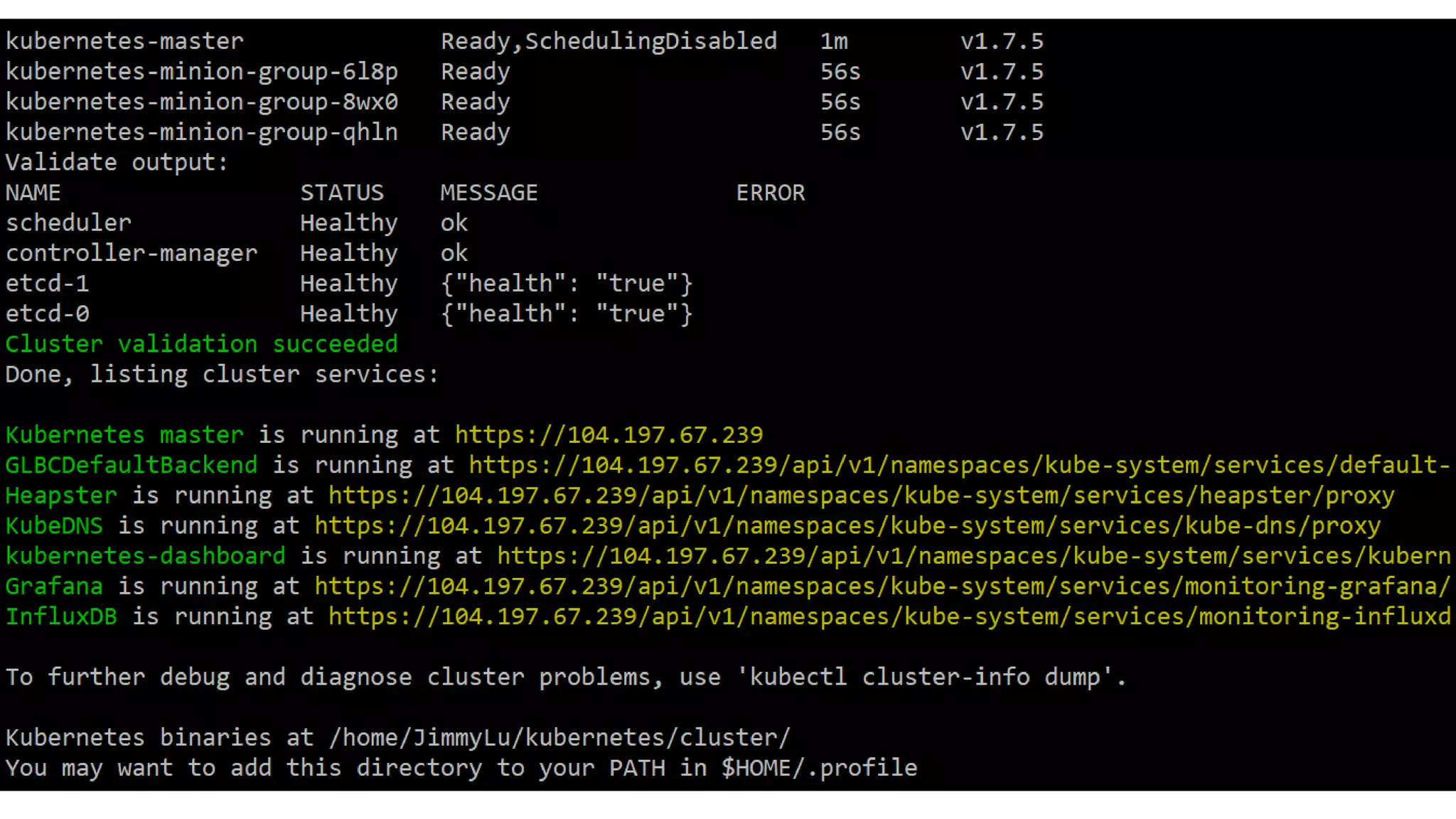
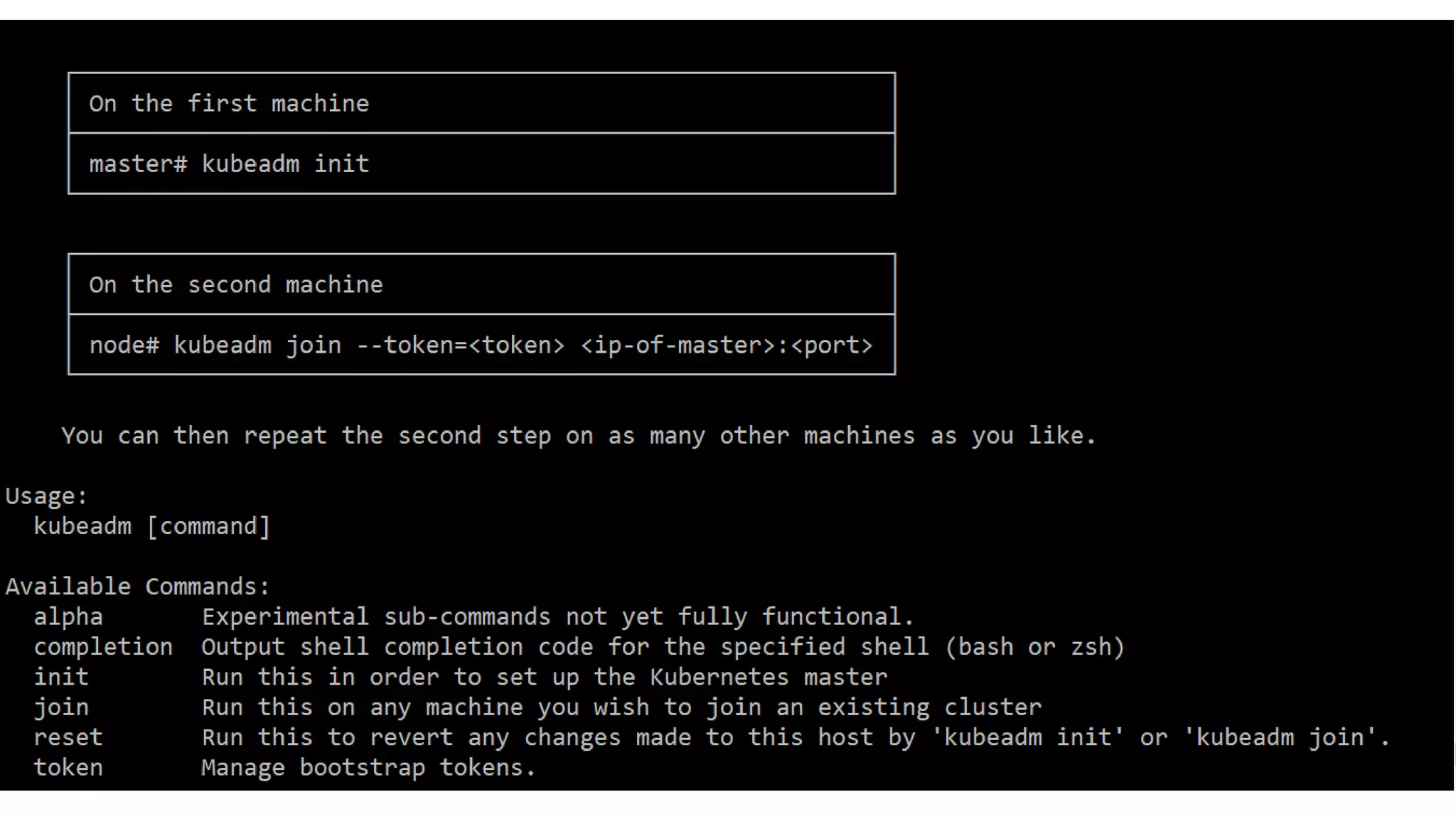
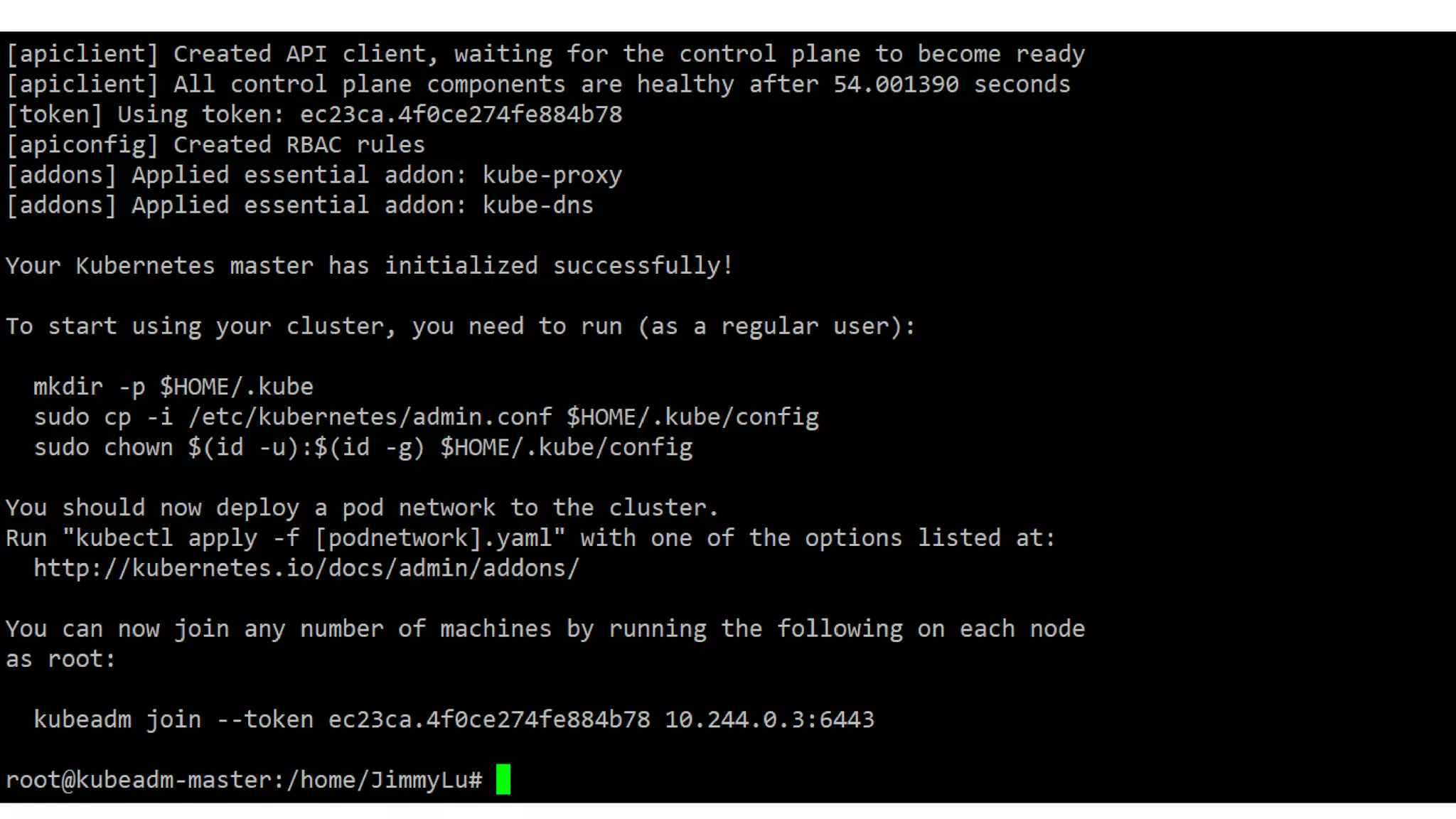
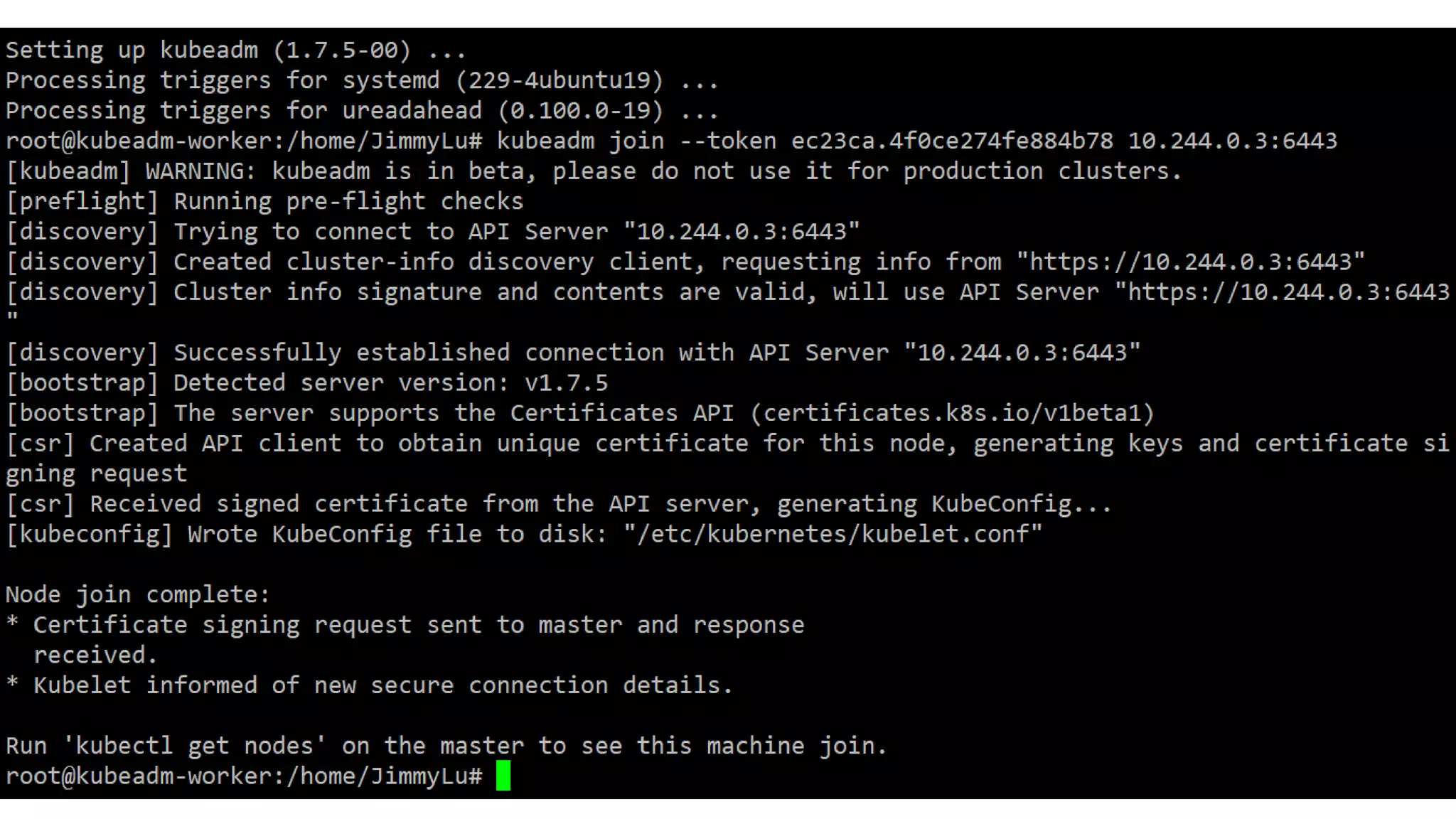
The document discusses various methods for deploying a Kubernetes cluster, highlighting tools such as Minikube, kubeadm, kops, and an in-house solution called Kubewizard developed by Linker Networks. It emphasizes the complexity and variety of options in the Kubernetes ecosystem, while also detailing the advantages and limitations of each deployment tool. The content also touches on the importance of community resources and tutorials for learning Kubernetes effectively.