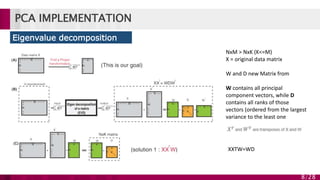
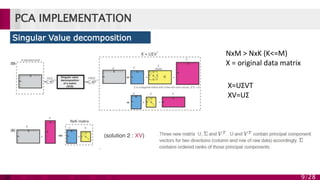
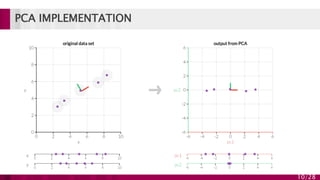
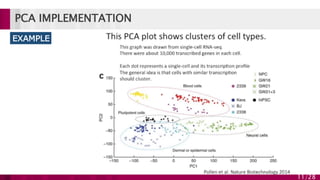
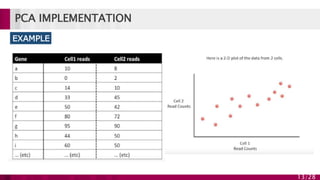
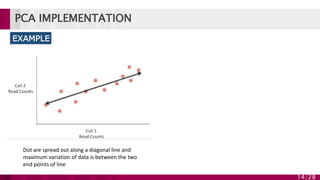
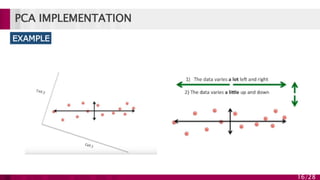
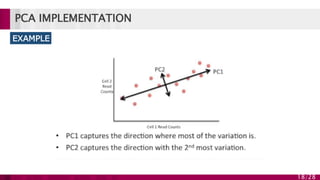
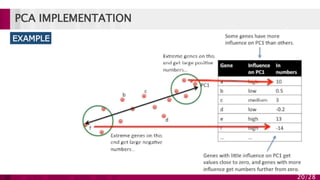
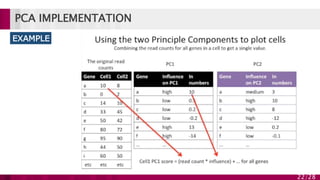
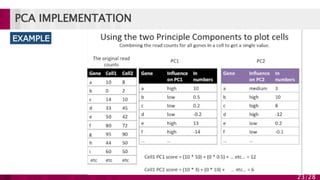
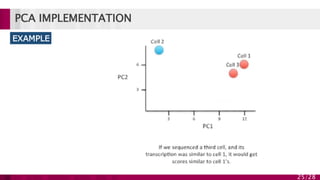
Principal component analysis (PCA) is a technique used to simplify complex datasets. It works by converting a set of observations of possibly correlated variables into a set of linearly uncorrelated variables called principal components. PCA identifies patterns in data and expresses the data in such a way as to highlight their similarities and differences. The main implementations of PCA are eigenvalue decomposition and singular value decomposition. PCA is useful for data compression, reducing dimensionality for visualization and building predictive models. However, it works best for data that follows a multidimensional normal distribution.