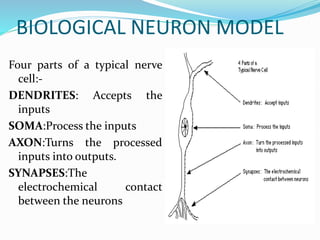
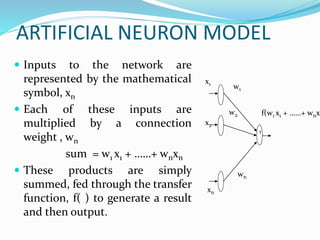
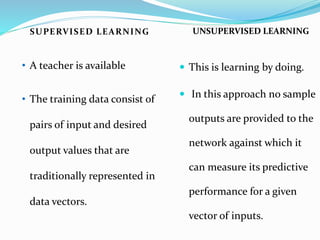
This document provides an overview of artificial neural networks. It describes the biological neuron model that inspired artificial networks, with dendrites receiving inputs, the soma processing them, the axon transmitting outputs, and synapses connecting neurons. An artificial neuron model is presented that uses weighted inputs, a summation function, and an activation function to generate outputs. The document discusses unsupervised and supervised learning methods, and lists applications such as character recognition, stock prediction, and medicine. Advantages include human-like thinking and handling noisy data, while disadvantages include the need for training and high processing times.