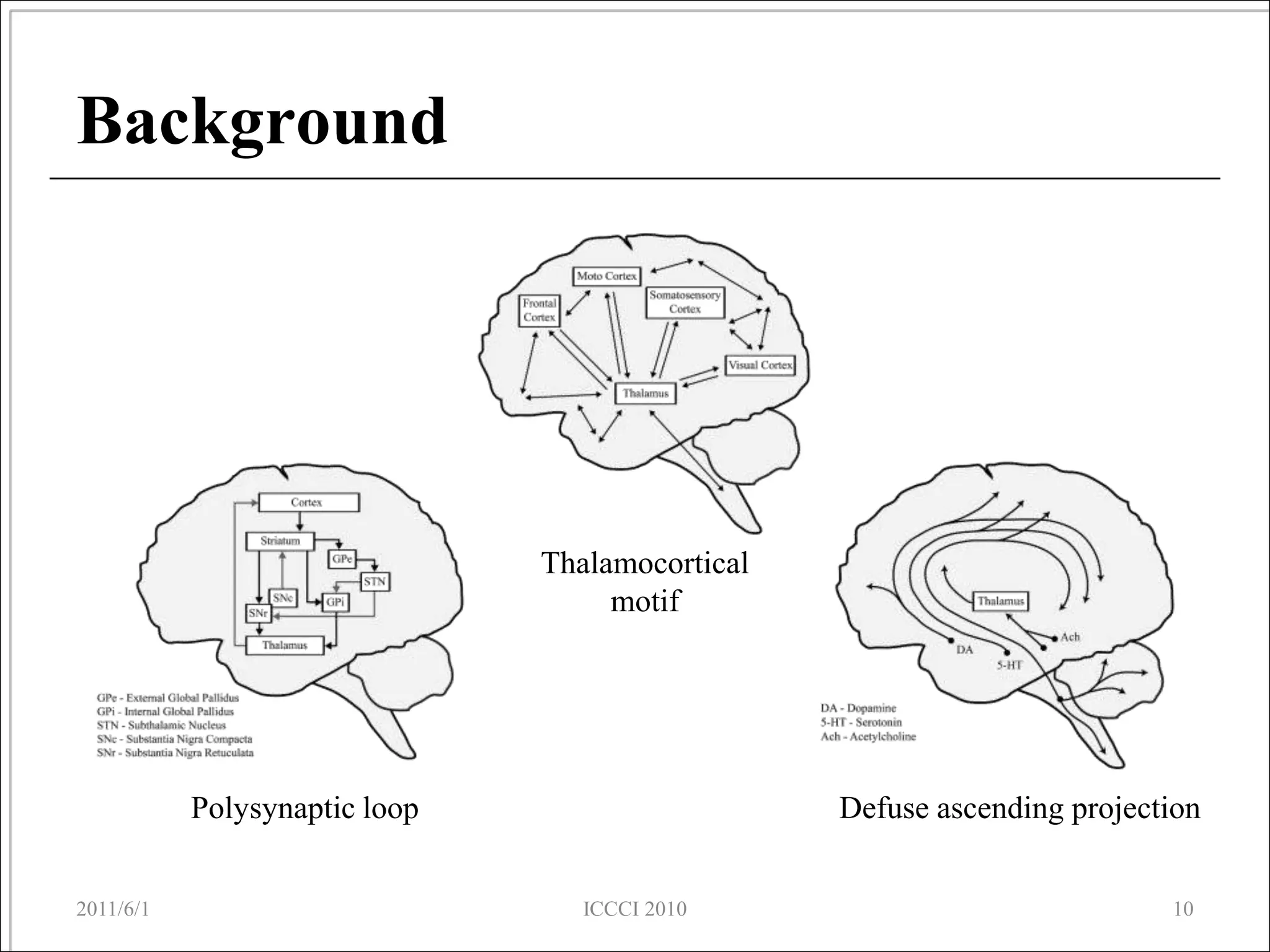
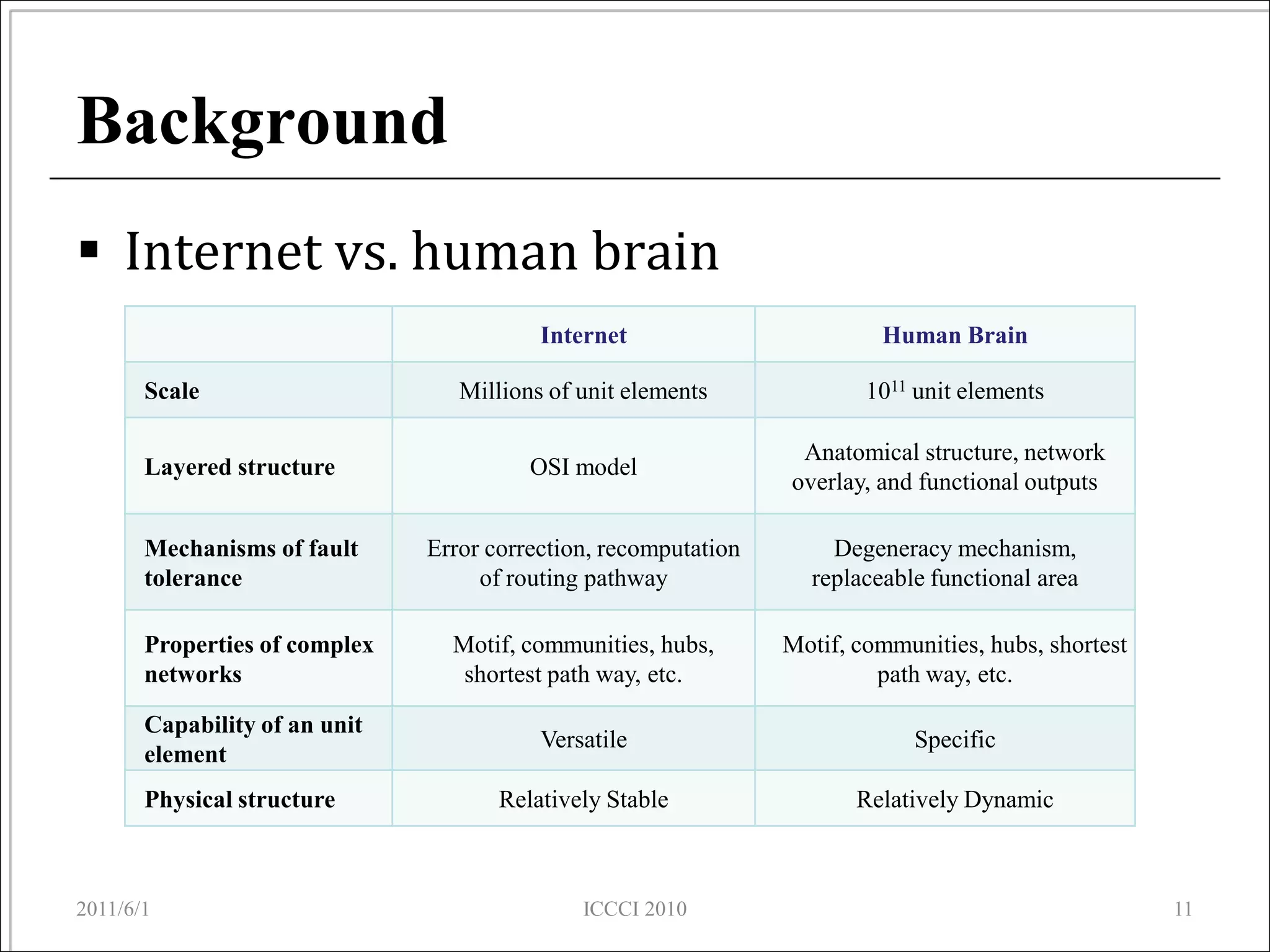
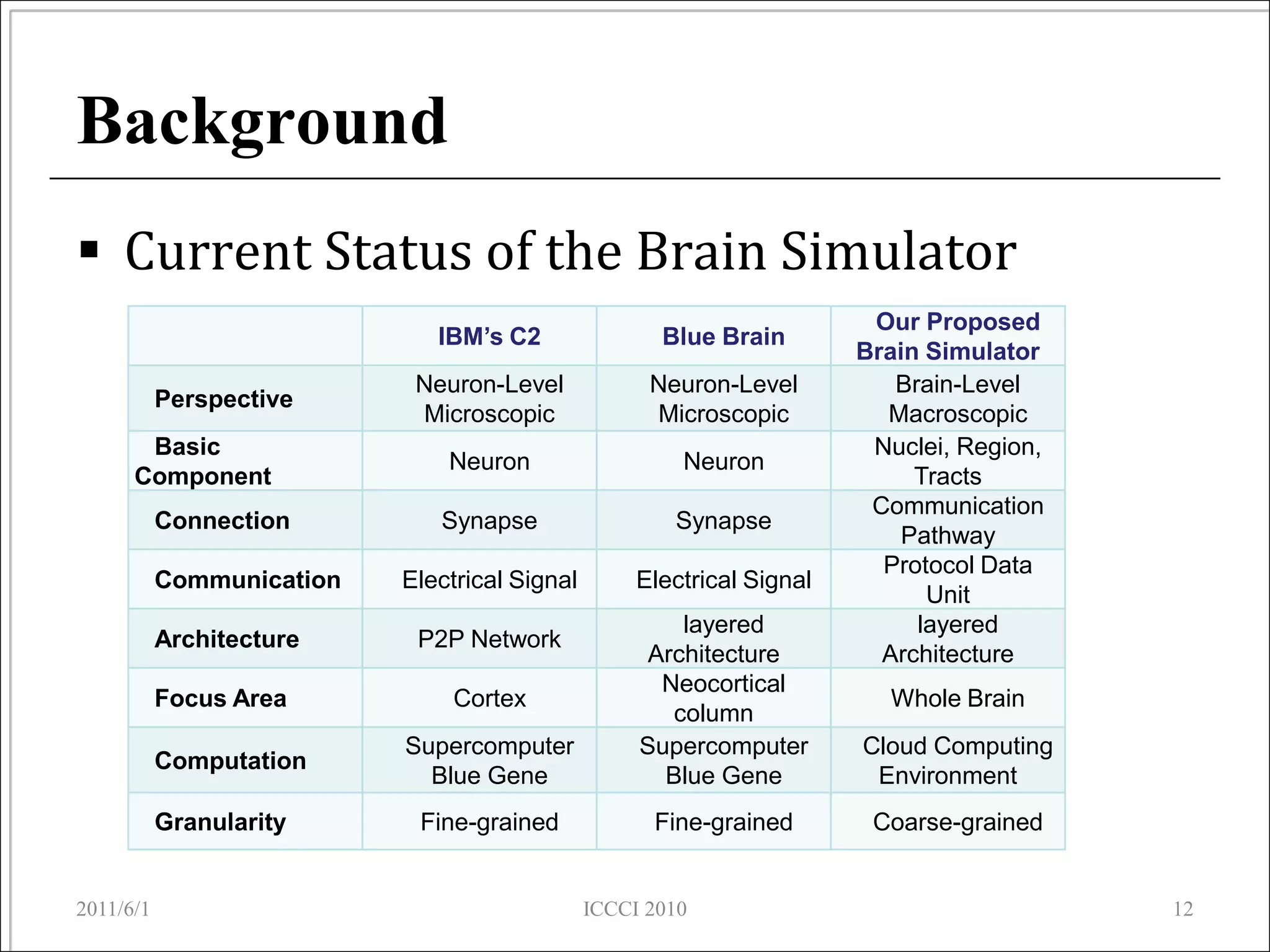
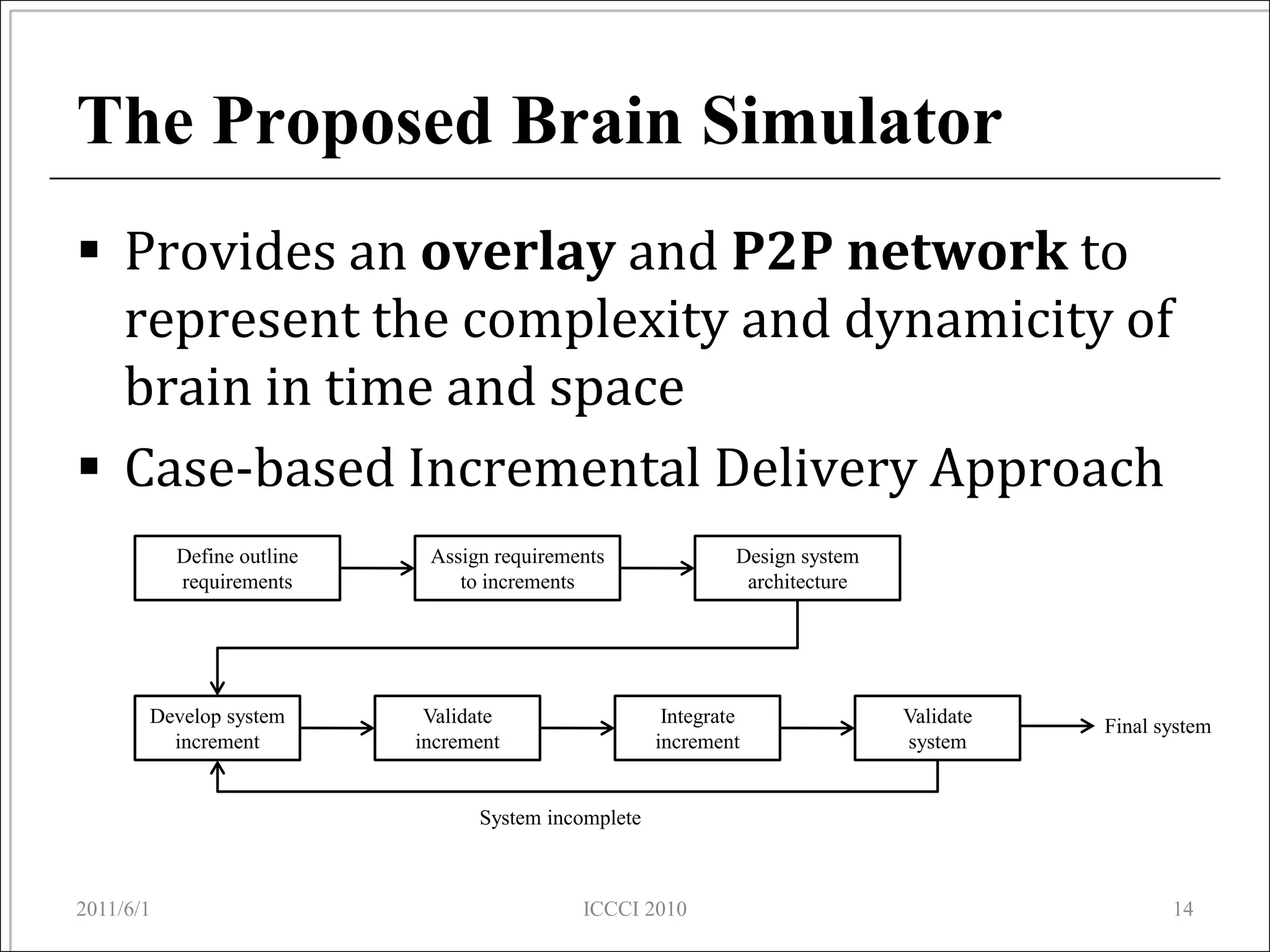
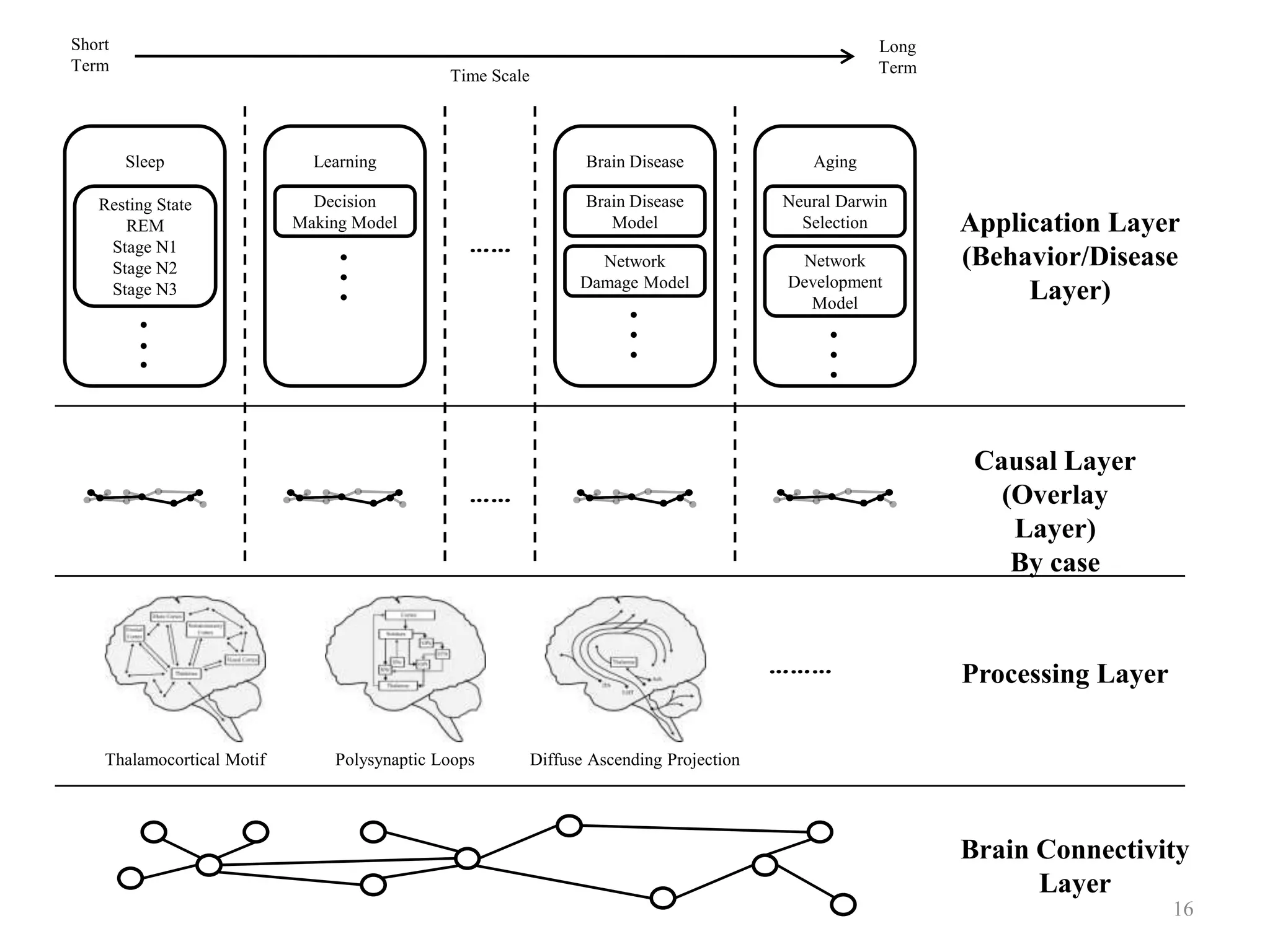
The document presents an overview of a proposed brain simulator that models brain structures and functions to enhance understanding of human cognition and related diseases. It highlights brain informatics as an interdisciplinary field that utilizes advanced technologies including network analysis to study complex brain networks. The ongoing development of the simulator aims to create an accurate representation of the human brain for further research and testing.