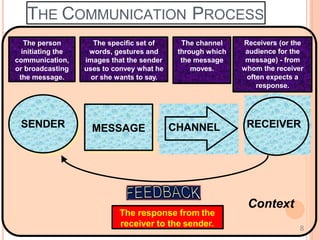
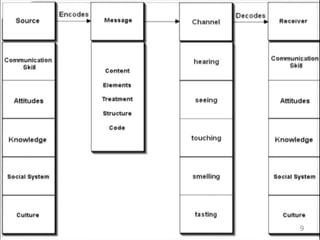
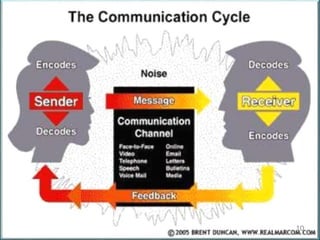
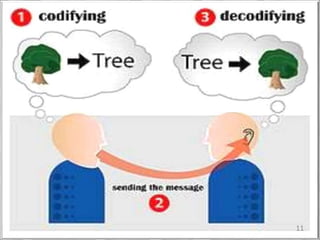
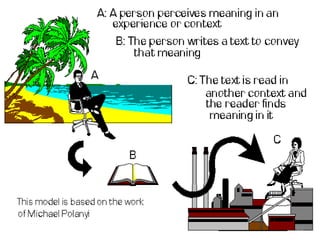
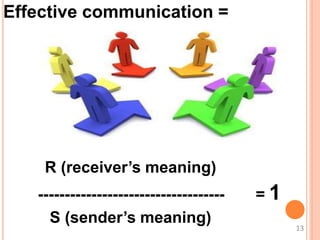
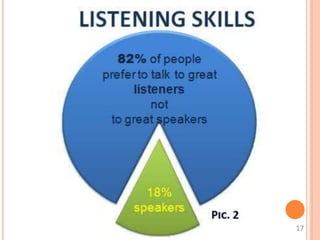
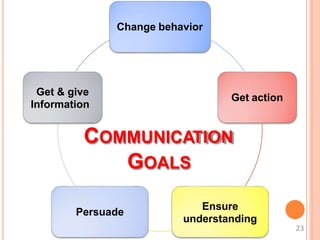
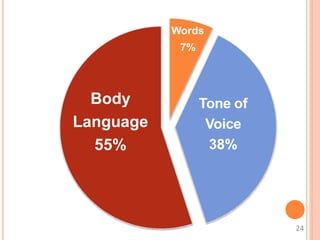
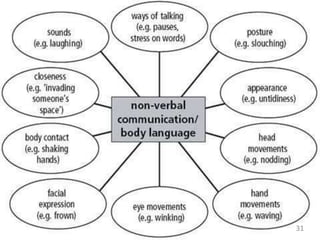
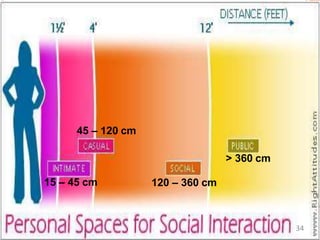
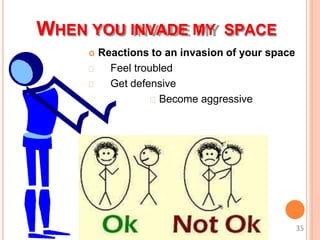
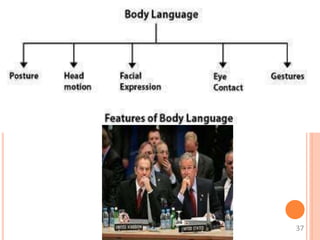
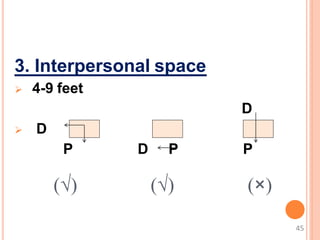
This document discusses communication skills and their importance in healthcare. It defines communication, outlines the communication process, and describes different types of communication including verbal, non-verbal, listening, and counseling. Effective communication skills are essential for healthcare professionals to properly diagnose patients, ensure patient understanding, and build trust. These skills include active listening, probing patients for information, observing non-verbal cues, and informing patients in a clear manner. The document emphasizes the need to practice communication skills to become a good role model and provider in healthcare.