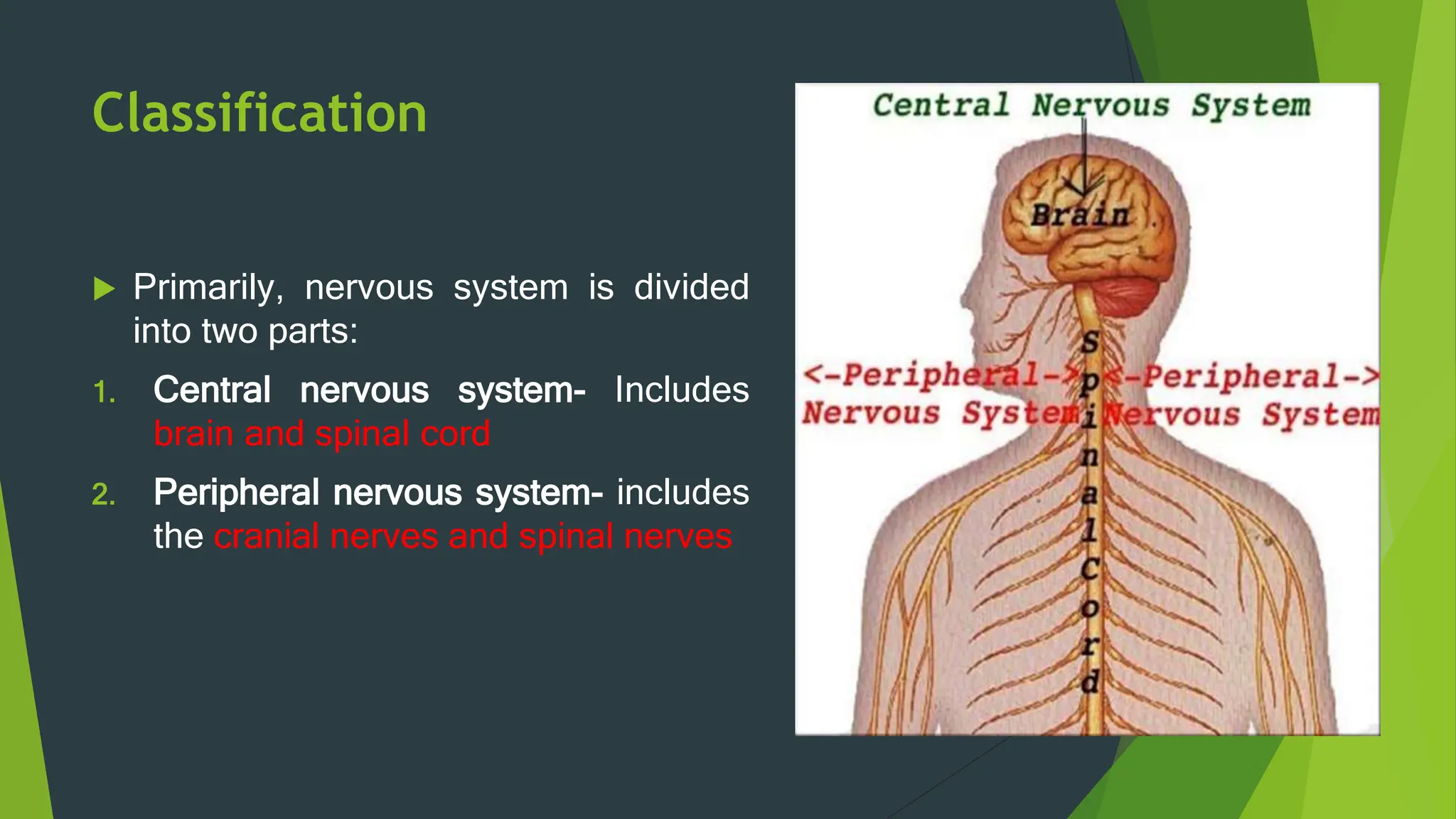
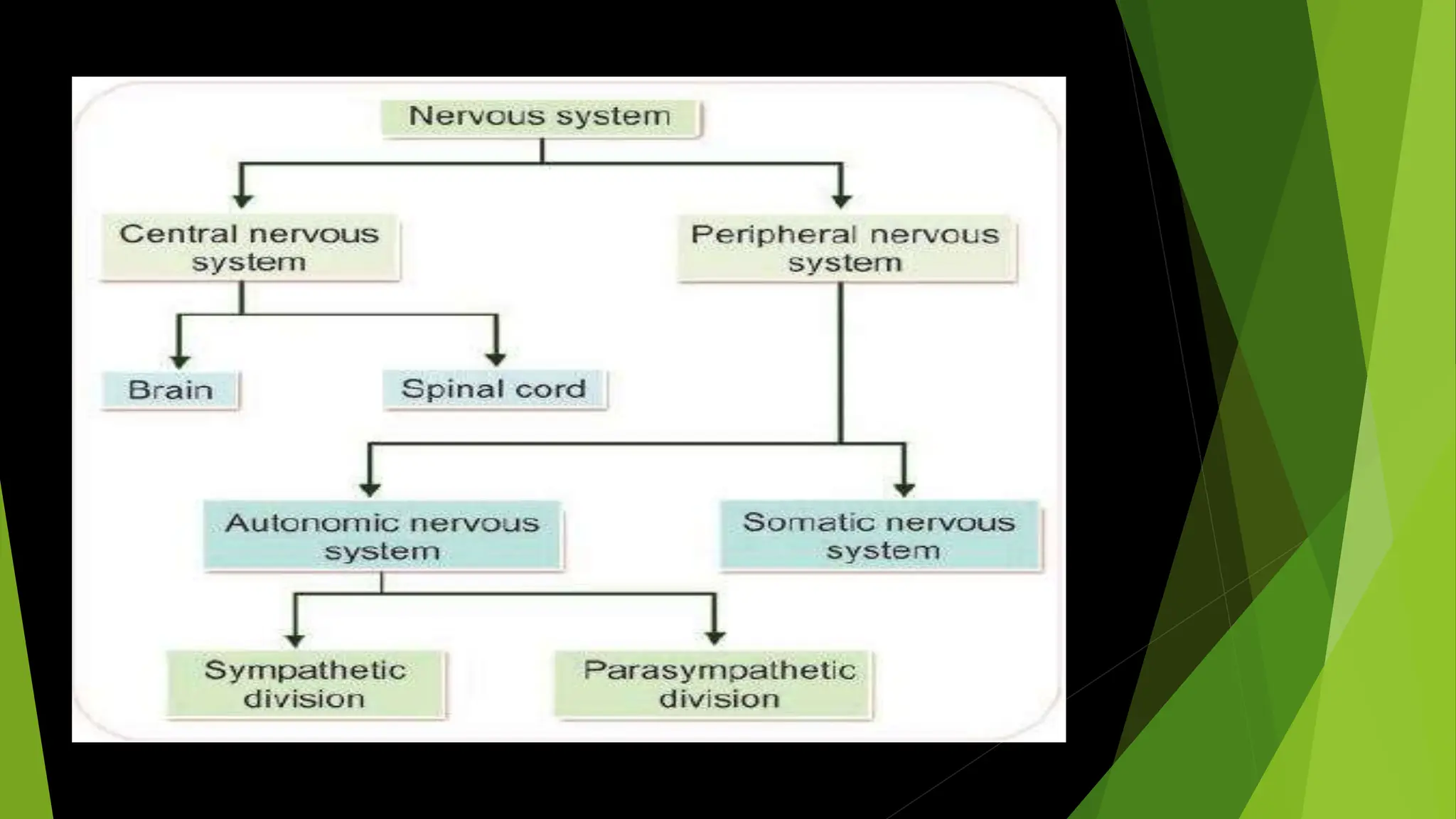
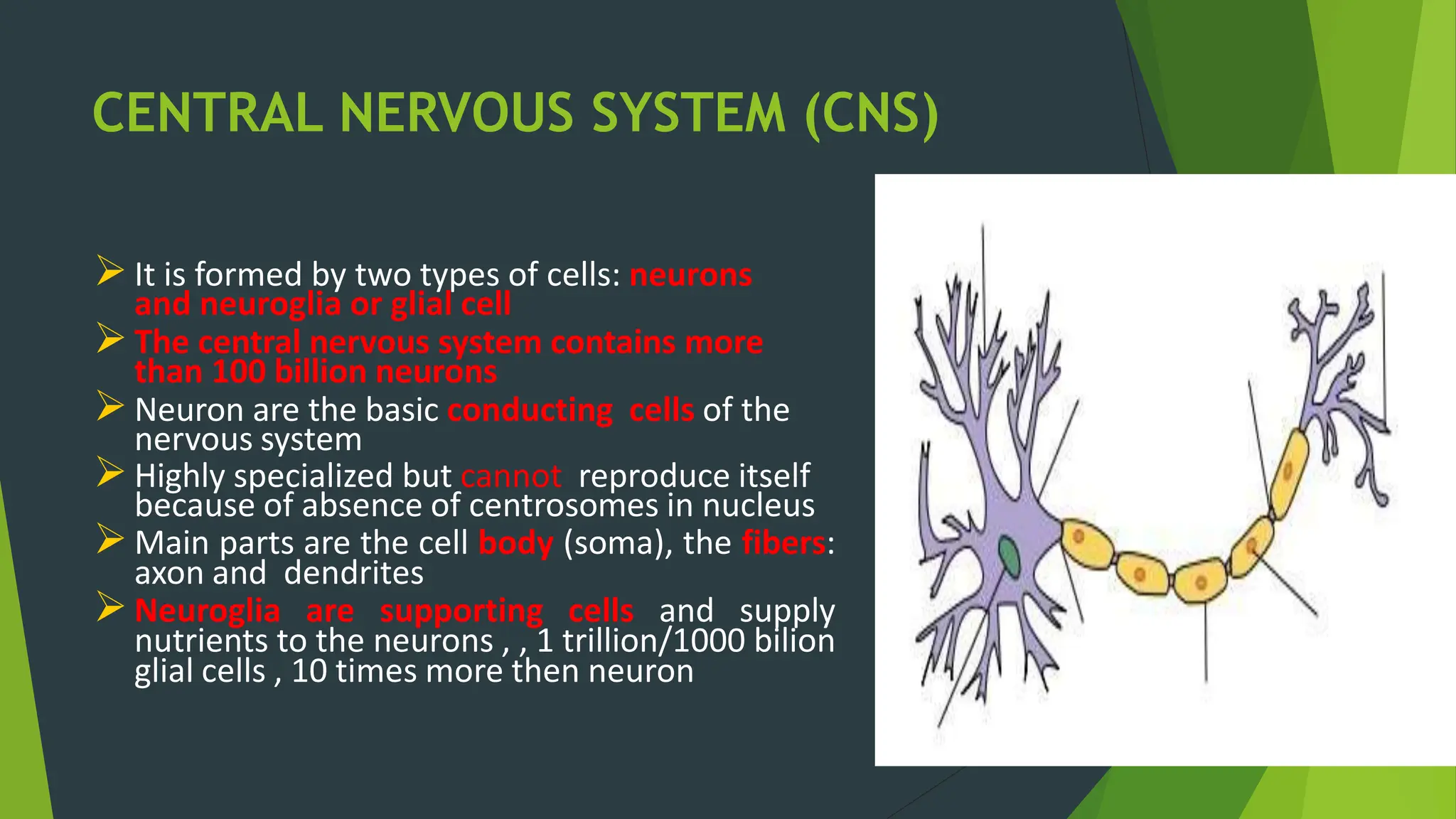
The nervous system has two main parts: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS is made up of the brain and spinal cord. It contains neurons and neuroglia, and is divided into gray matter and white matter. The PNS includes nerves that branch throughout the body from the CNS, and is divided into the somatic and autonomic systems. The somatic system controls skeletal muscles, while the autonomic system regulates involuntary functions like respiration and digestion.