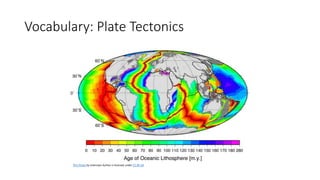
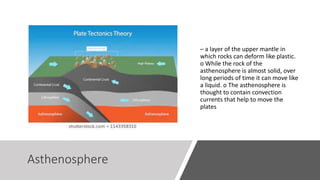
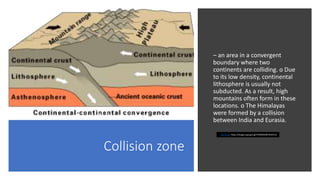
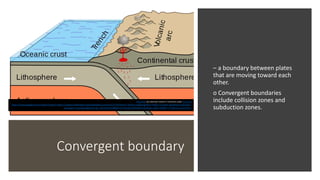
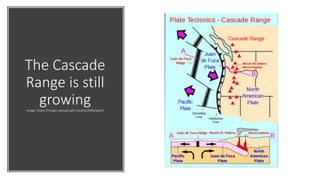
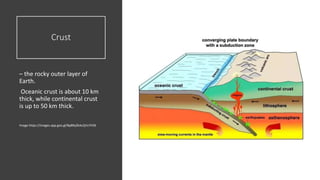
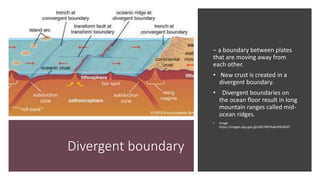
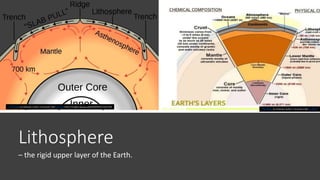
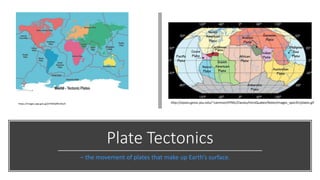
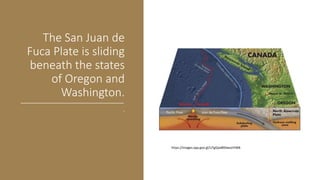
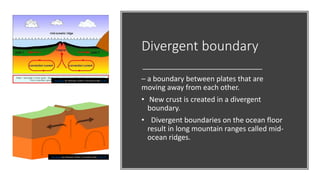
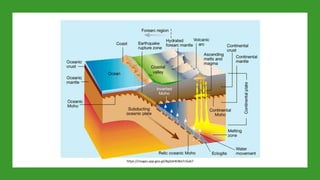
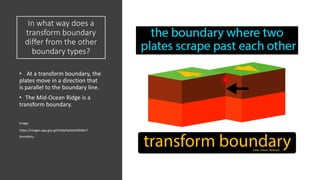
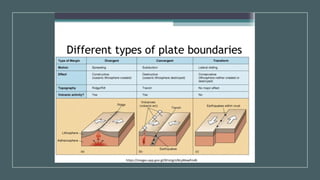
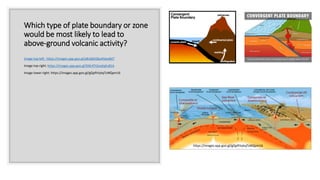
Plate tectonics refers to the movement of tectonic plates that make up Earth's surface. There are several types of plate boundaries that control this movement, including divergent boundaries where plates move apart and new crust is created, convergent boundaries where plates collide or one slides under the other, and transform boundaries where plates slide past each other horizontally. Volcanic activity is most likely to occur above subduction zones, where one plate is pushed deep into the Earth's mantle. The movement and collisions of tectonic plates over millions of years have shaped Earth's surface and continue to cause geological events like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.