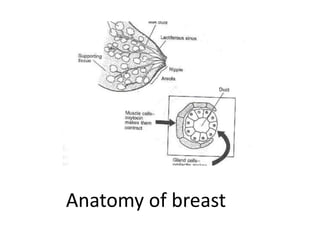
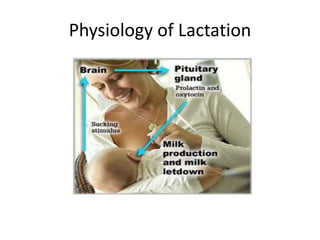
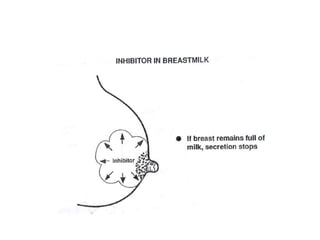
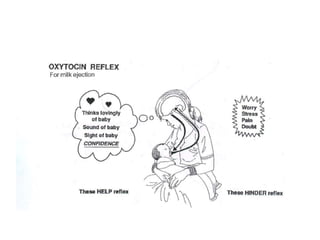
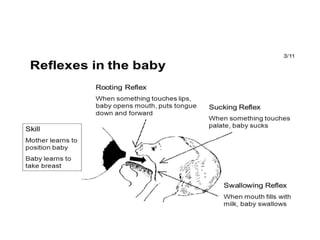
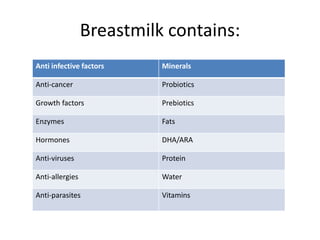
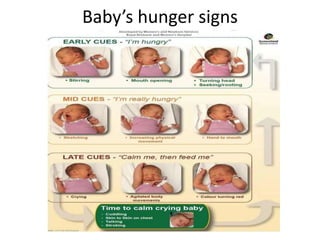
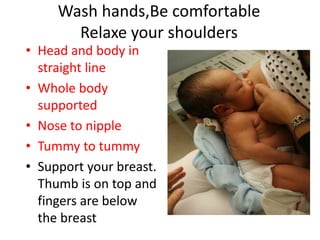
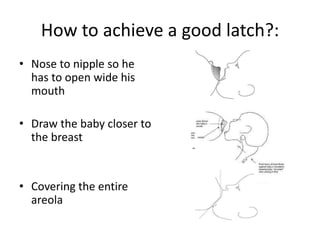
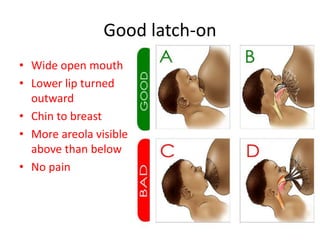
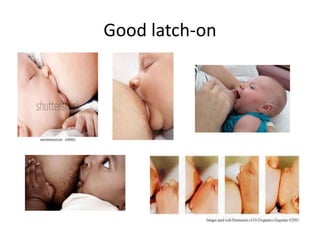
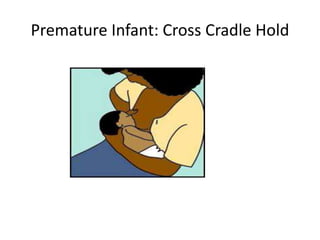
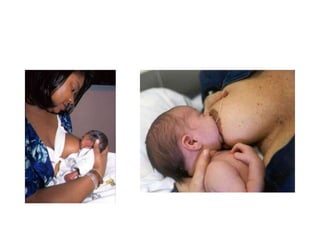
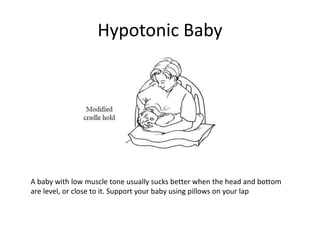
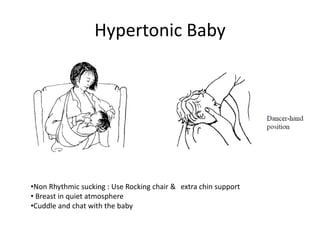
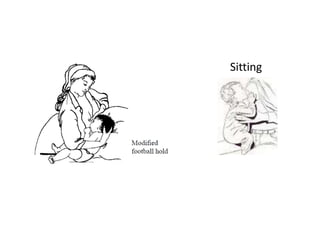
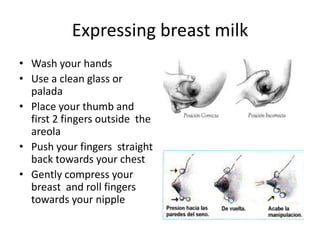
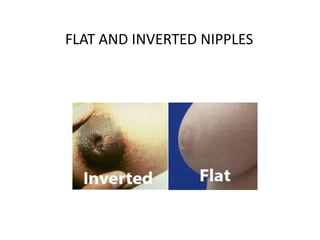
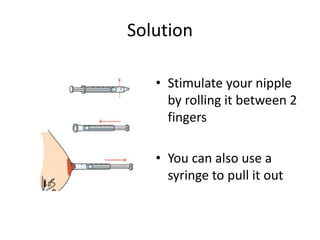
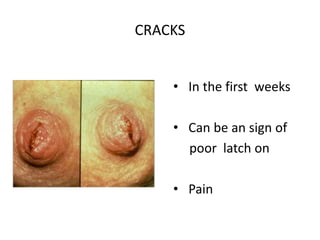
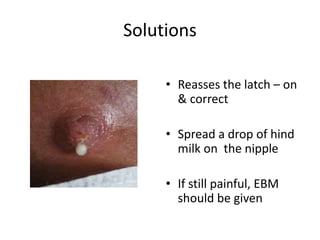
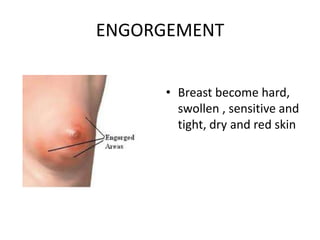
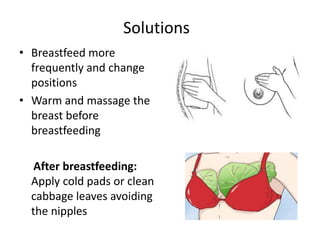
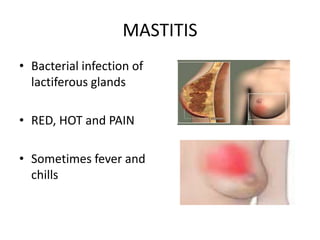
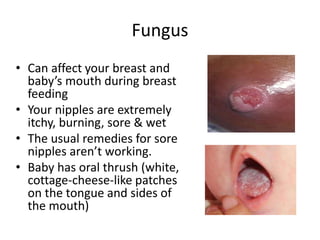
Breastfeeding is essential as breast milk is the most natural and adaptive food for infants, providing protection against infections and promoting maternal health. Newborns should be breastfed exclusively for the first 6 months, with complementary foods introduced up to 2 years or beyond, emphasizing correct latching and recognizing hunger signs. Various challenges during breastfeeding, such as engorgement and poor latch, can be managed with proper techniques and assistance.