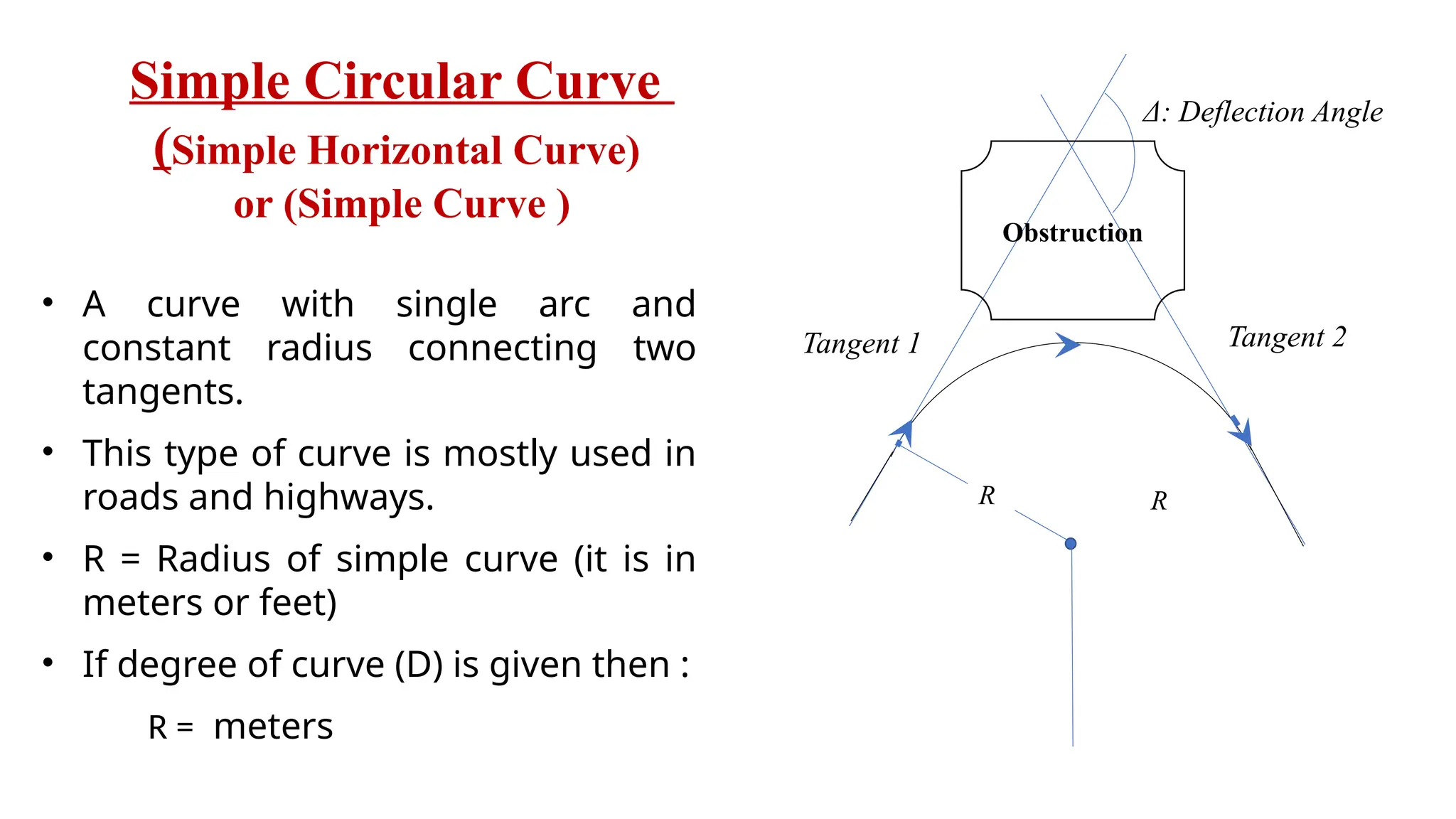
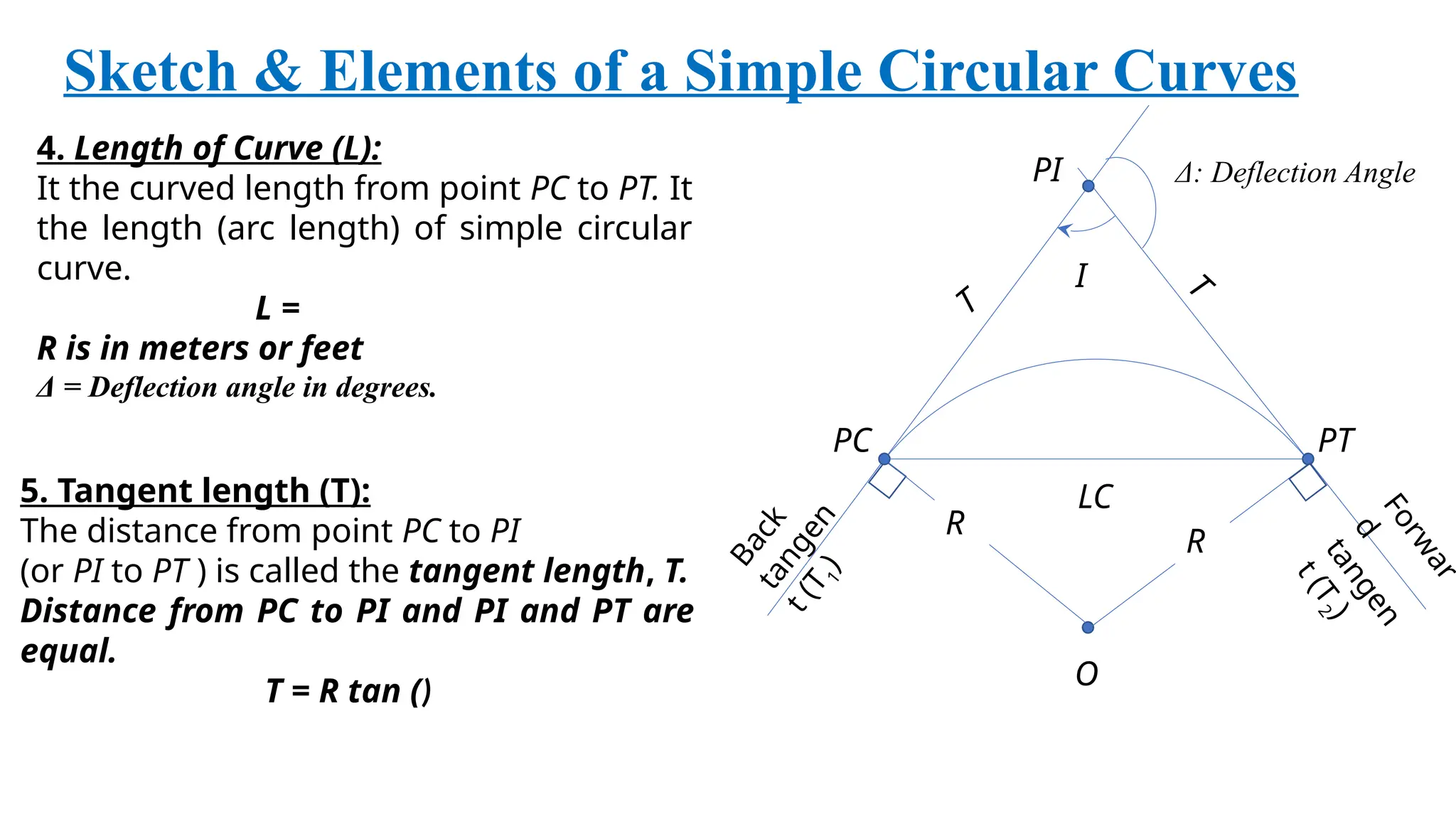
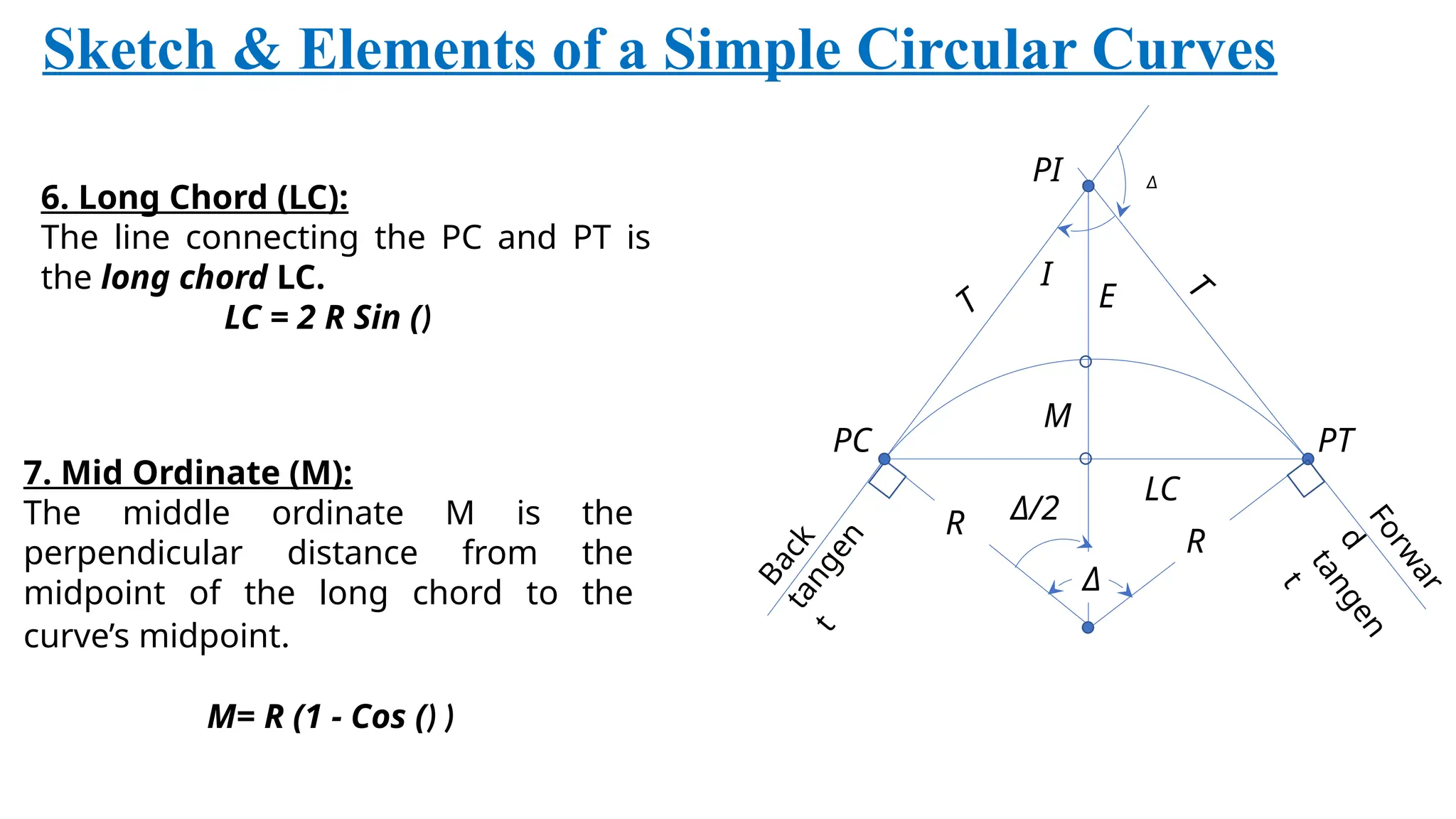
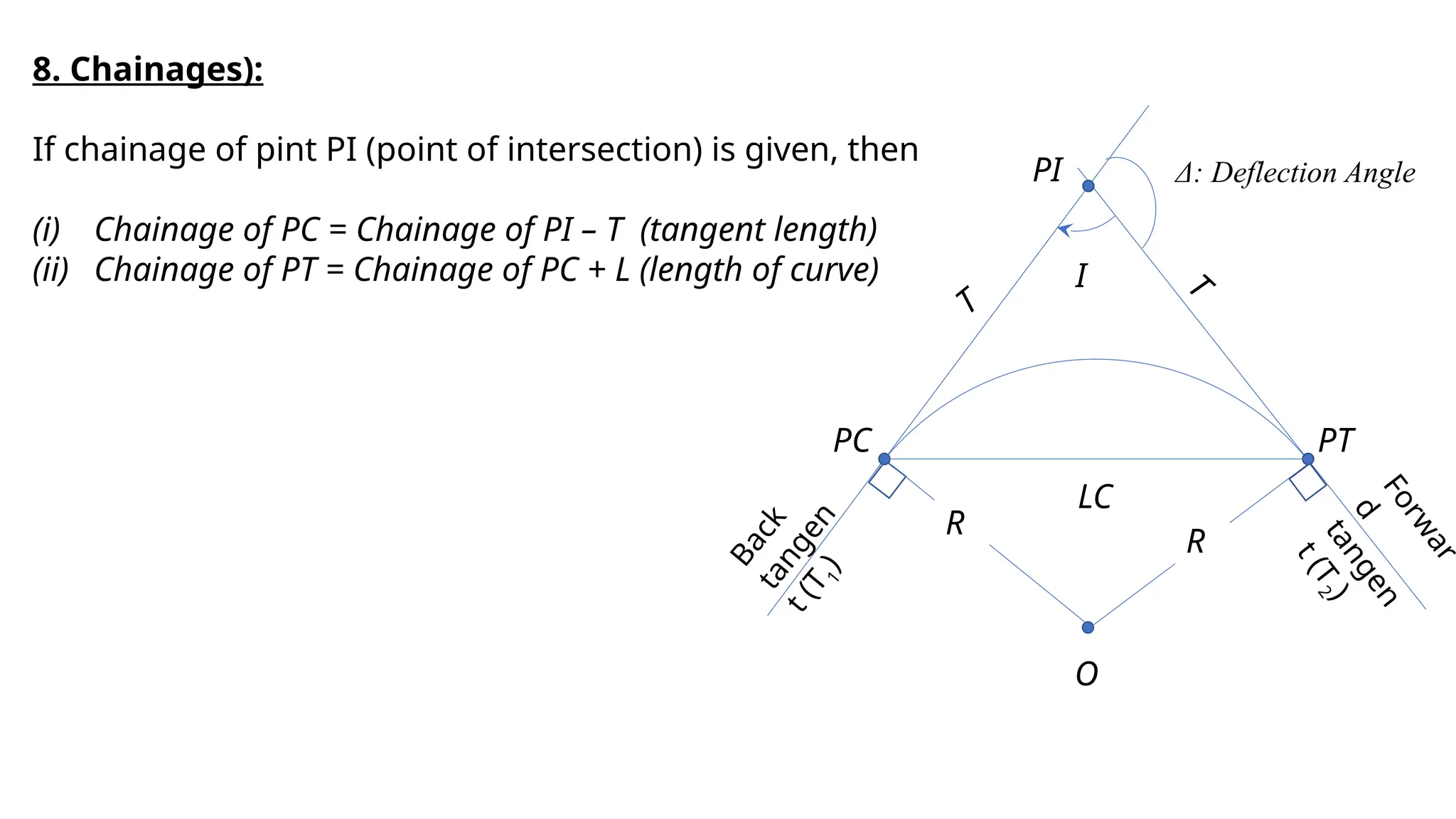
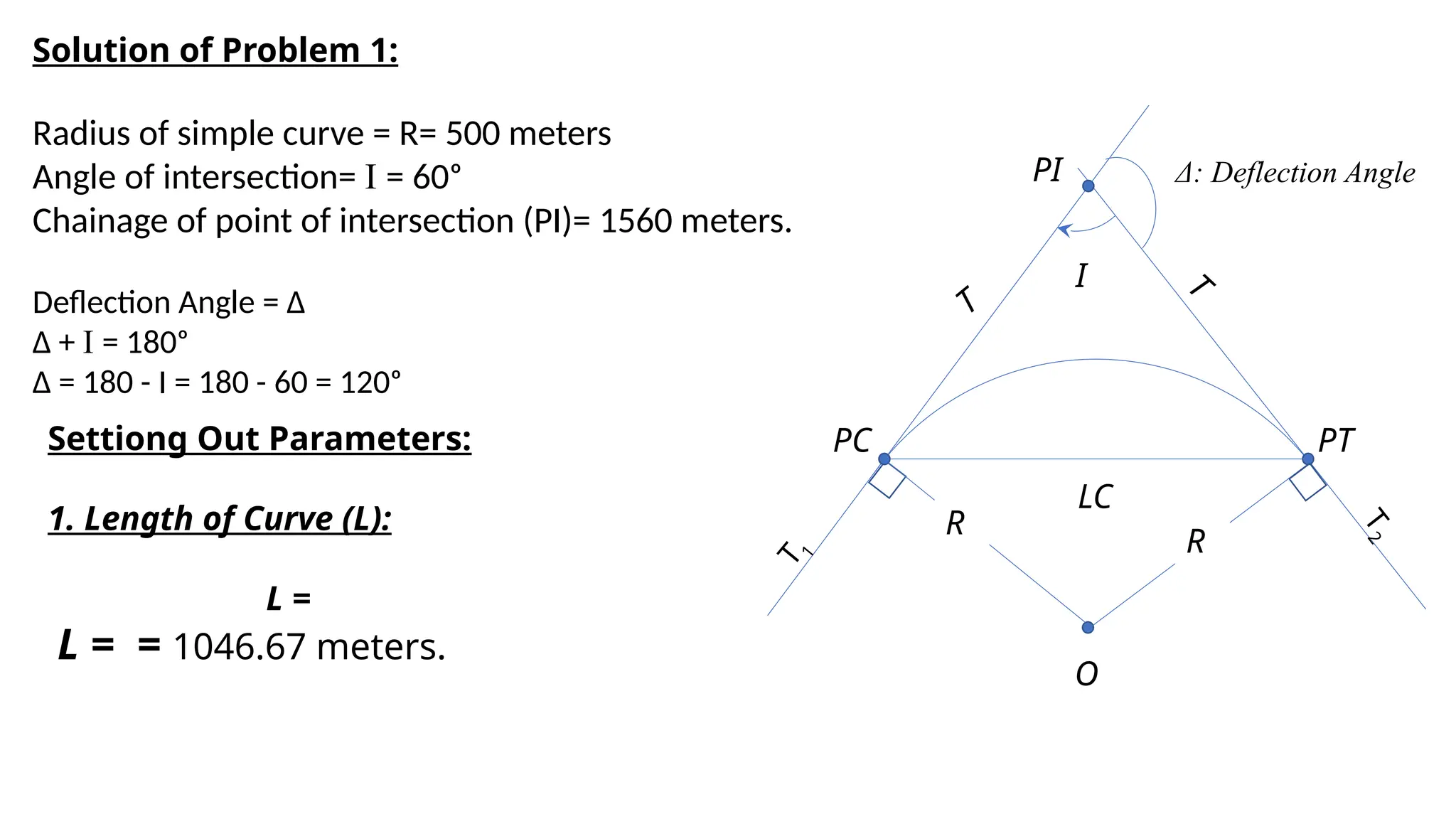
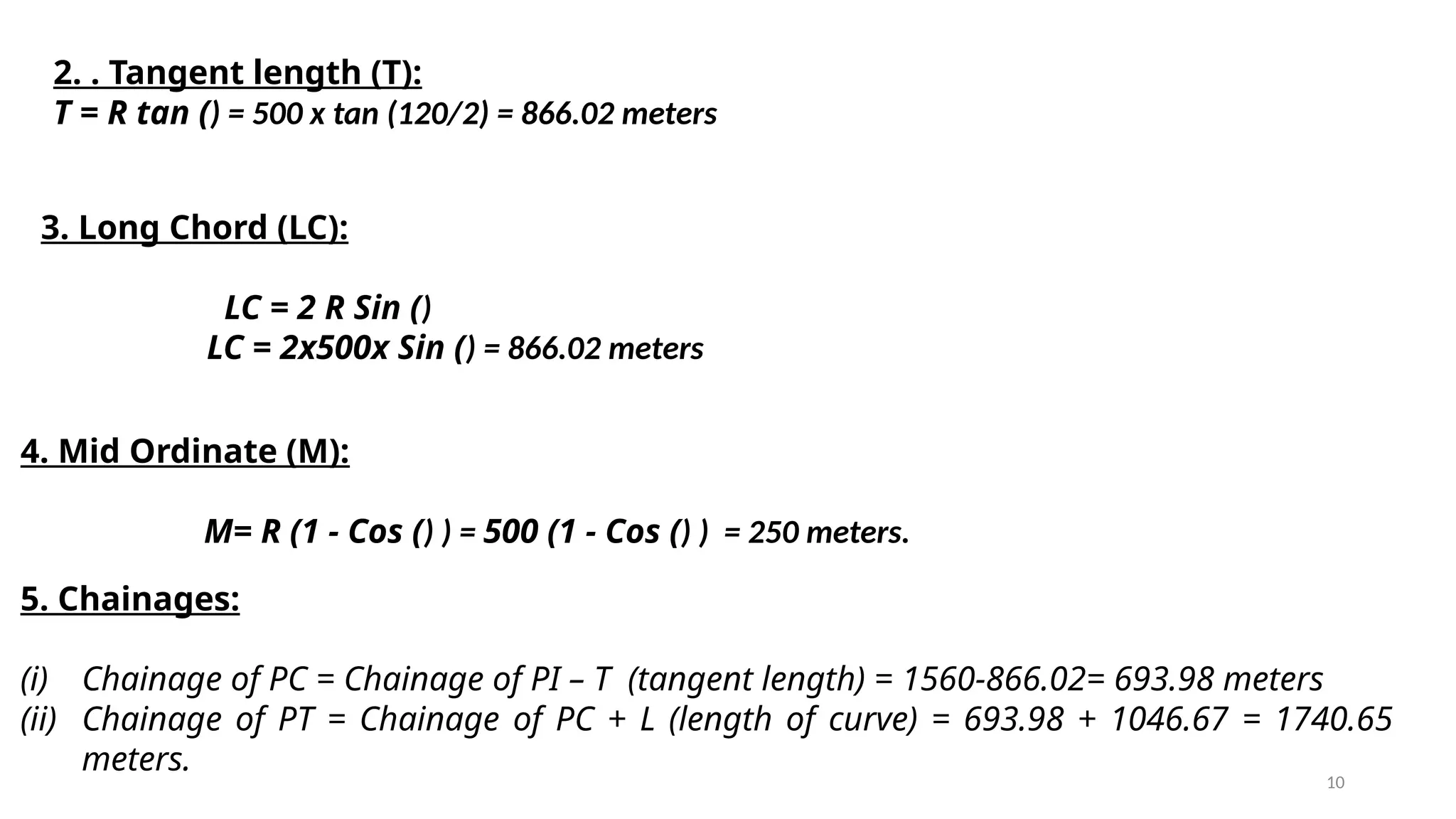
The document outlines the characteristics and calculations related to simple circular curves used in road and highway construction, including definitions of key points and parameters such as radius, deflection angle, tangent length, length of curve, long chord, and mid ordinate. It provides equations for these parameters and examples of calculations based on specified data. Additionally, it addresses problems related to curve setting out parameters and chainages for specific scenarios.