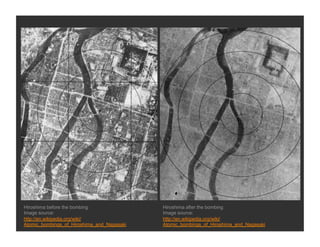
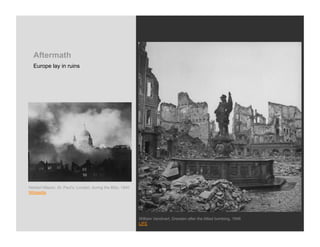
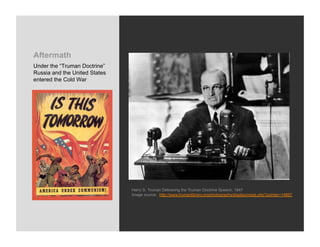
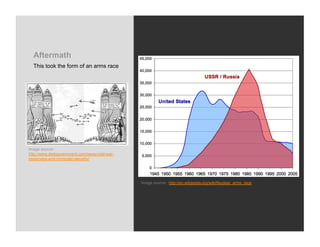
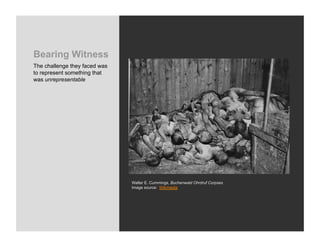
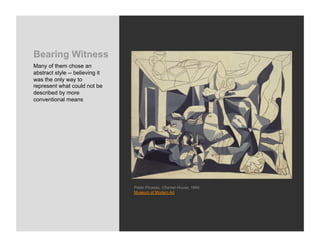
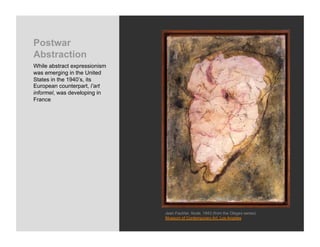
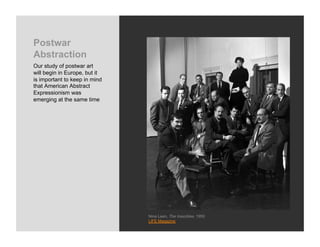
World War 2 began in 1939 with Germany invading Poland and ended in 1945 with the US bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki. The war devastated Europe and brought revelations of the Holocaust where an estimated 6 million Jews were killed. Many artists felt compelled to bear witness through their work, grappling with how to represent the indescribable horrors of war and the concentration camps. This led to the emergence of abstract styles in Europe and America as artists searched for ways to represent the trauma that seemed beyond conventional means.