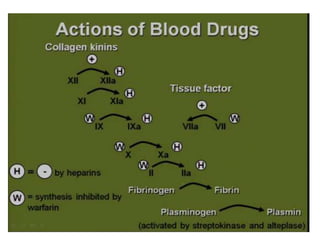
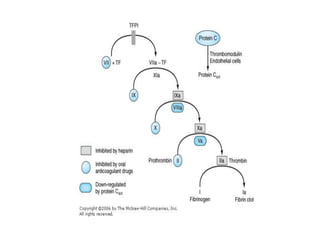
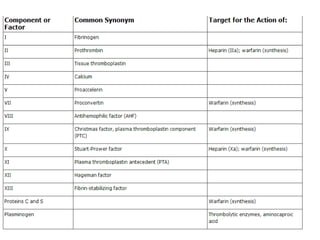
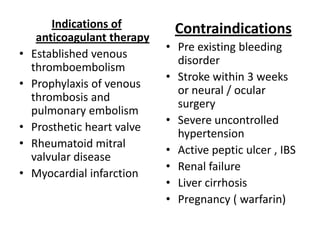
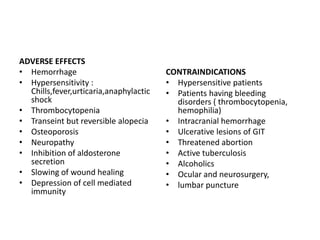
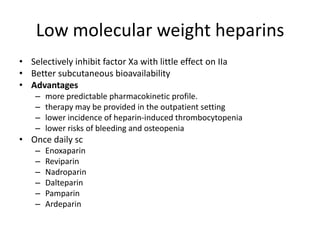
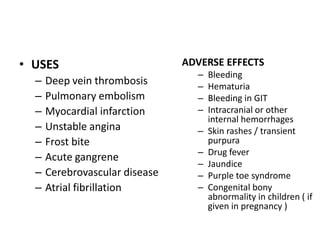
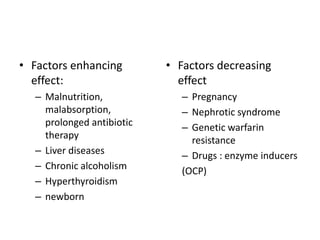
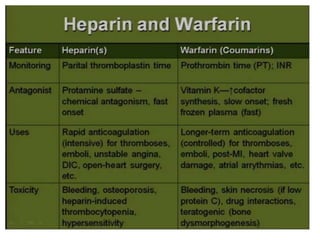
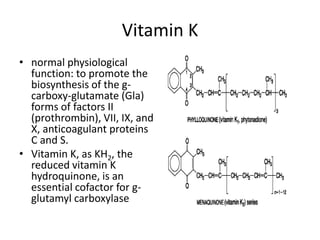
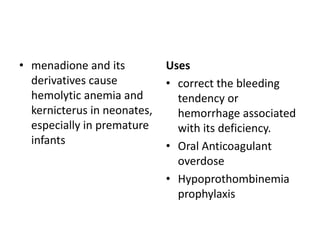
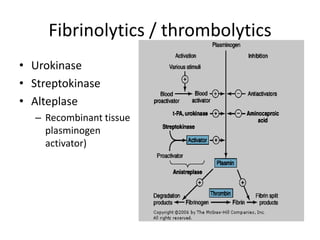
Heparin is a powerful anticoagulant that acts indirectly by binding to antithrombin III and inactivating clotting factors. It can be given intravenously or subcutaneously. Heparin is used to treat and prevent conditions involving blood clots such as deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and arterial thromboembolism. Adverse effects include bleeding and heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Warfarin is an oral anticoagulant that works by interfering with vitamin K dependent clotting factor synthesis in the liver. It is used long-term for conditions requiring anticoagulation like atrial fibrillation. Risks include bleeding and fetal harms