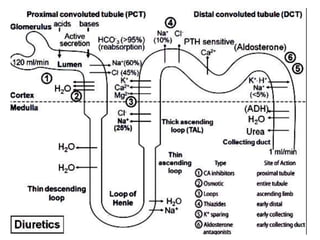
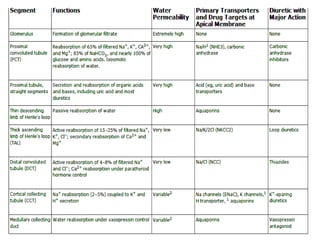
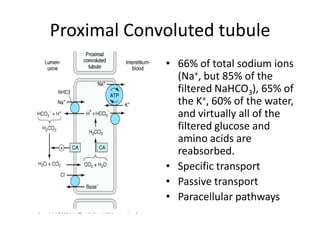
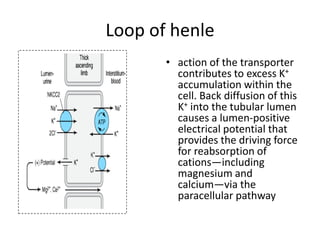
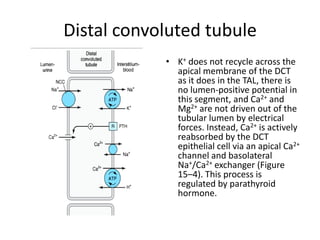
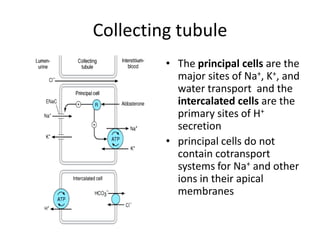
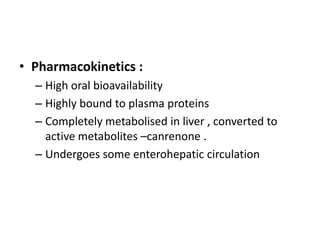
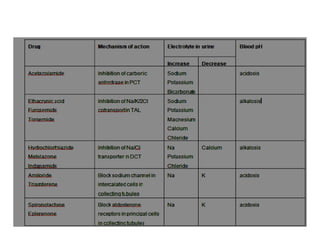
Diuretics work by inhibiting sodium reabsorption in the kidney, which increases water excretion and urine output. They are classified based on their site of action along the nephron. Loop diuretics like furosemide act in the ascending loop of Henle. Thiazides such as hydrochlorothiazide act in the distal convoluted tubule. Potassium-sparing diuretics including spironolactone and amiloride act in the collecting duct. Each class of diuretic has distinct mechanisms of action, pharmacokinetics, indications, and toxicities.