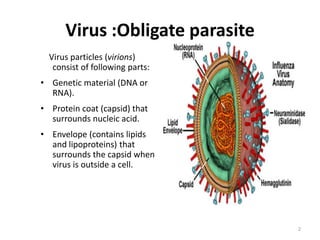
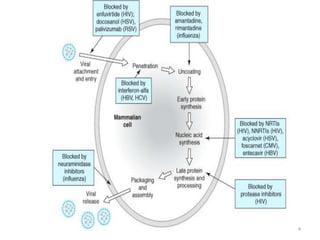
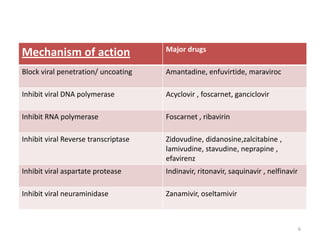
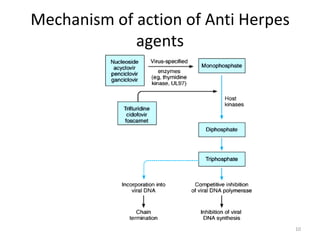
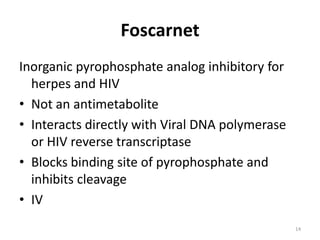
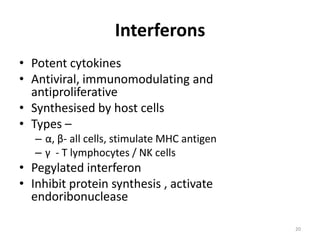
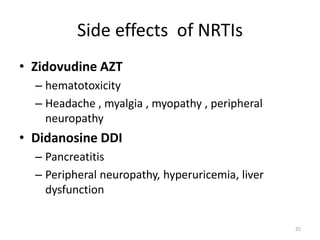
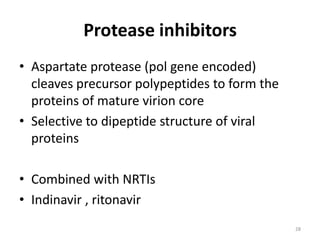
This document provides information on antiviral drugs, including their mechanisms of action and examples of major drugs used to treat different viral infections. It discusses how antiviral drugs work by blocking viral penetration, inhibiting viral DNA or RNA polymerase, or inhibiting reverse transcriptase. Major antiviral drugs mentioned include acyclovir, ganciclovir, foscarnet for herpes viruses, amantadine and rimantadine for influenza, entecavir and adefovir for hepatitis B, and various nucleoside and nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors as well as protease inhibitors for HIV. The document also reviews the adverse effects and guidelines for use of these various antiviral agents.