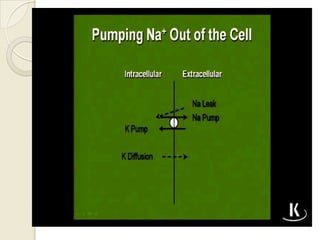
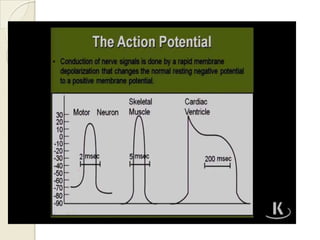
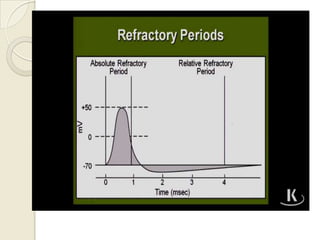
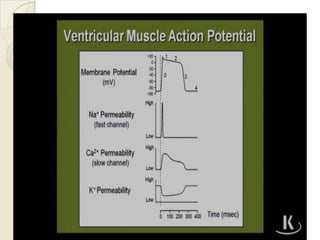
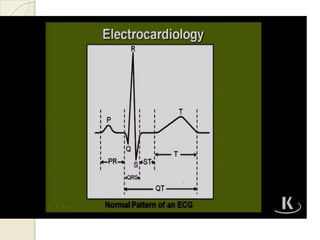
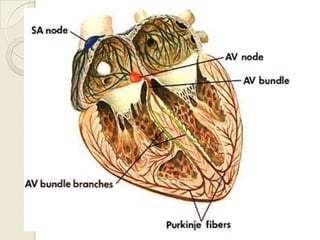
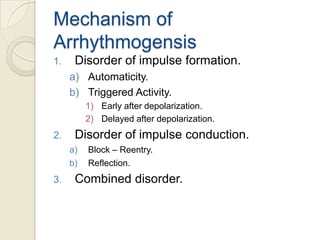
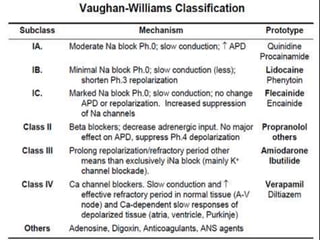
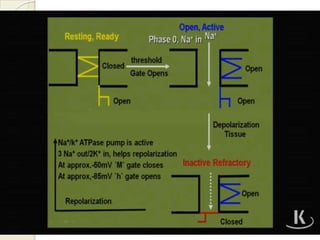
Cardiac arrhythmia refers to abnormal cardiac rhythm involving changes in rate or regularity. Causes can be physiological due to autonomic nervous system changes or pathological factors like valvular heart disease, ischemic heart disease, cardiomyopathies, or drug effects. Clinical evaluation involves physical exam findings like palpitations or abnormal pulse, and diagnostic tests like ECG, EP testing, or lab tests checking electrolyte levels. Arrhythmias occur via disorders of impulse formation, conduction, or a combination. They are described by rate, origin, pattern, and duration. Treatment involves antiarrhythmic drugs that alter automaticity, conduction velocity, or refractory periods.