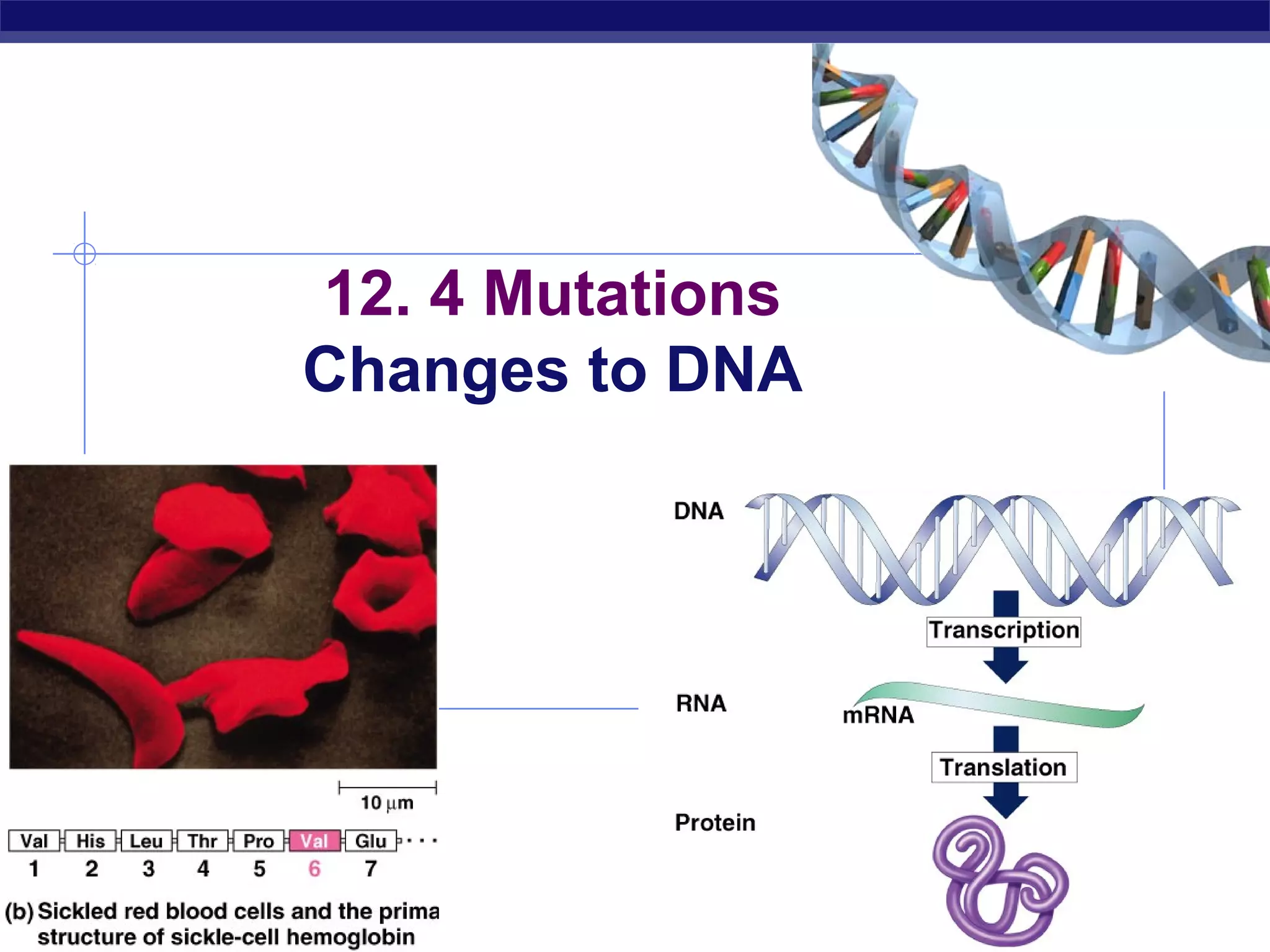
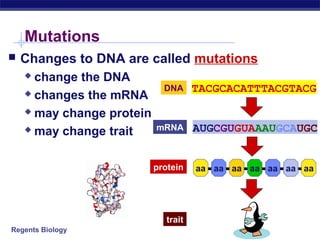
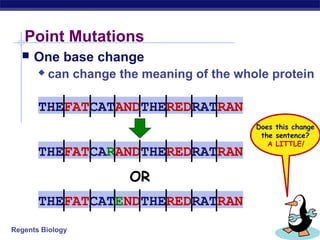
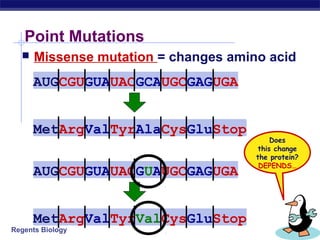
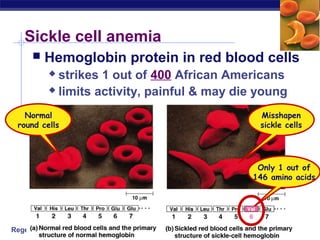
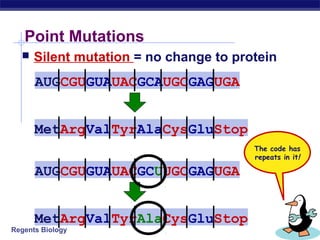
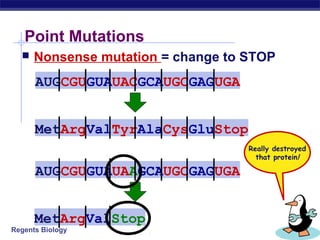
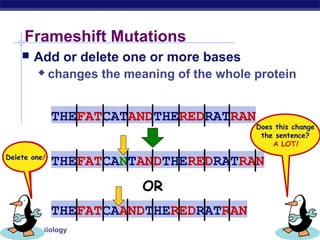
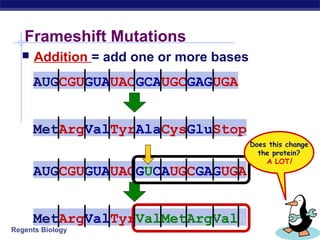
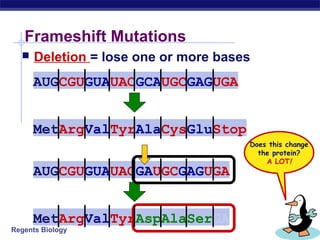
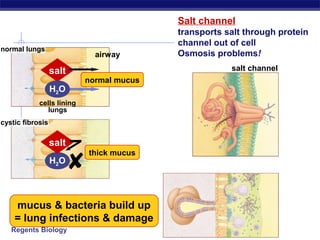
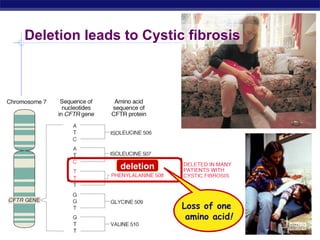
Mutations are changes to DNA that can alter genes and traits. There are two main types of mutations: point mutations, which change a single DNA nucleotide, and frameshift mutations, which add or delete nucleotides, altering the reading frame. Point mutations can be silent, changing no amino acids, missense, changing an amino acid, or nonsense, creating a stop codon. Frameshift mutations typically have more significant effects by changing all subsequent amino acids. Examples given are sickle cell anemia from a point mutation and cystic fibrosis from a frameshift deletion.