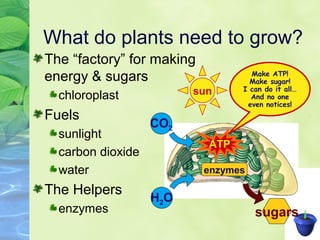
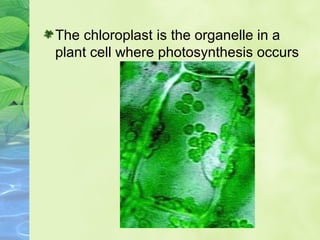
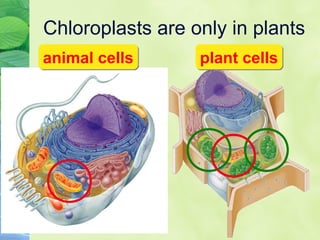
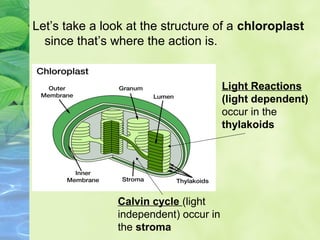
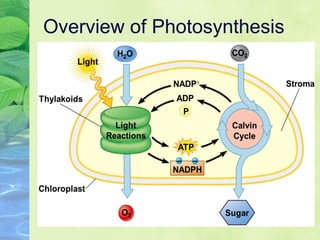
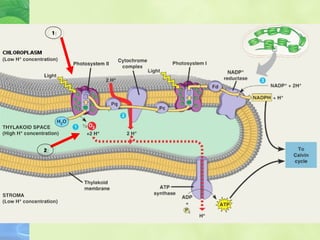
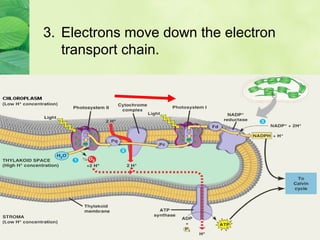
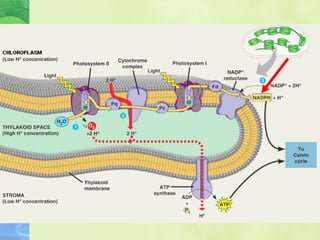
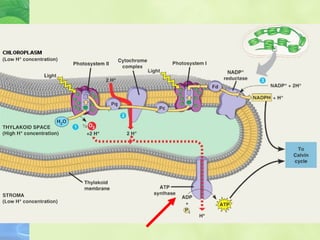
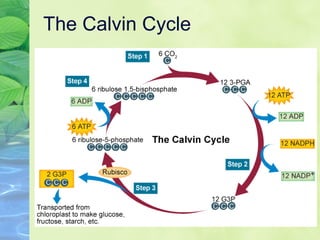
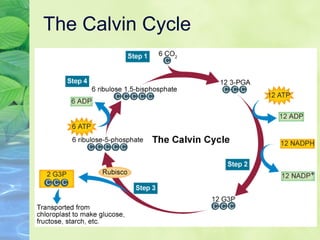
Photosynthesis allows plants to convert sunlight, carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. It occurs in two phases within the chloroplast - the light dependent reactions where ATP and NADPH are produced, and the light independent Calvin cycle where glucose is assembled from carbon dioxide using ATP and NADPH. The overall equation is carbon dioxide + water + energy (sunlight) → glucose + oxygen.