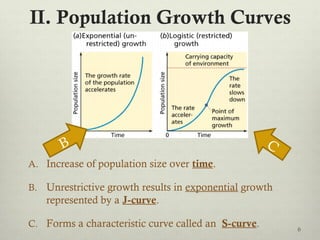
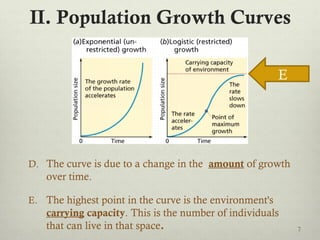
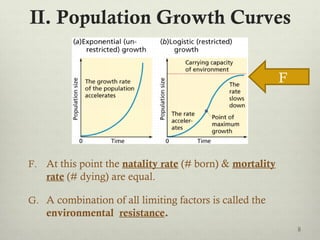
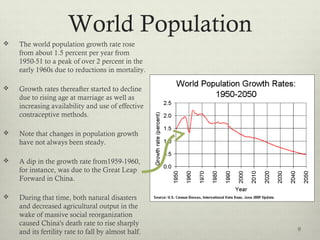
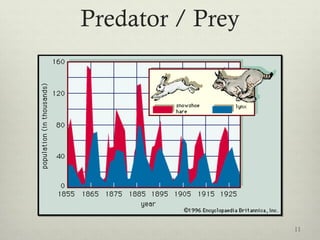
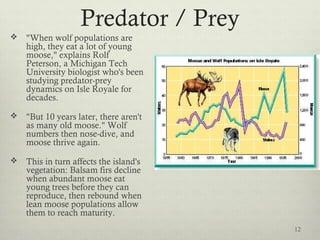
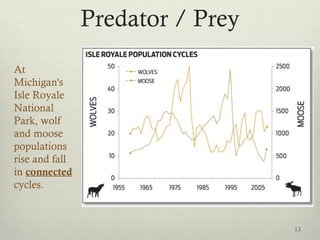
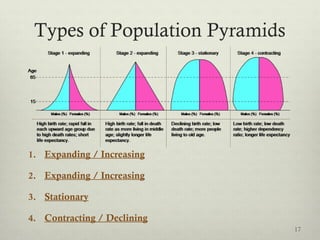
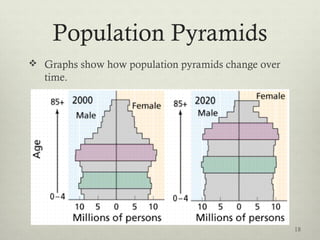
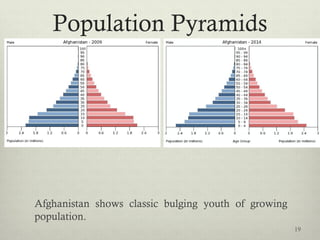
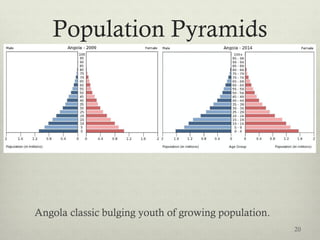
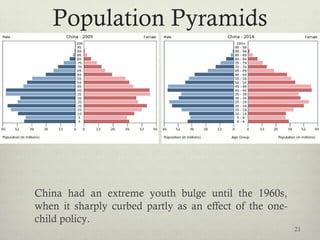
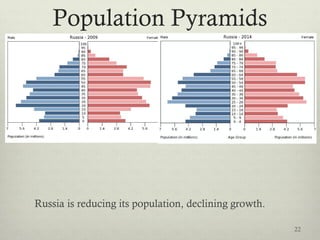
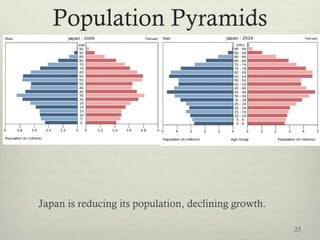
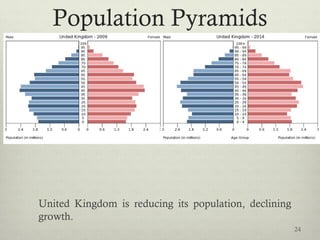
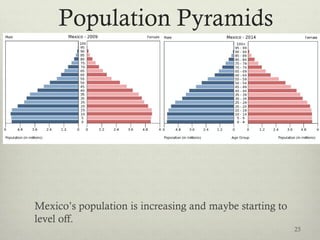
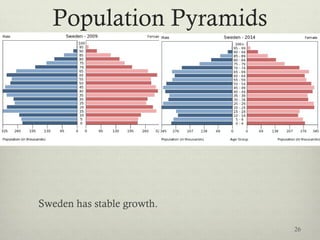
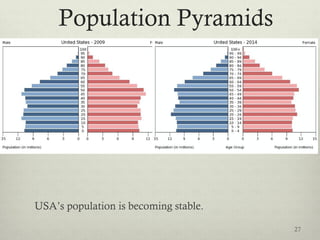
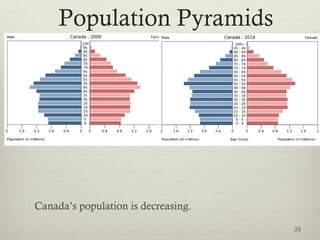
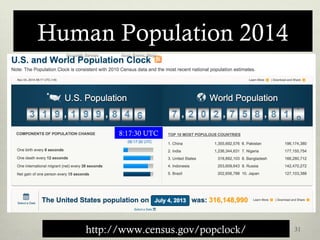
This document discusses populations in biology. It defines key population concepts like niche, habitat, and limiting factors. It describes how populations grow over time in characteristic S-curves from exponential growth to stabilizing at the environment's carrying capacity. Predator-prey relationships are examined as well as density-dependent and density-independent limiting factors. Different types of population pyramids are shown representing expanding, stable, and contracting growth. Examples of various countries' population pyramids through history are provided to illustrate changing growth patterns over time.