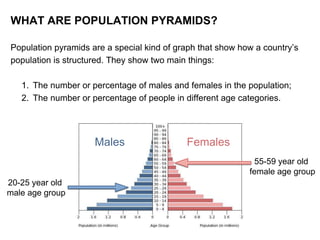
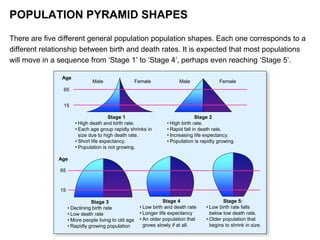
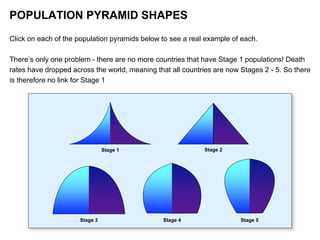
Population pyramids are graphs that show the distribution of a country's population across different age groups and sex. The shape of a population pyramid provides information about a population's growth trends, history, and future opportunities and challenges. There are five general population pyramid shapes that correspond to different relationships between birth and death rates and represent stages of demographic transition as countries develop from high birth and death rates to low rates.