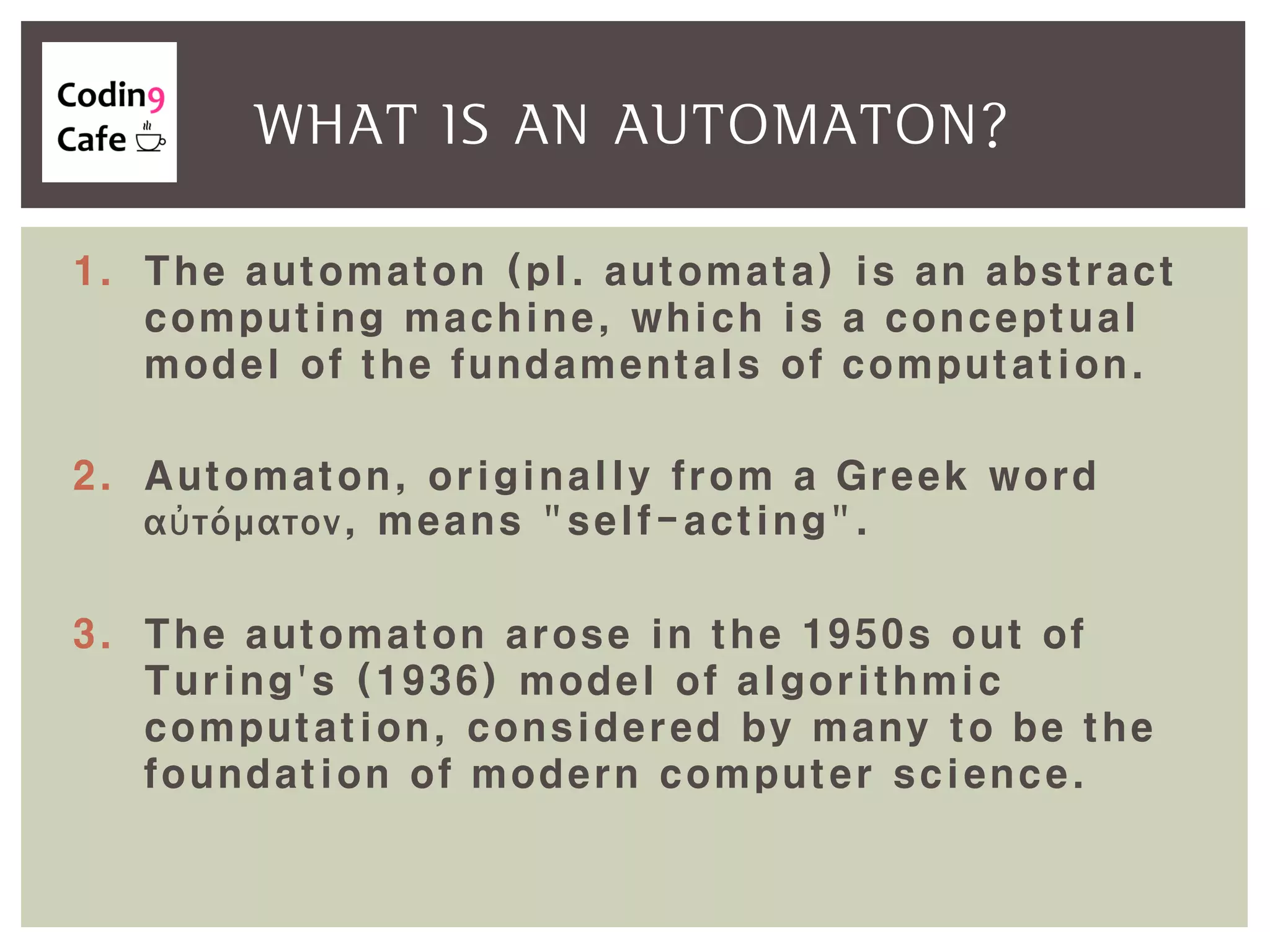
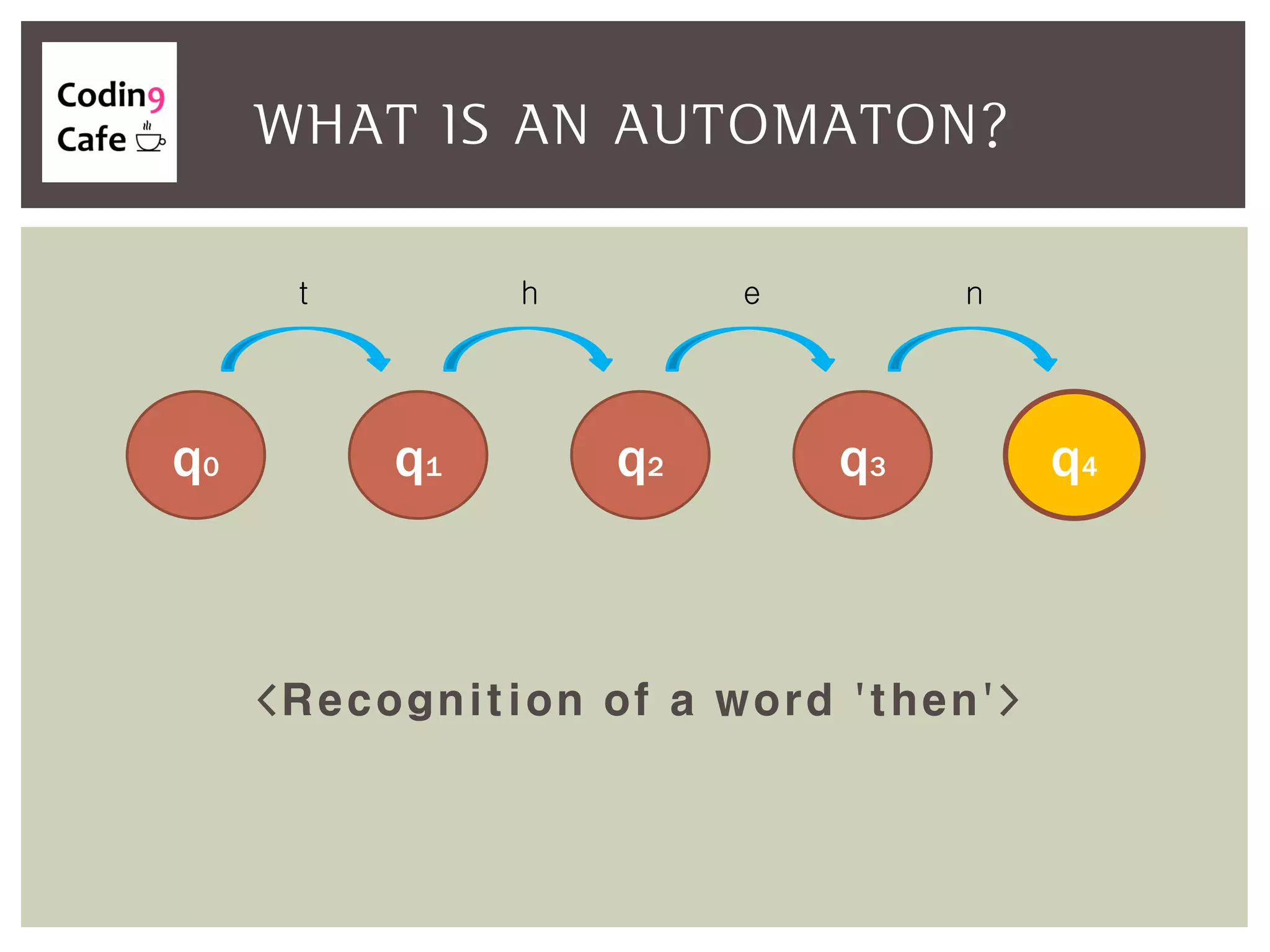
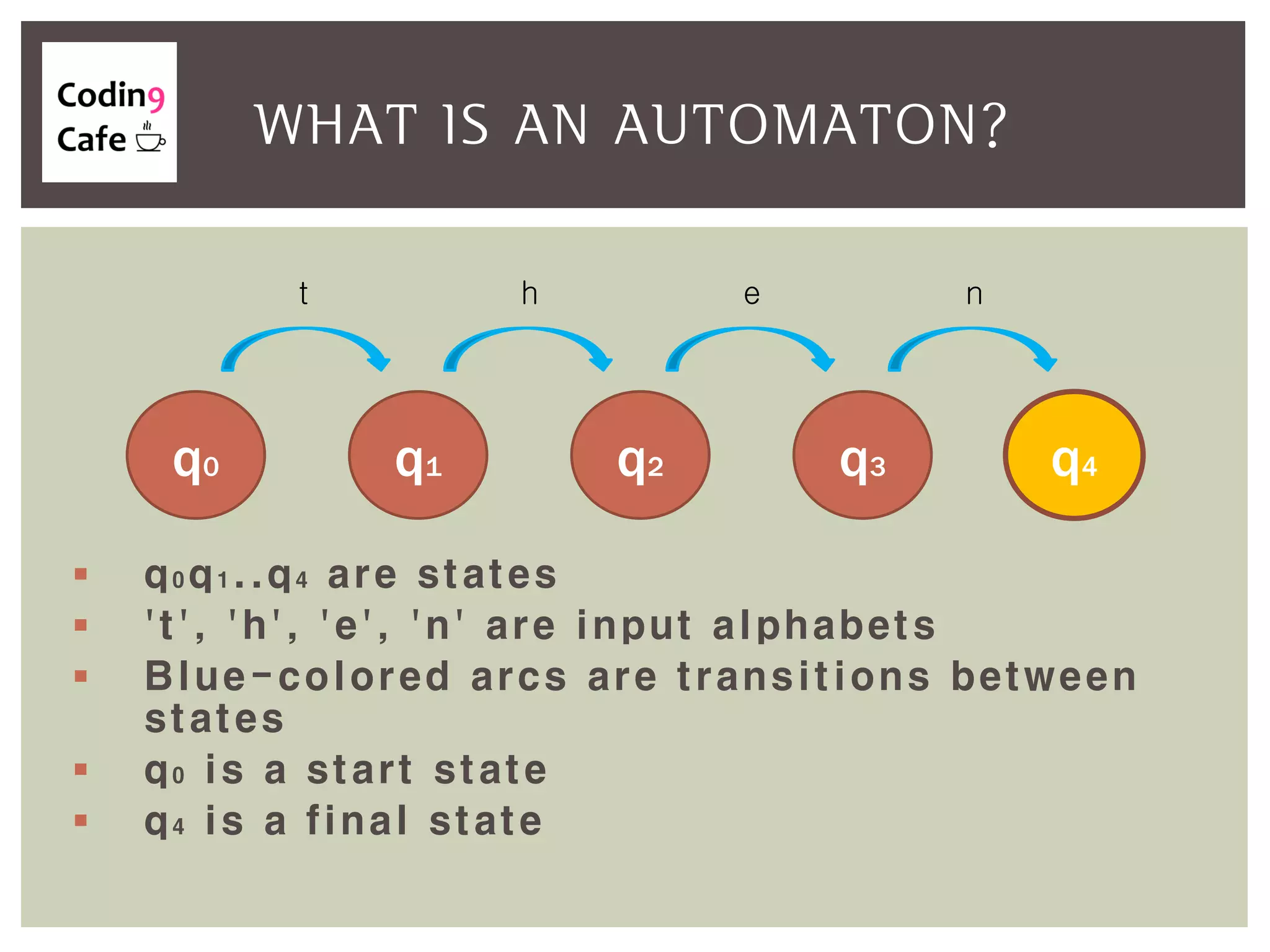
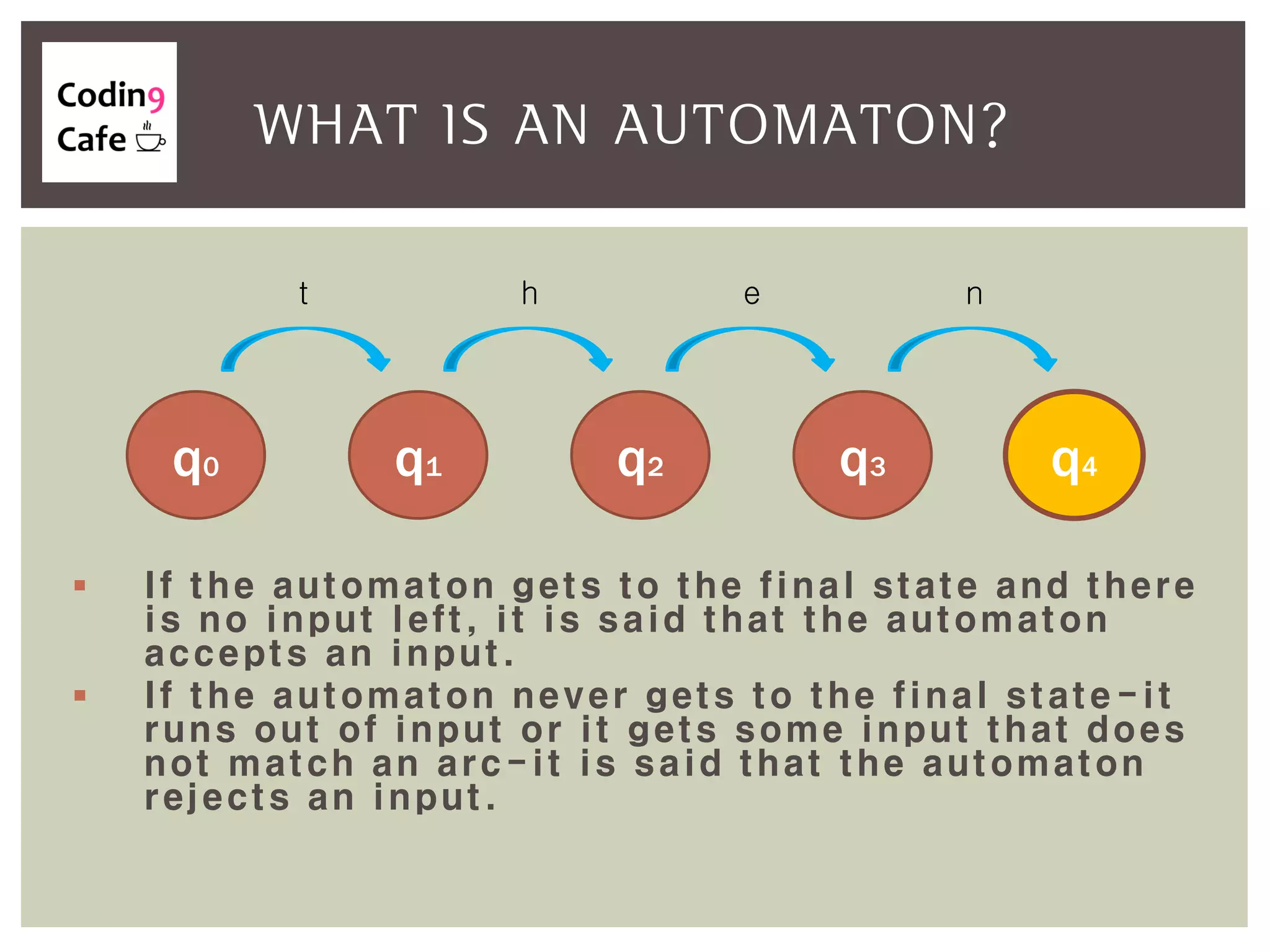
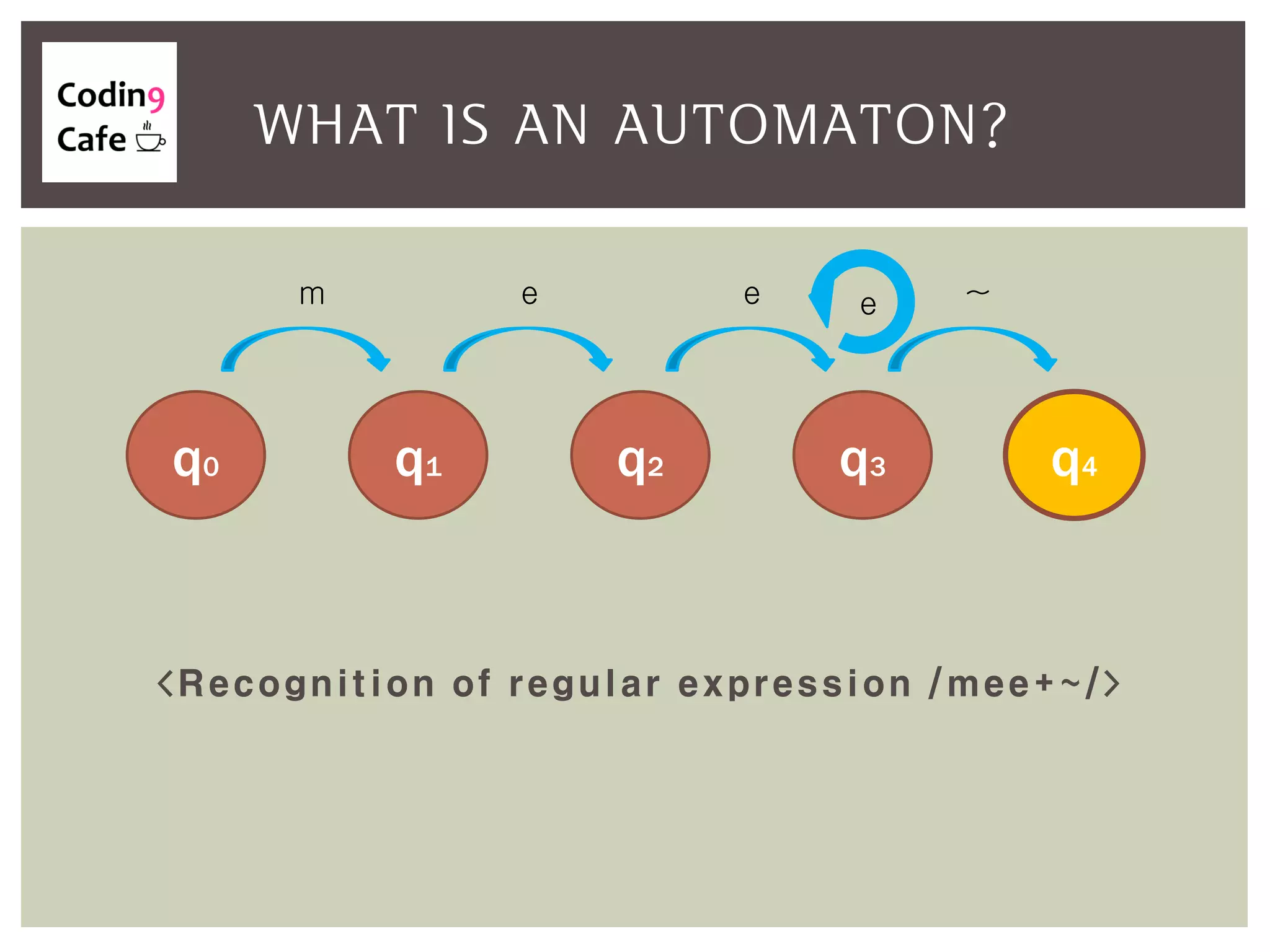
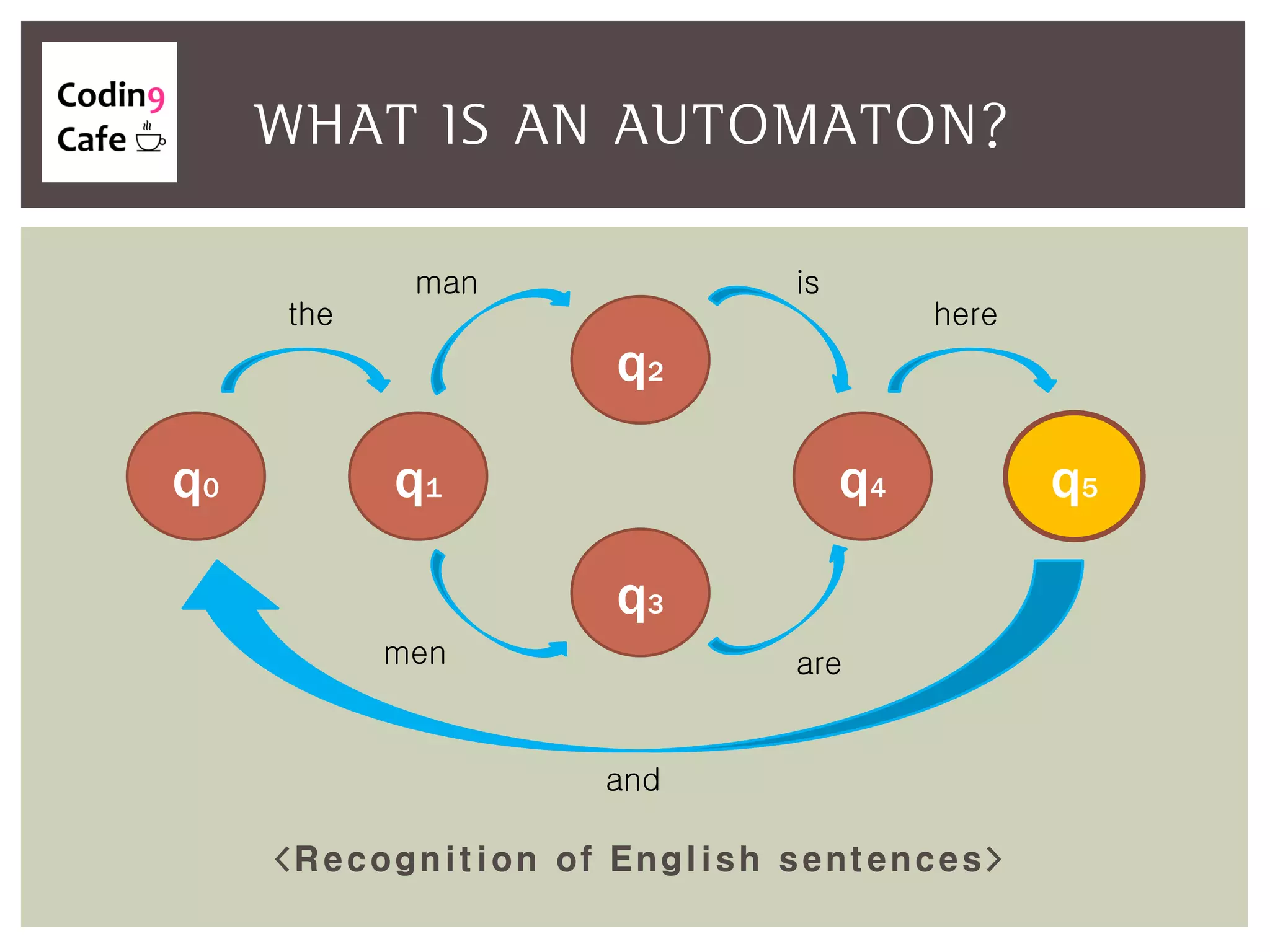
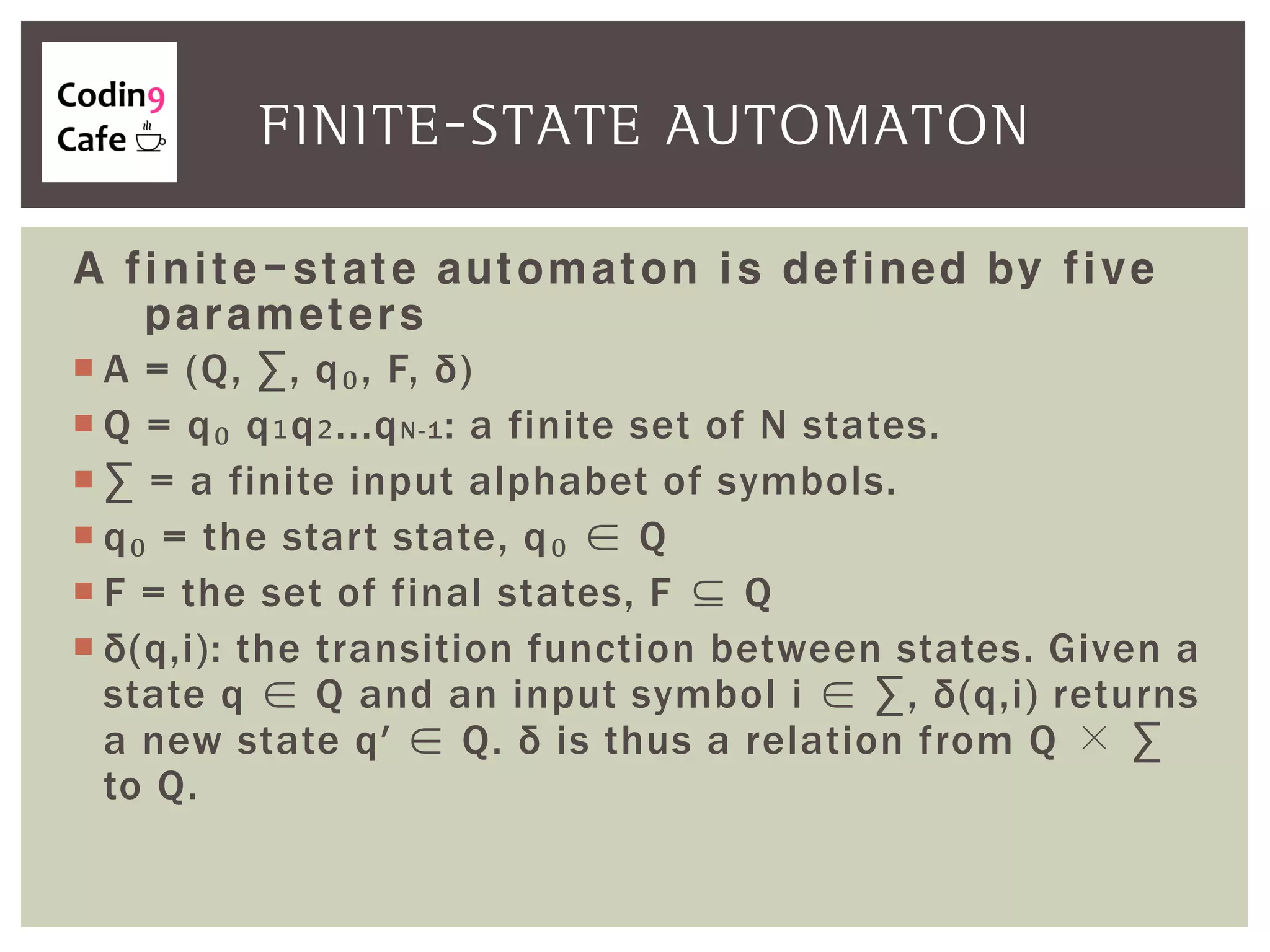
An automaton is an abstract computing machine central to the theory of computation, emerging from Turing's model in the 1950s. It processes inputs through states and transitions to determine acceptance of these inputs according to defined languages and grammars. Finite-state automata are characterized by a set of states, an input alphabet, a start state, final states, and a transition function.