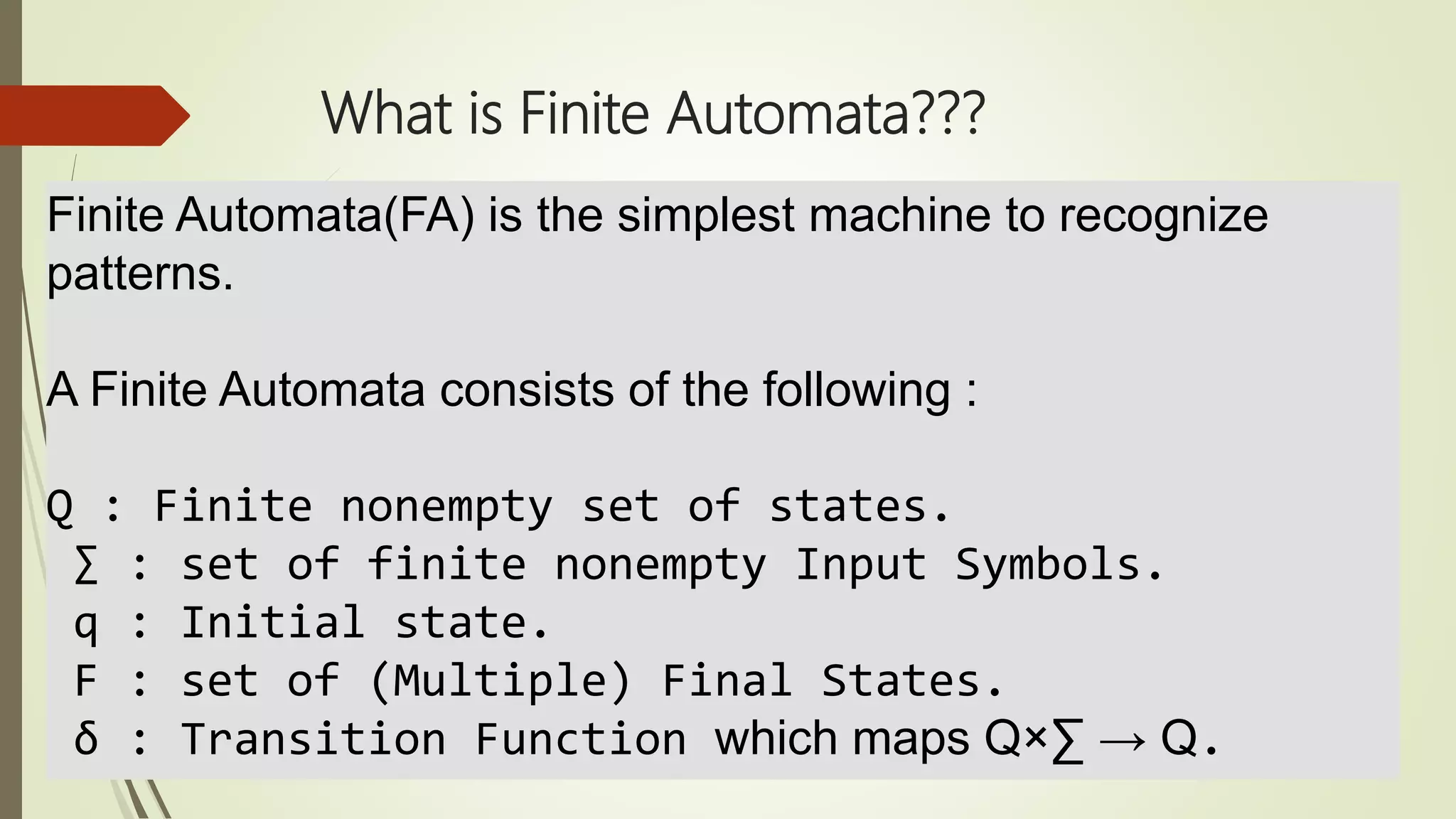
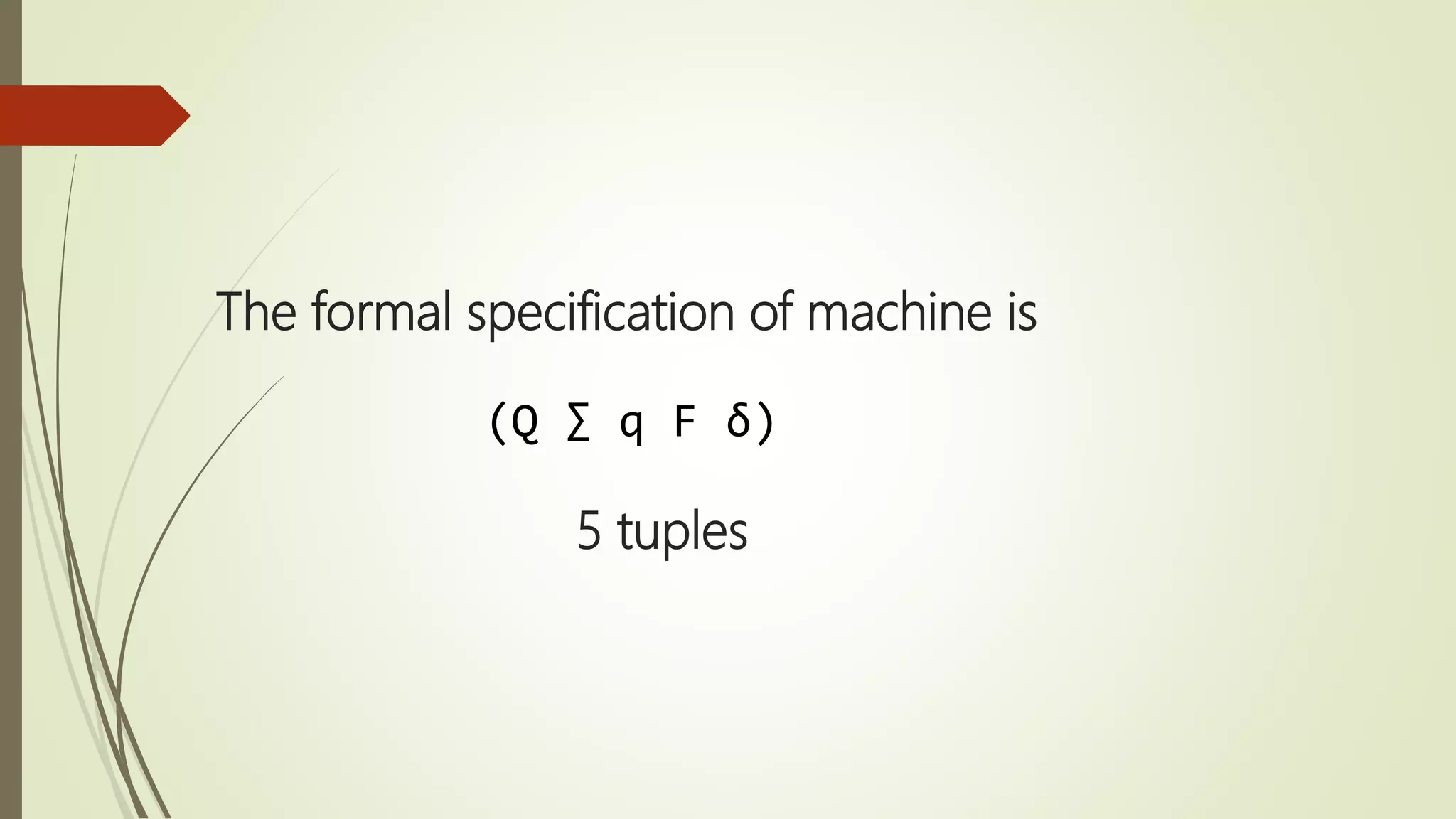
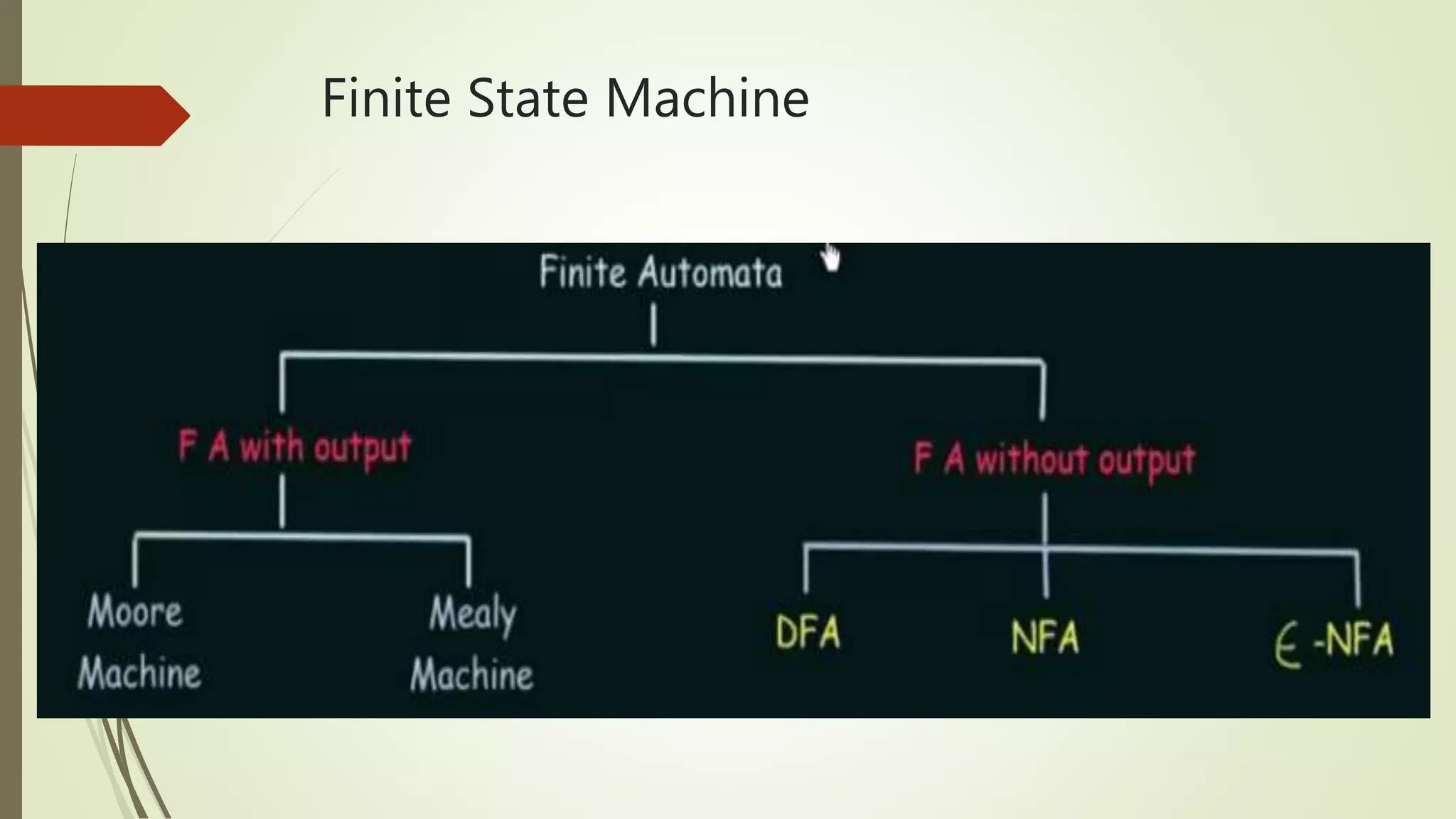
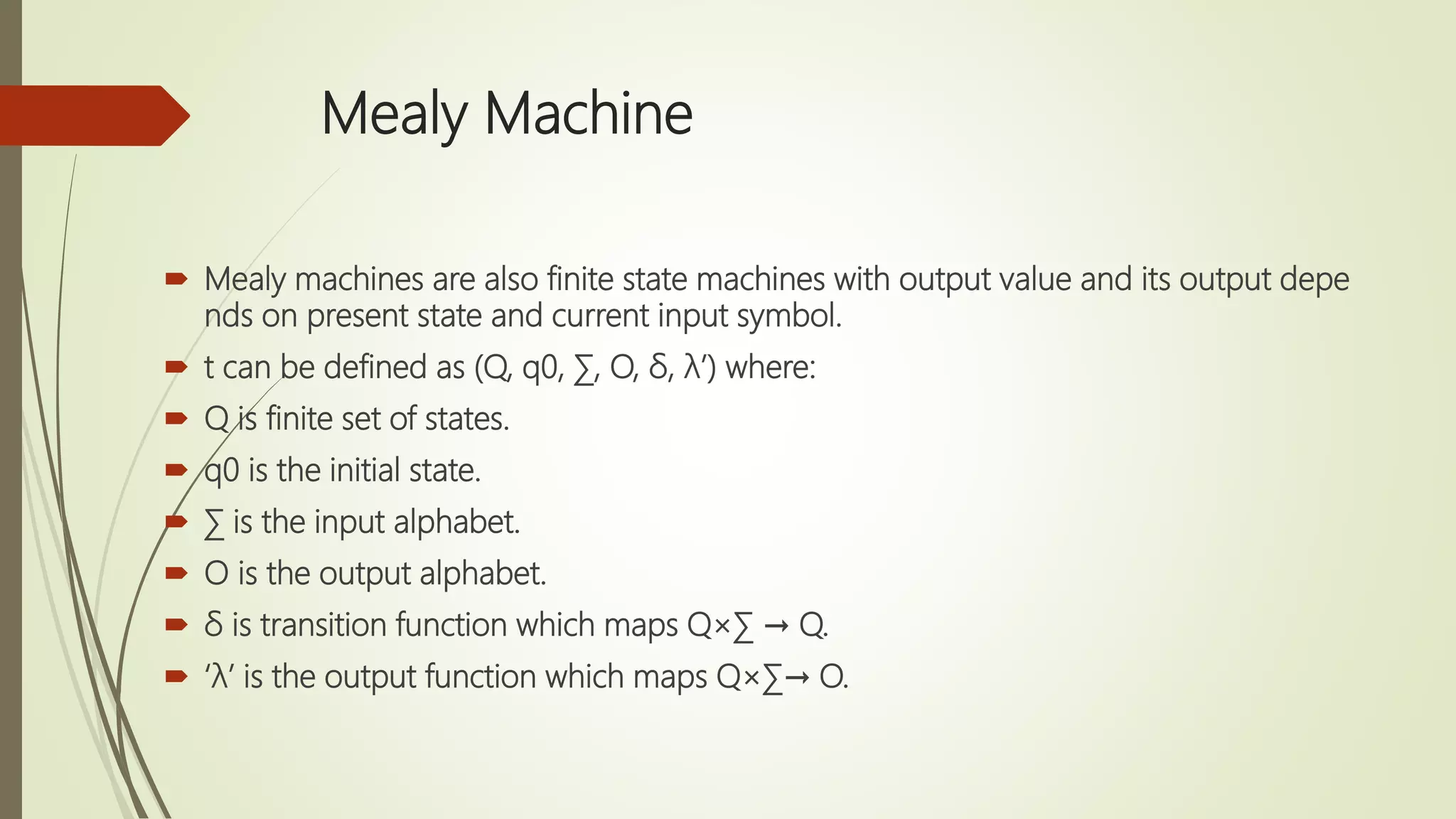
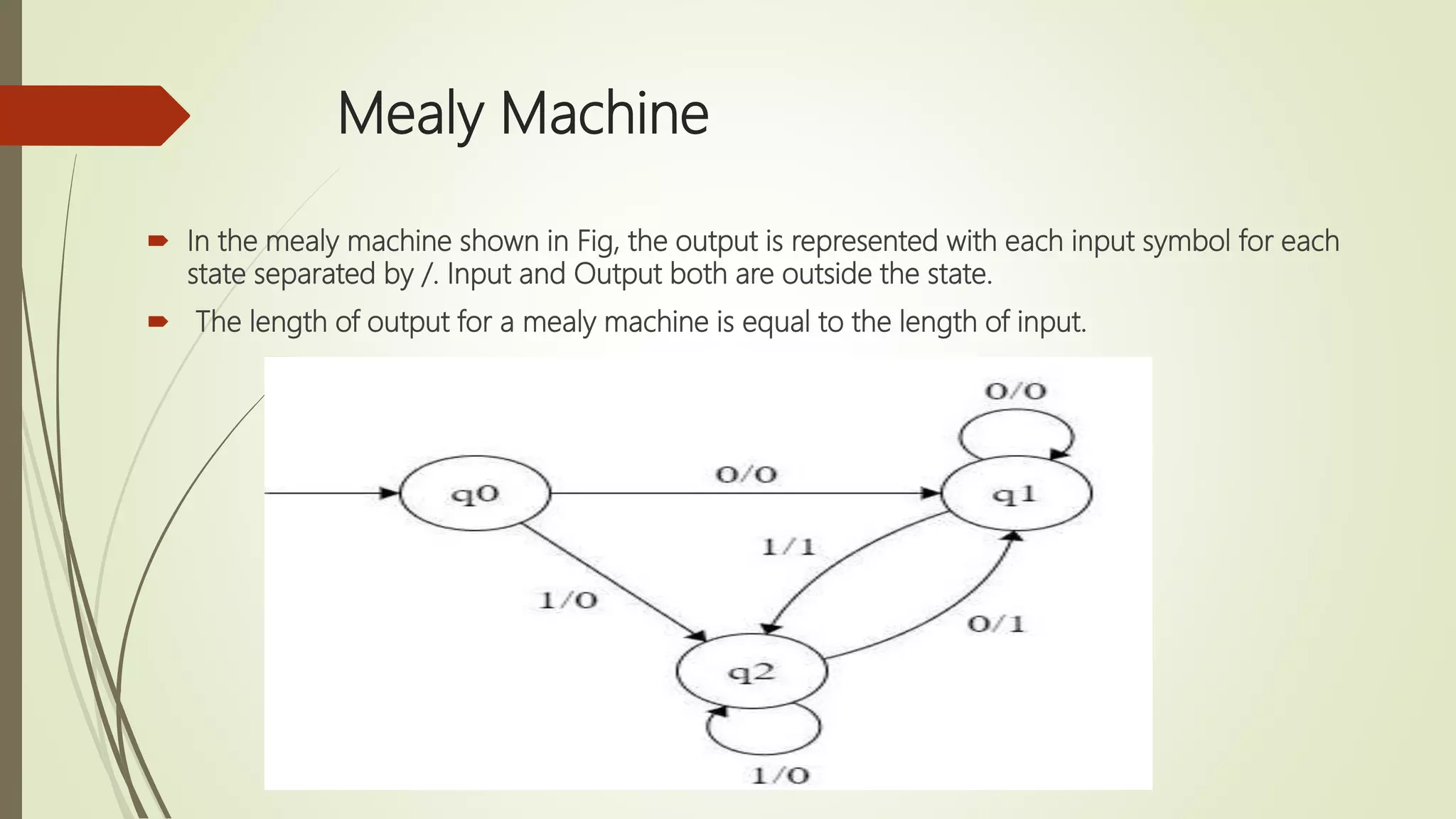
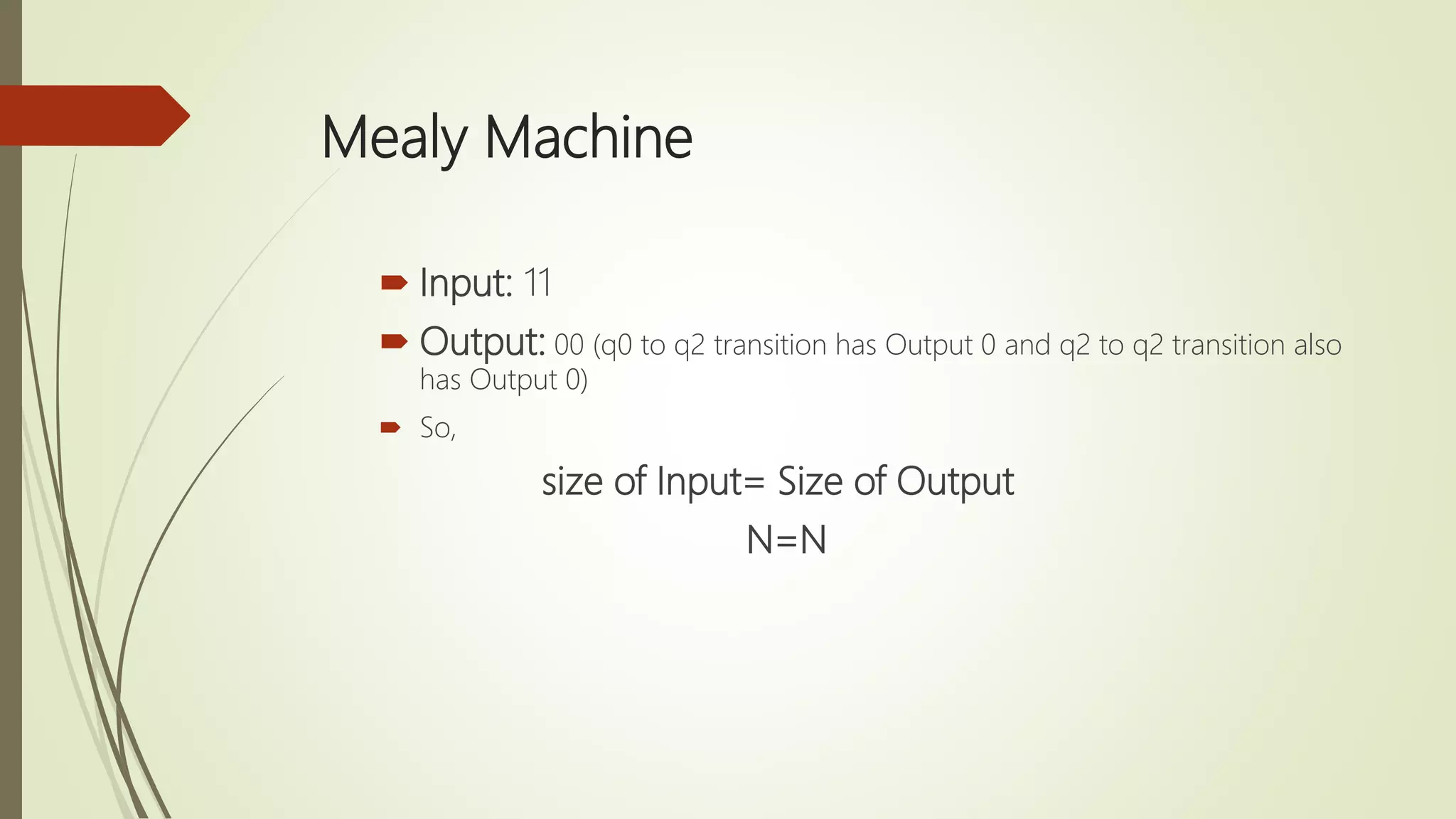
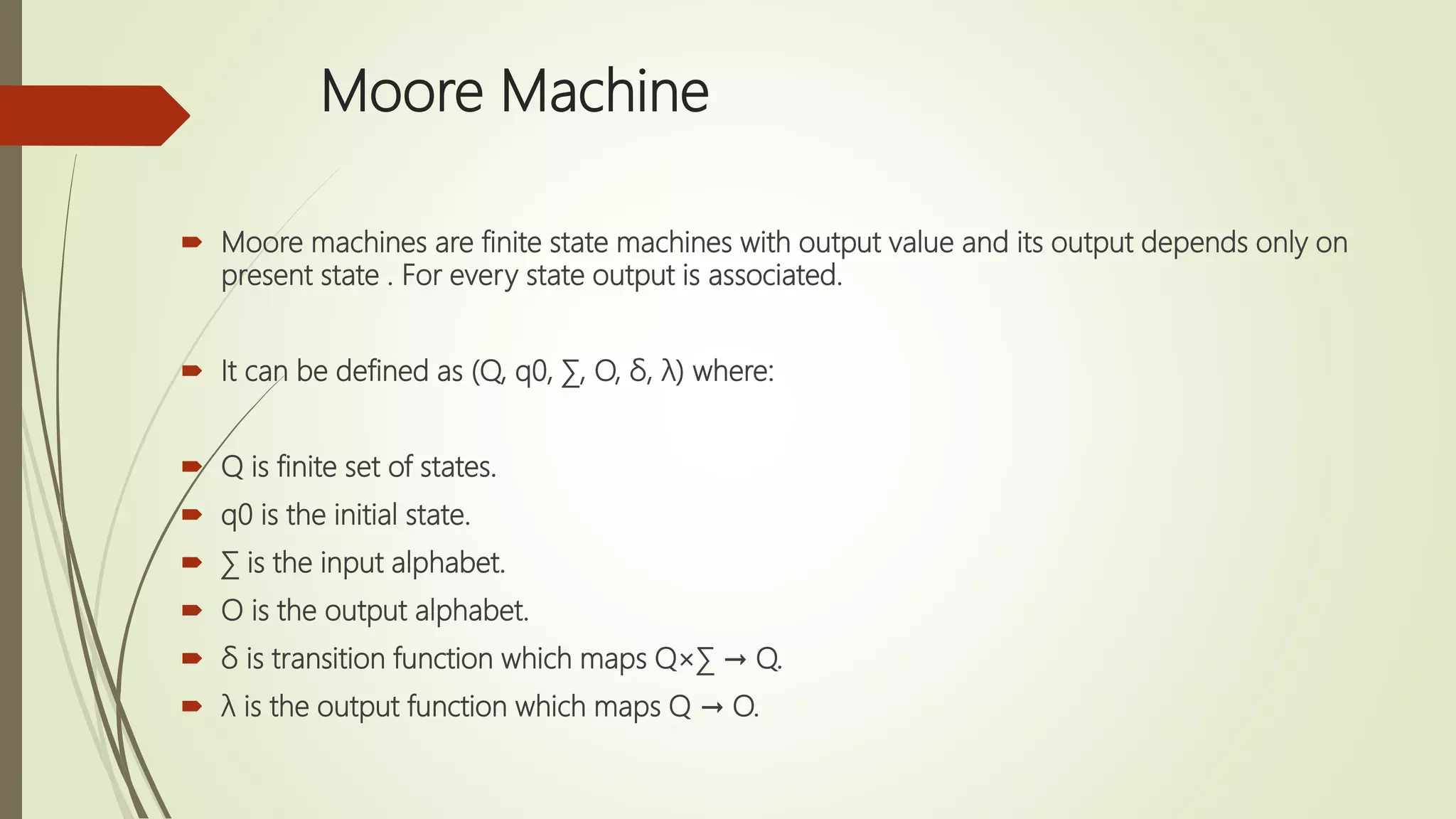
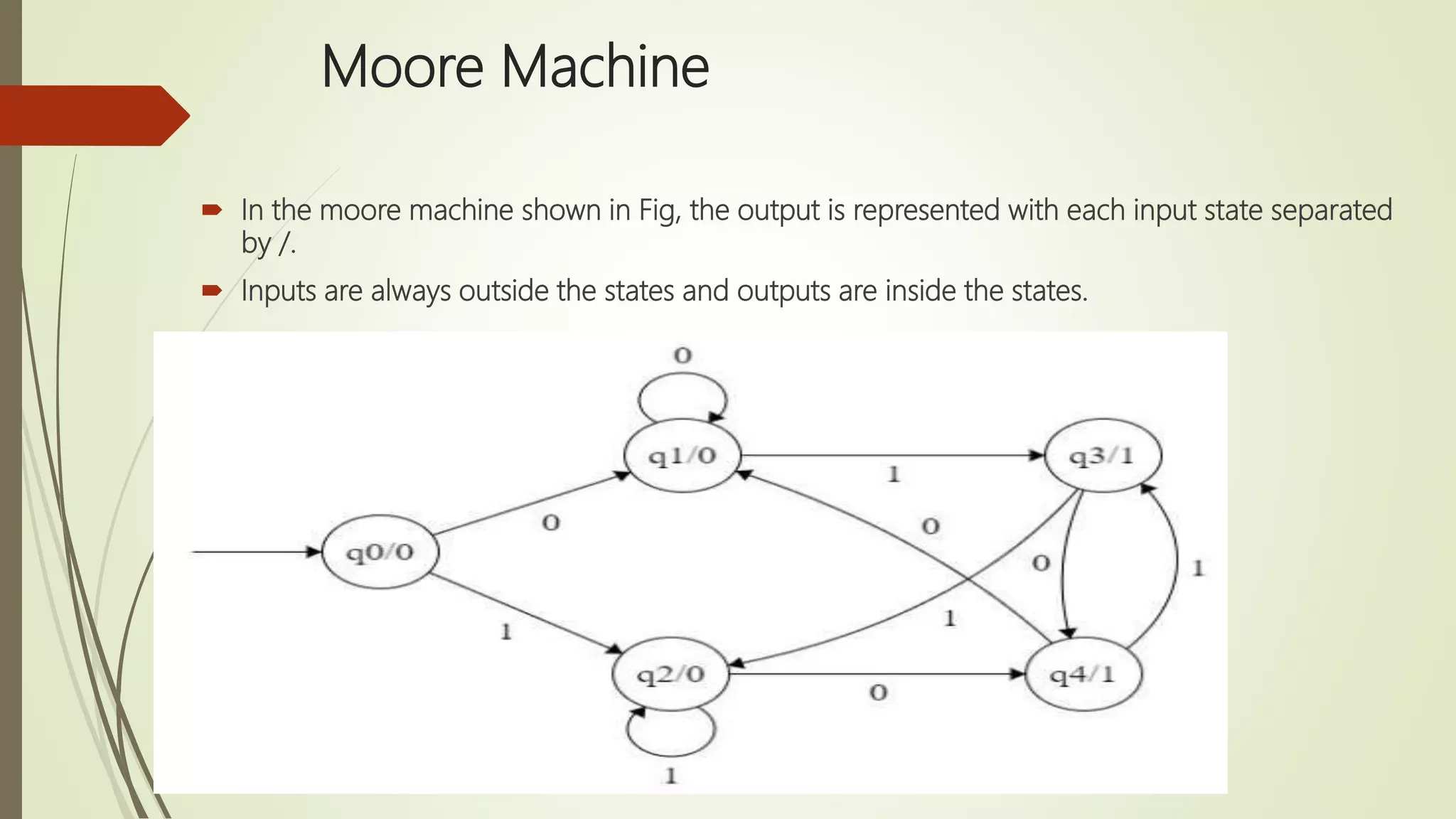
Moore and Mealy machines are two types of finite state machines. A Mealy machine's output depends on the current state and input, and its output size equals its input size. A Moore machine's output depends only on the current state, and its output size is one larger than its input size. Mealy machines are defined as tuples including states, inputs, outputs, transitions, and an output function. Moore machines are similarly defined except the output function maps states to outputs rather than states and inputs. Examples of Moore and Mealy machine applications include elevators, compilers, SRAM, and vending machines.