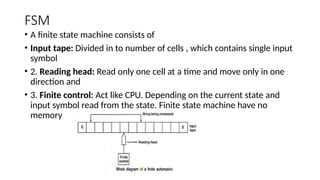
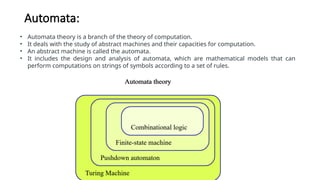
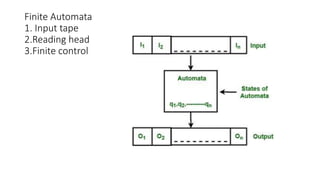
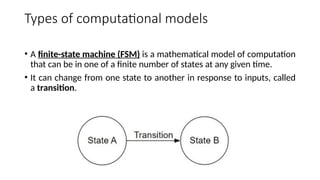
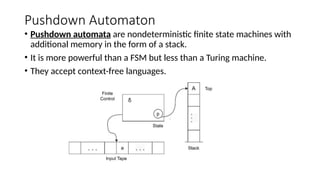
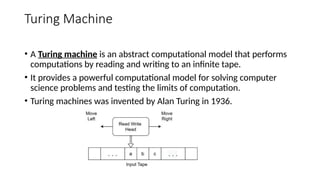
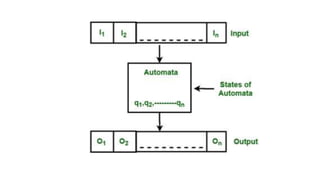
A finite-state machine (FSM) is a mathematical model that can exist in one of a finite number of states and change states based on inputs, defined by its states, initial state, and transition inputs. Automata theory studies abstract machines, including FSMs and more powerful models like pushdown automata, which utilize stacks for additional memory, and Turing machines, which can perform computations with an infinite tape. Finite automata are the simplest form of these machines, capable of recognizing patterns based on their defined states and transitions.