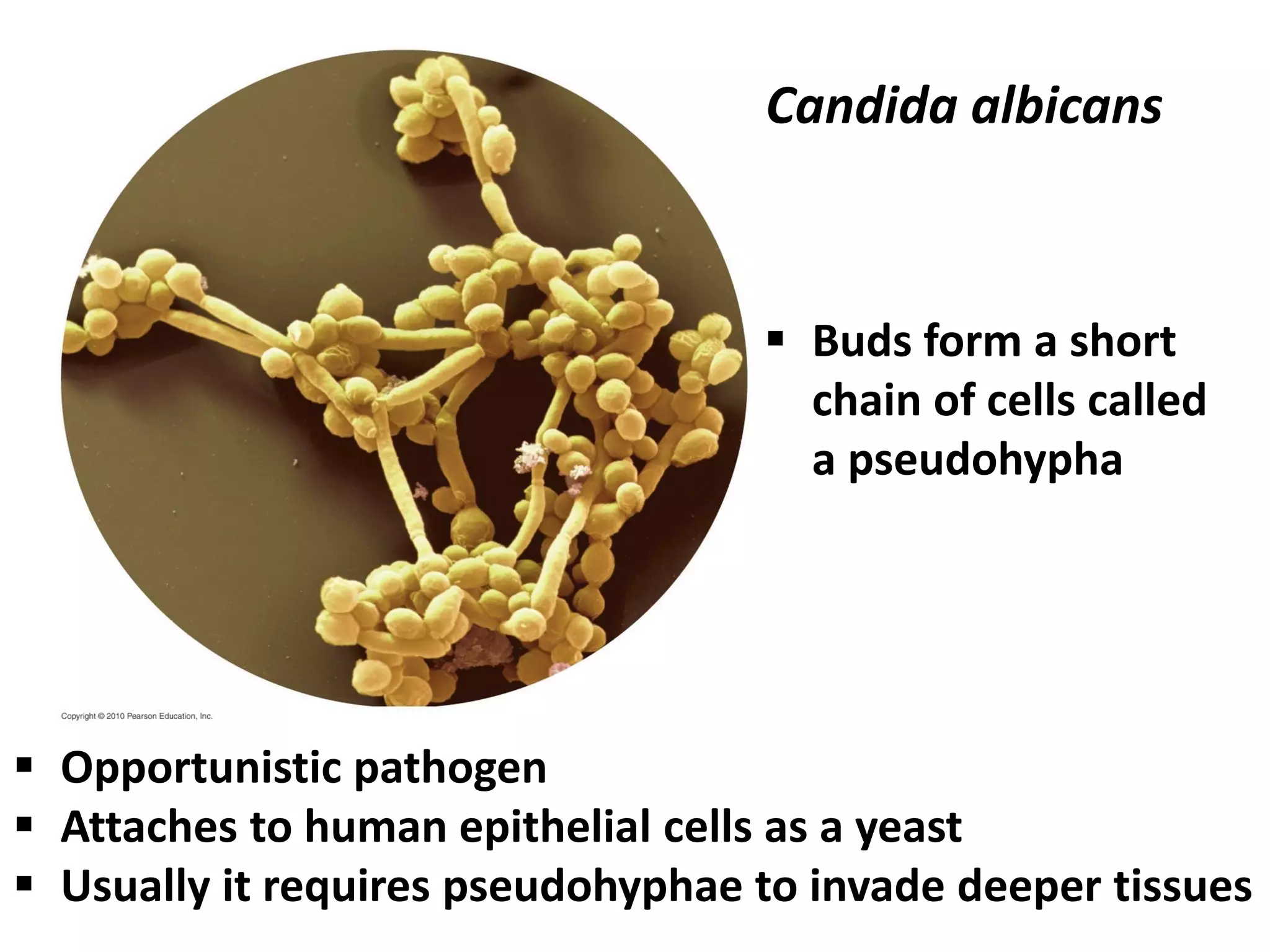
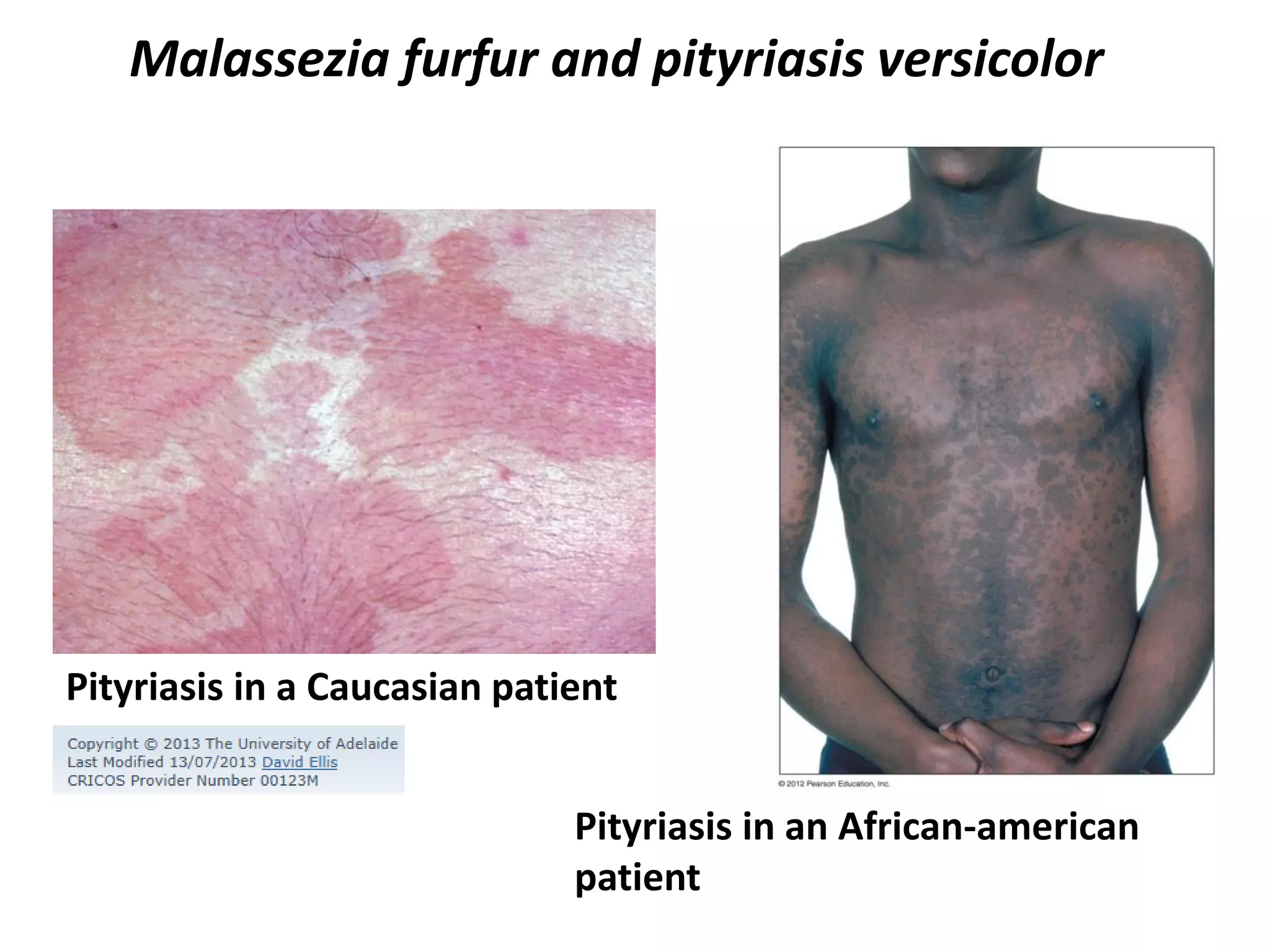
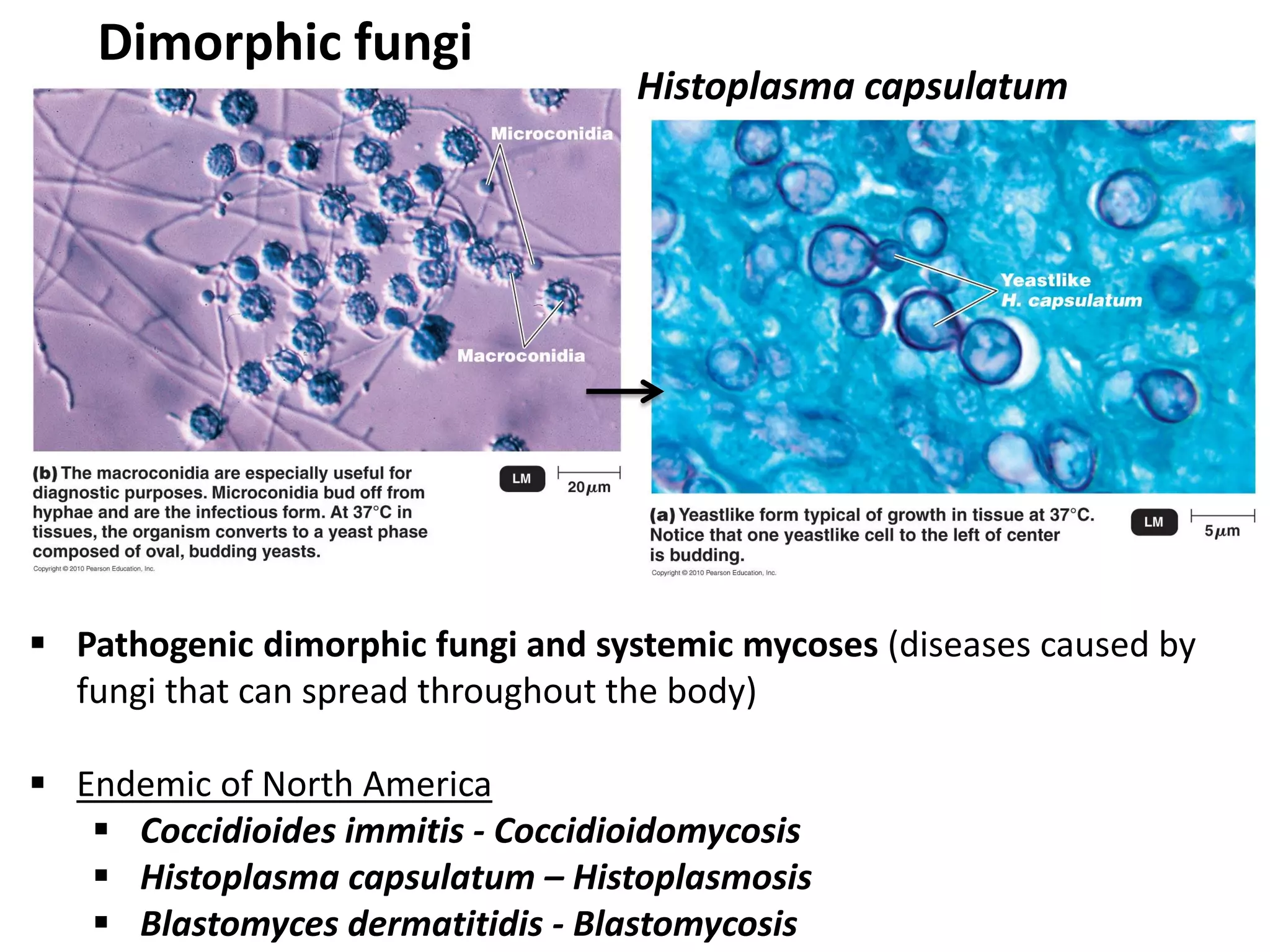
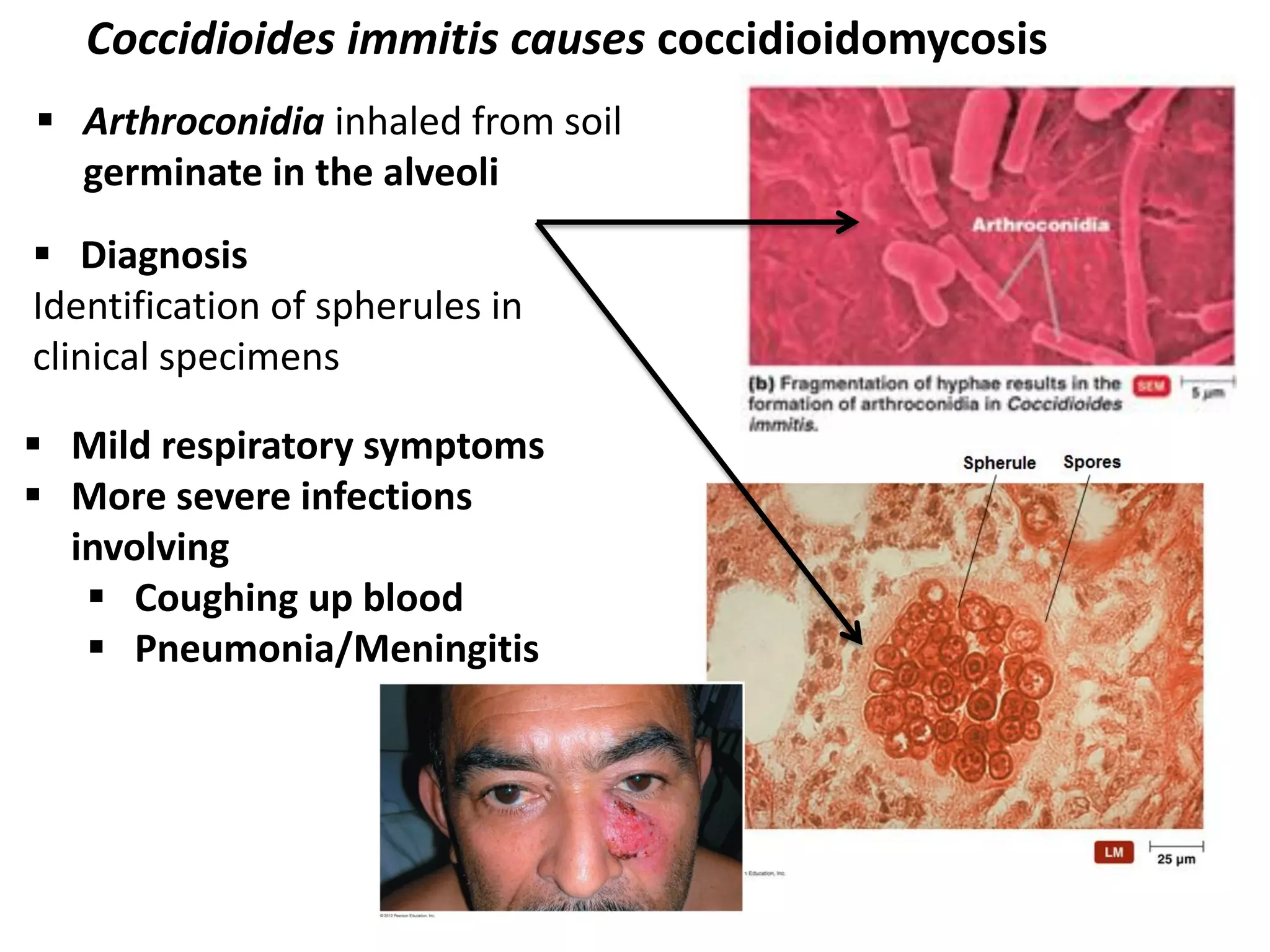
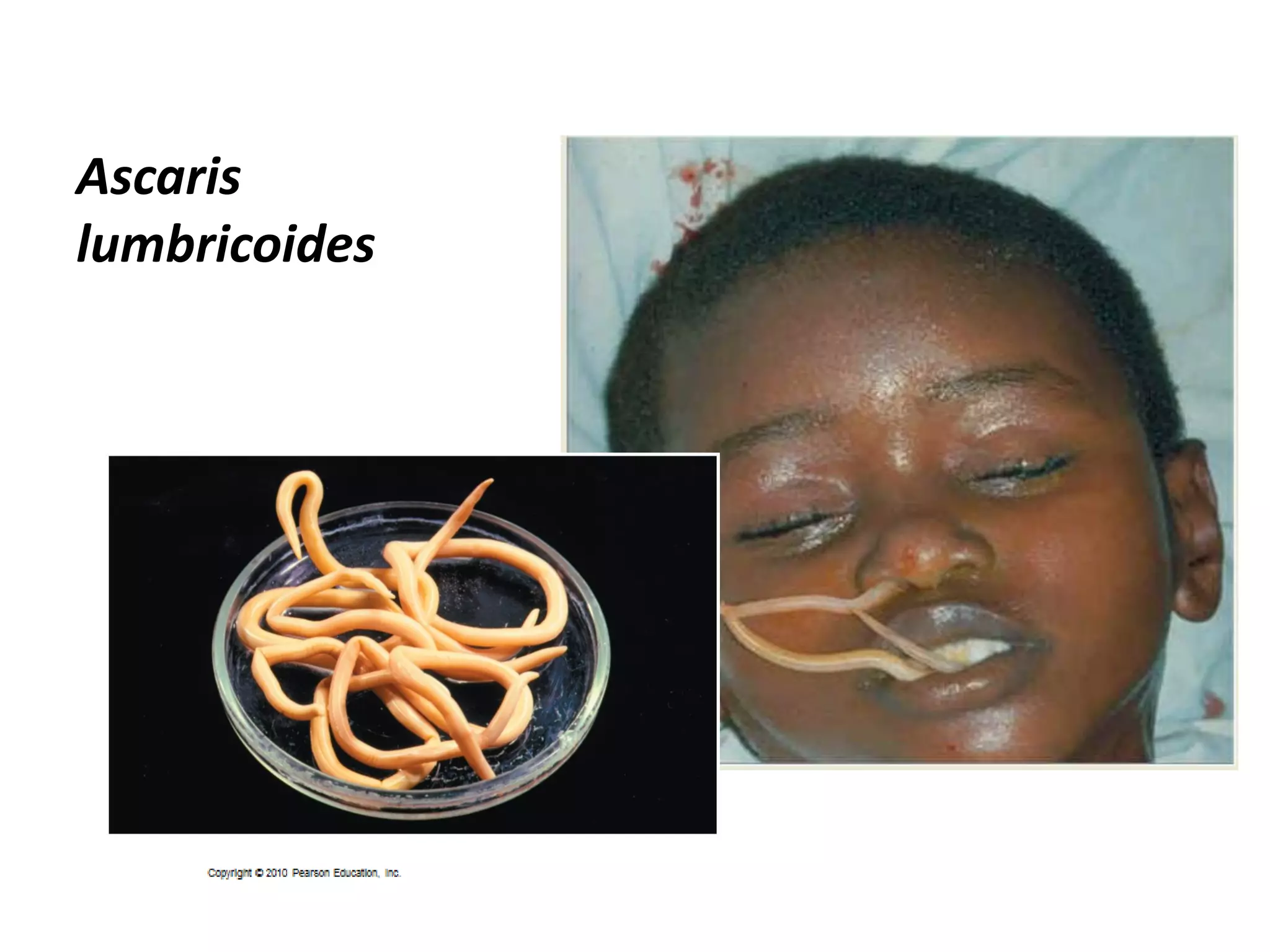
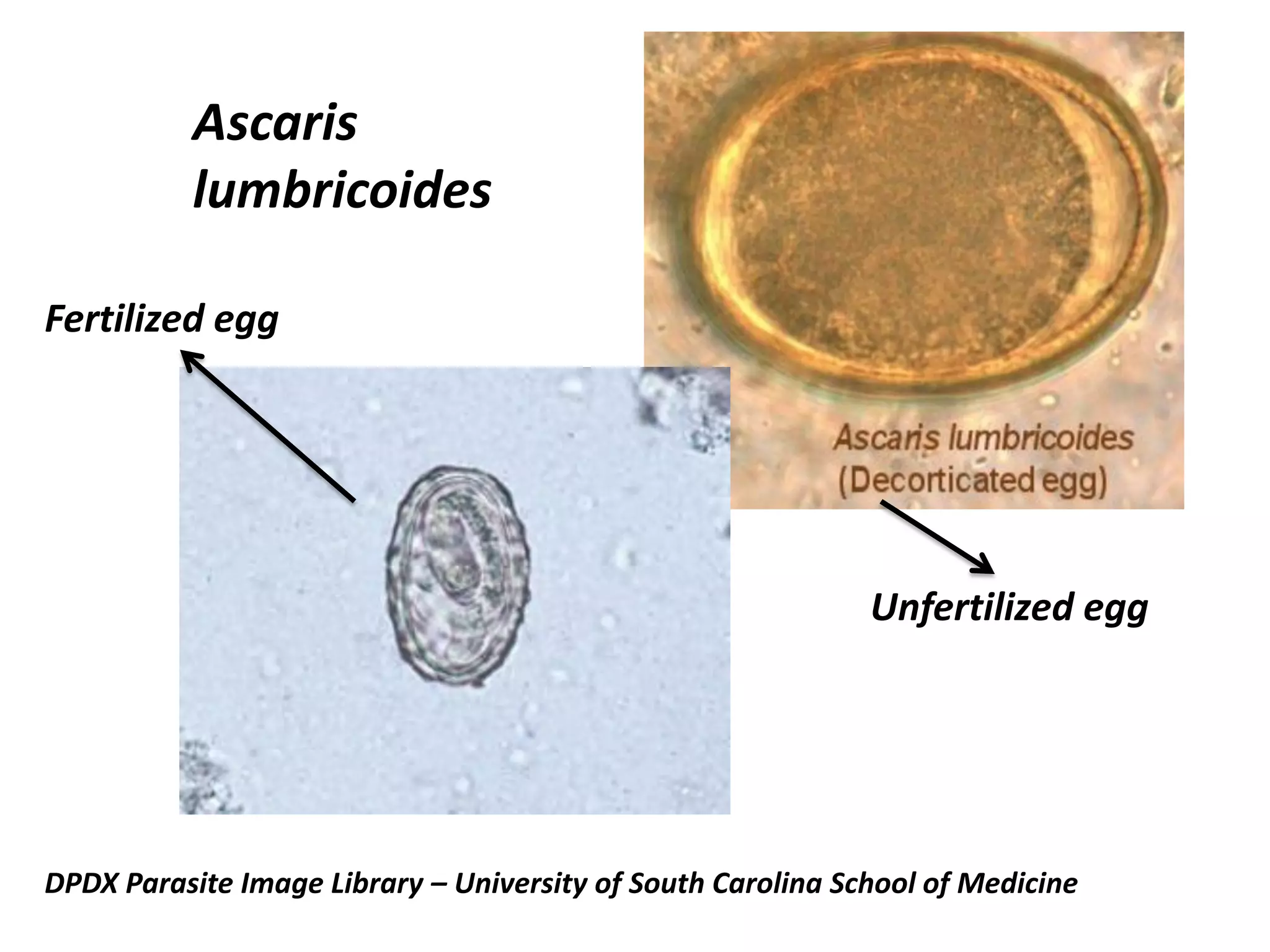
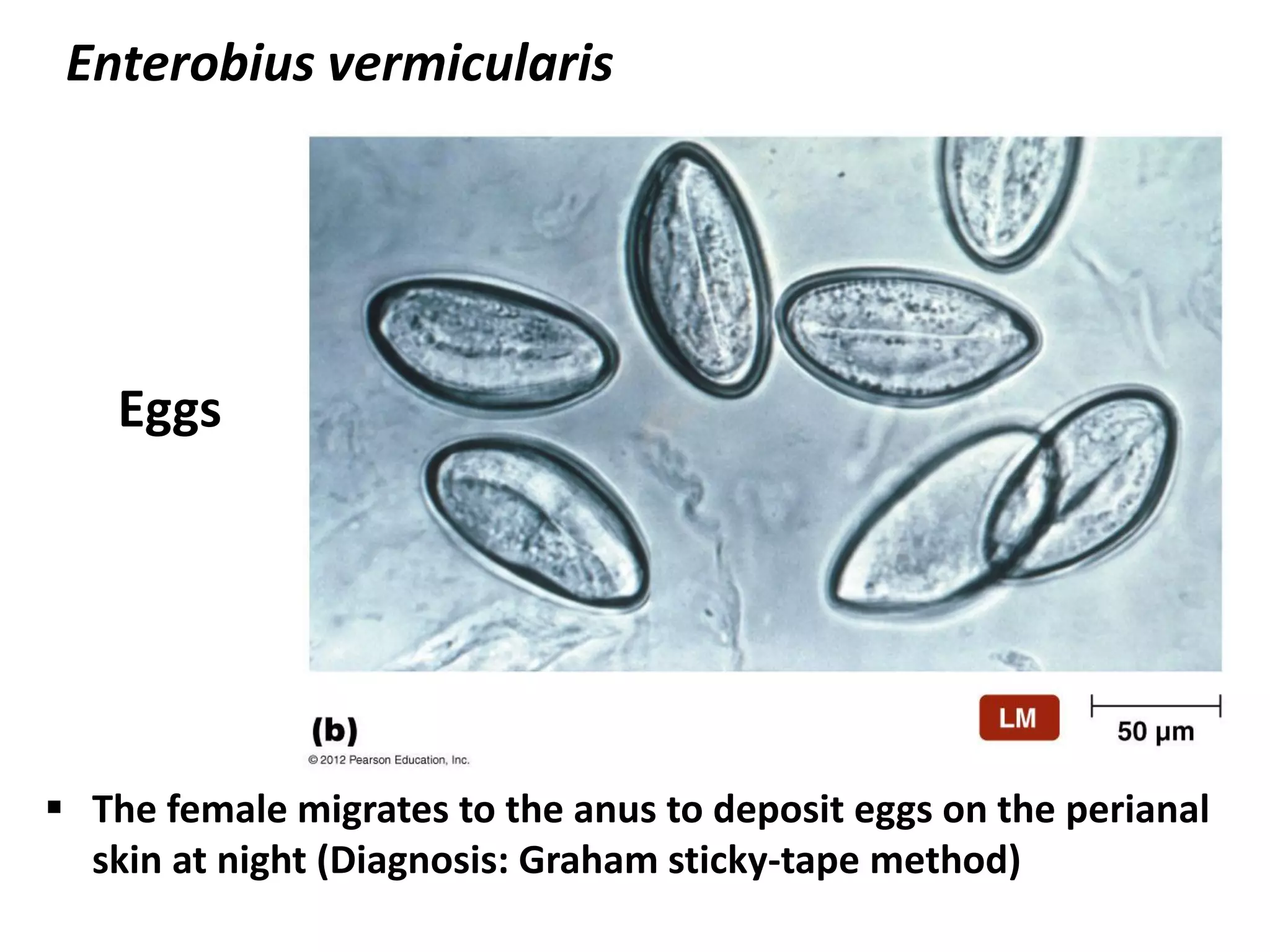
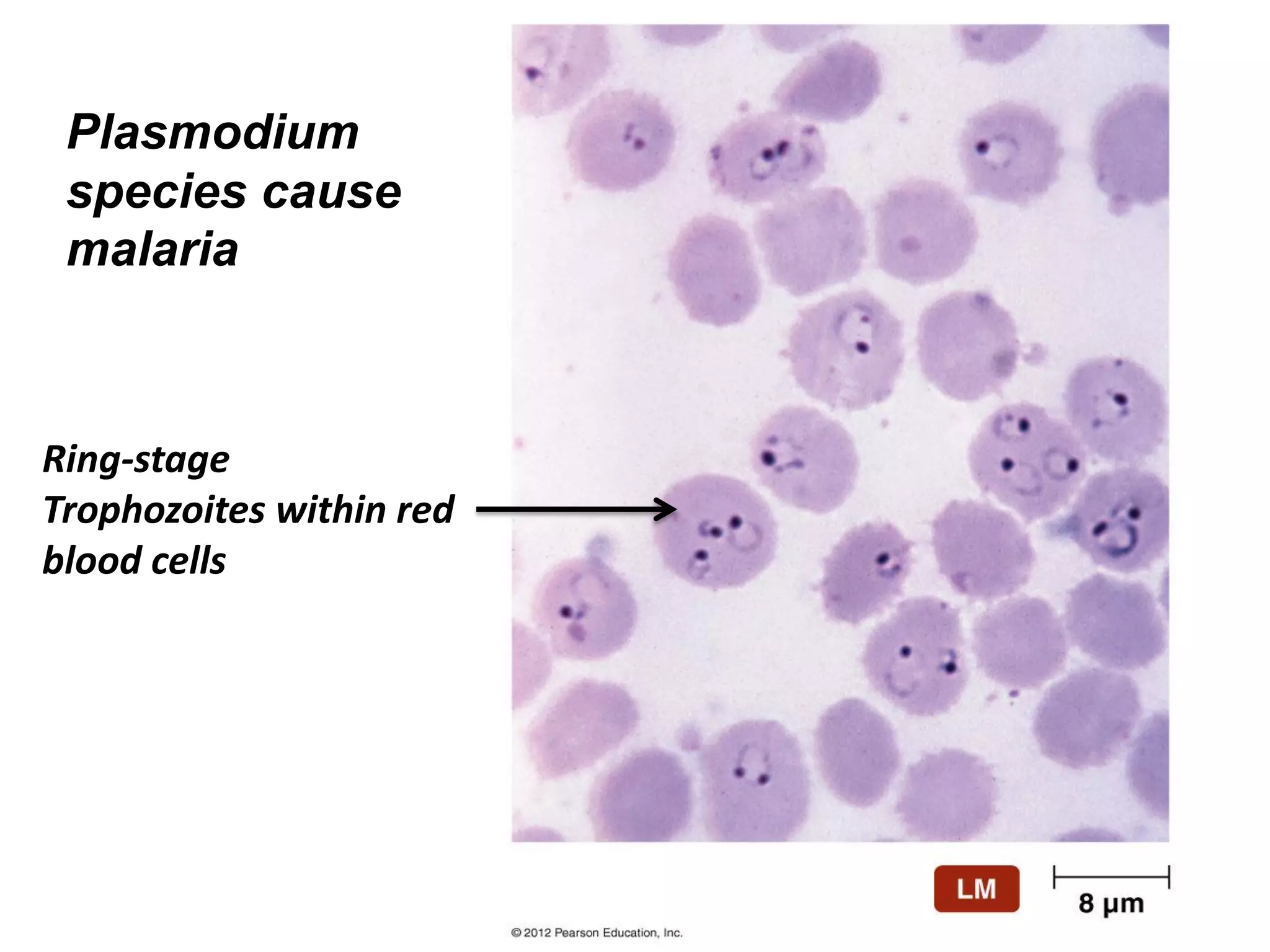
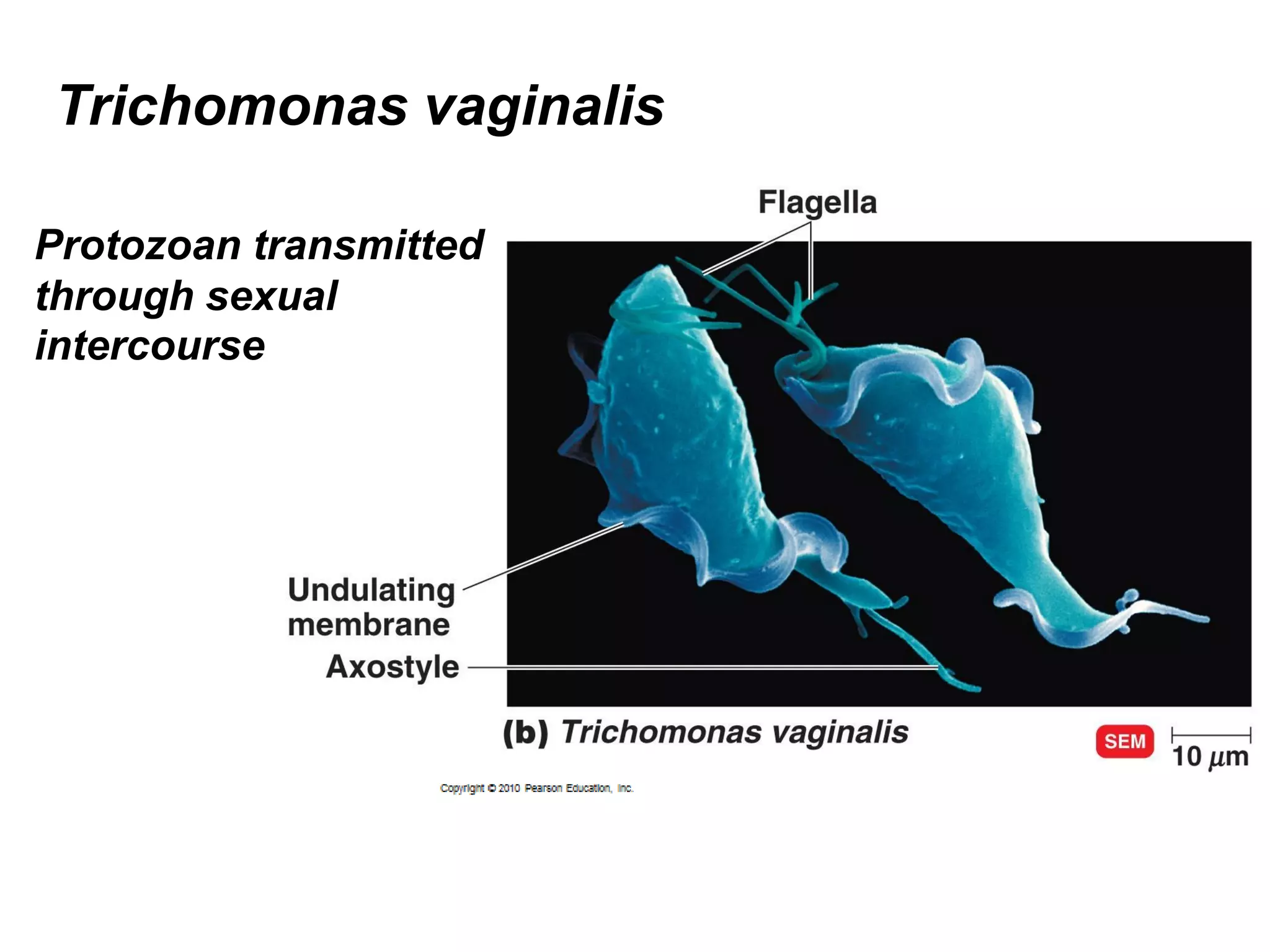
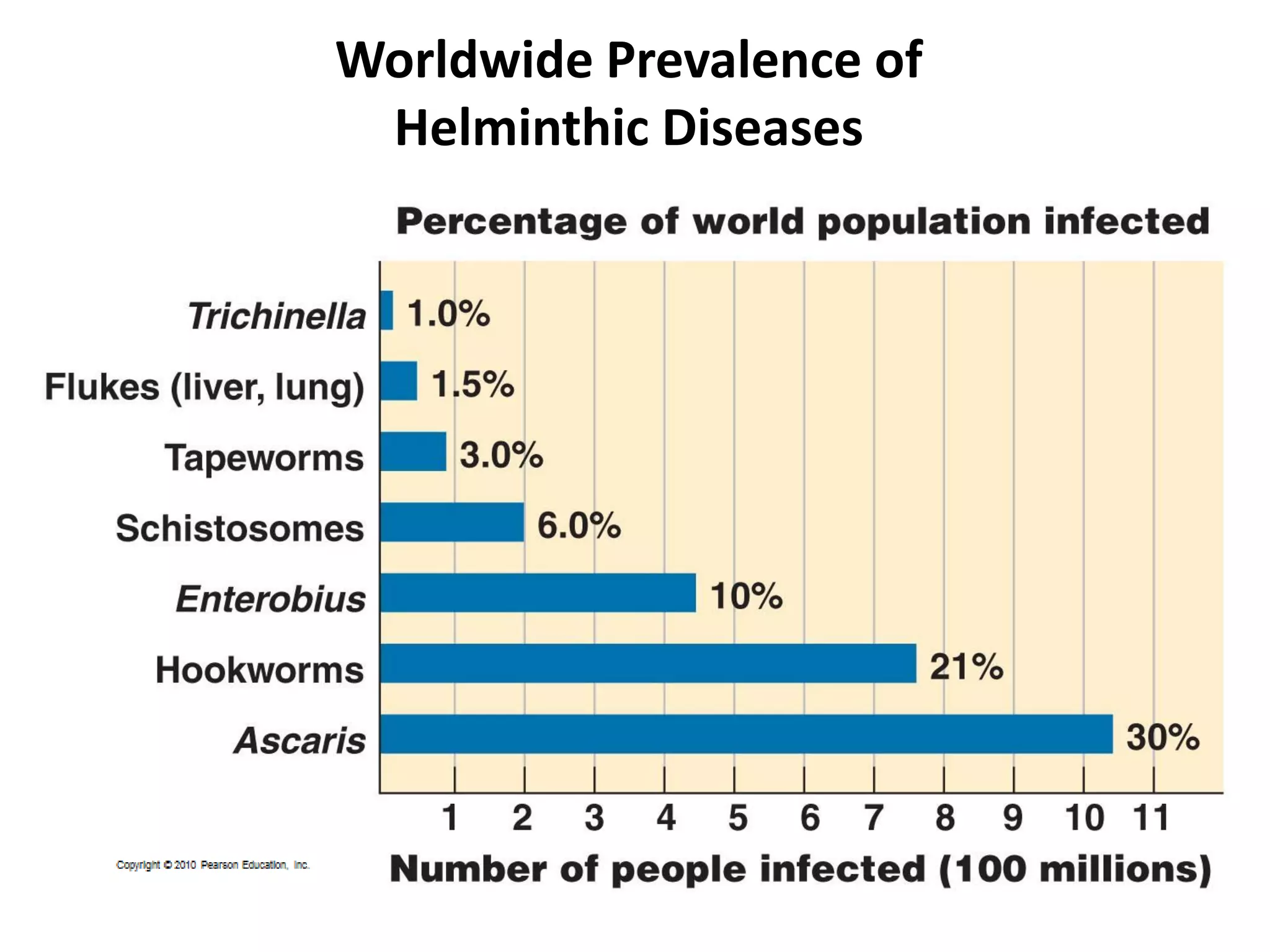
This document summarizes several fungi, parasites, and protozoa that can infect humans. It describes key characteristics of pathogens like Candida albicans, Cryptococcus neoformans, Histoplasma capsulatum, Coccidioides immitis, Schistosoma mansoni, Taenia species, Ascaris lumbricoides, Enterobius vermicularis, hookworms, Trichinella spiralis, Plasmodium species, Giardia intestinalis, Entamoeba histolytica, Trypanosoma cruzi, and Trichomonas vaginalis. For each organism, it outlines the infectious stage, transmission method, sites of infection in the body