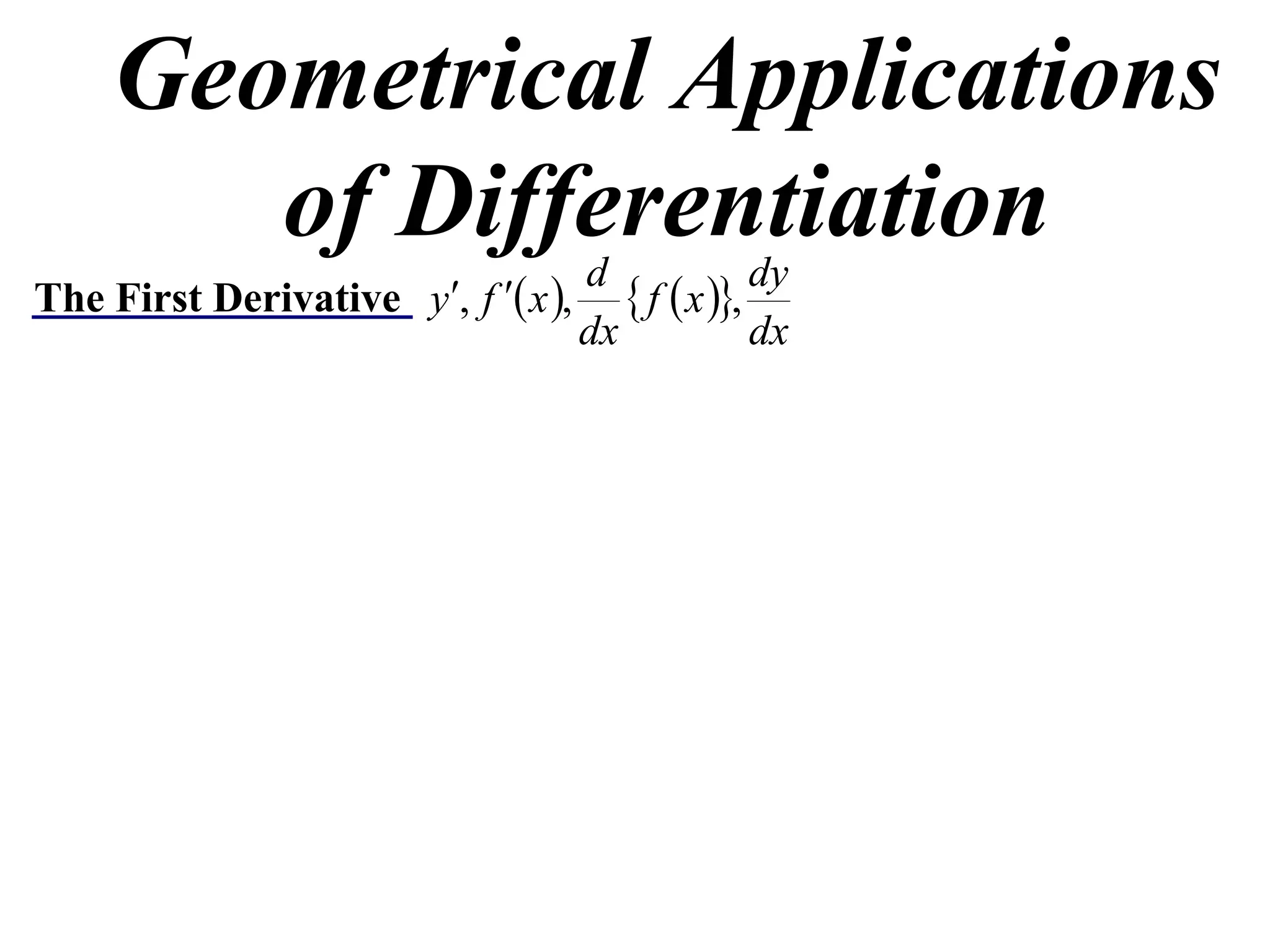
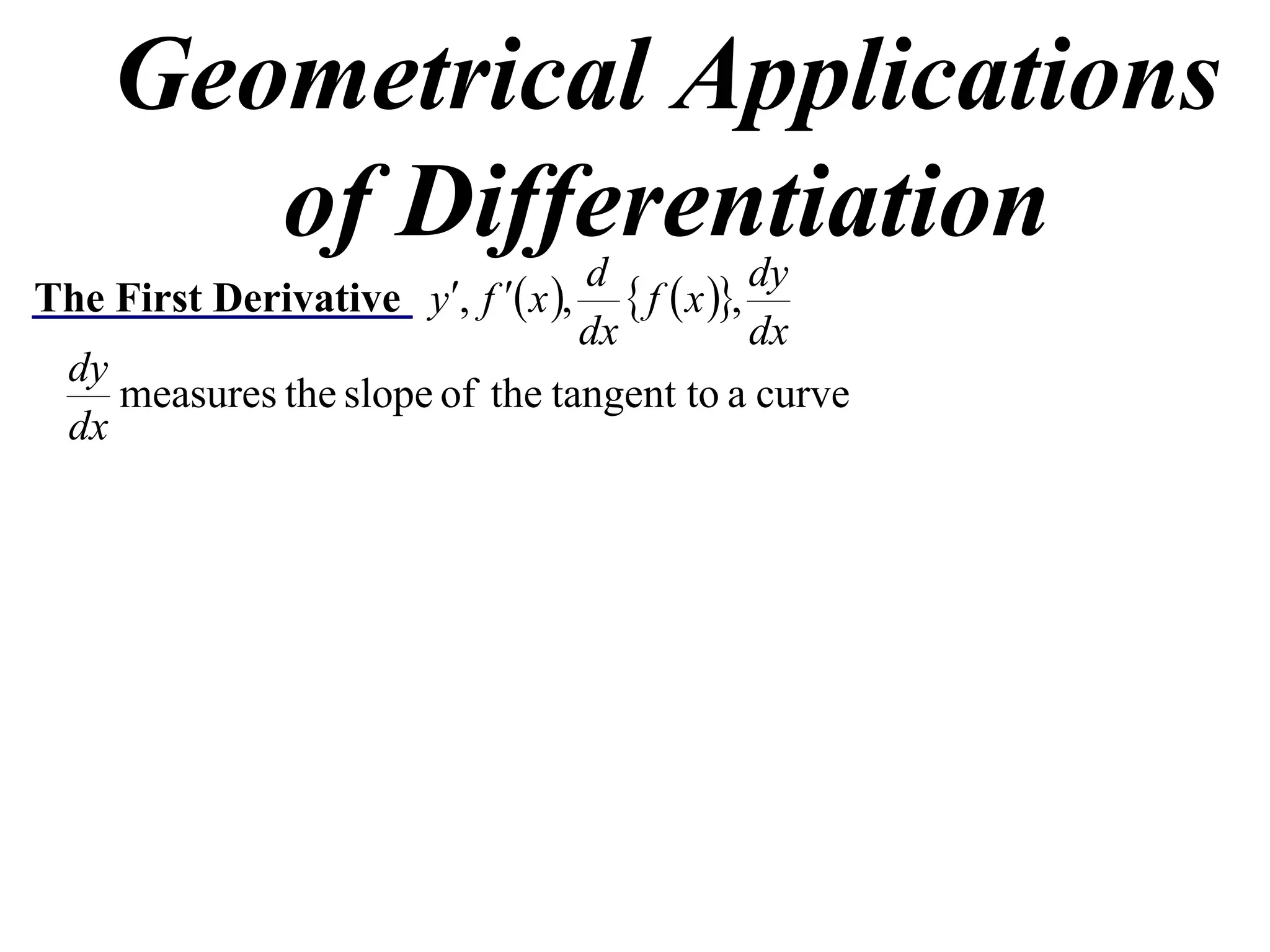
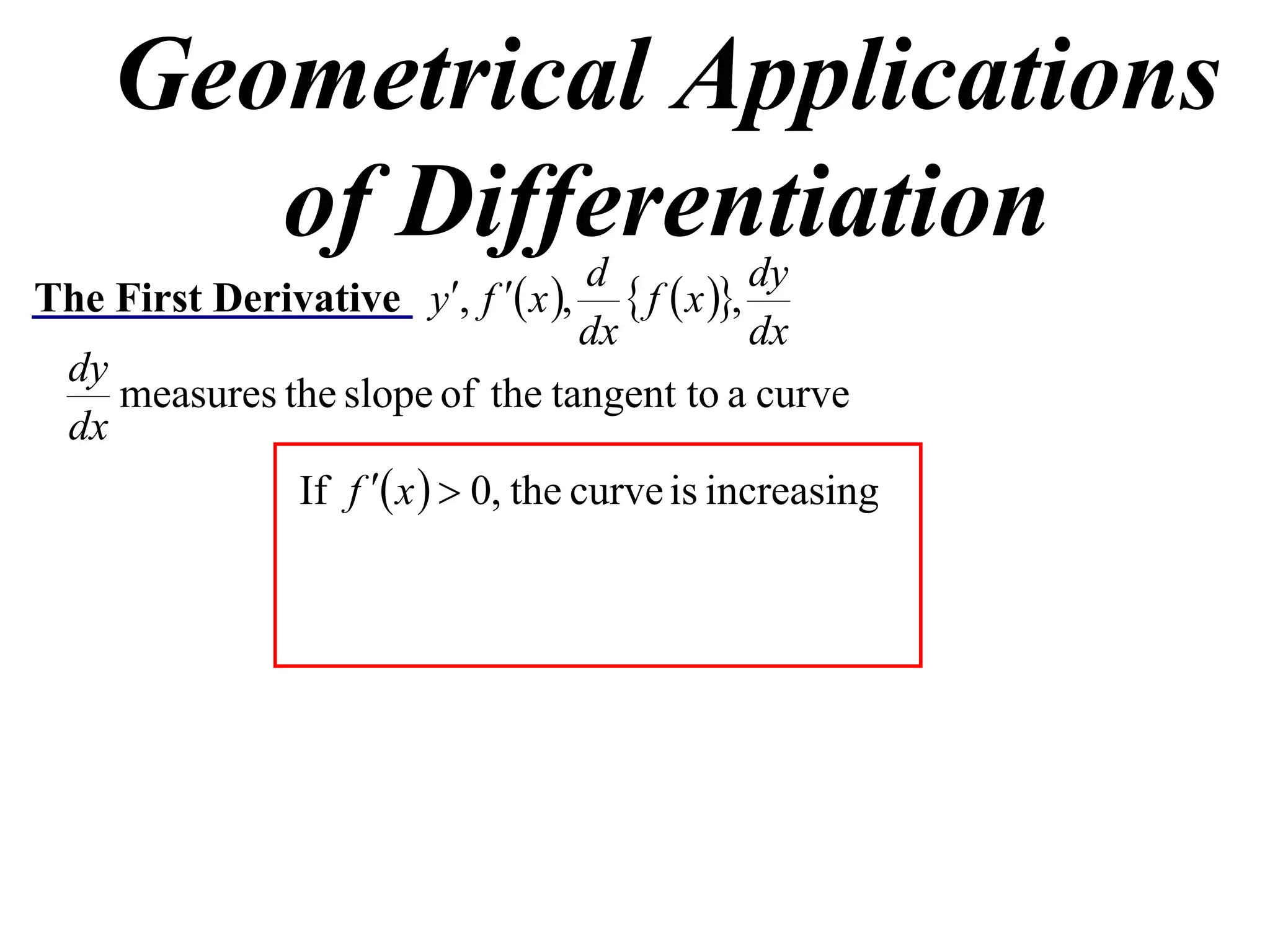
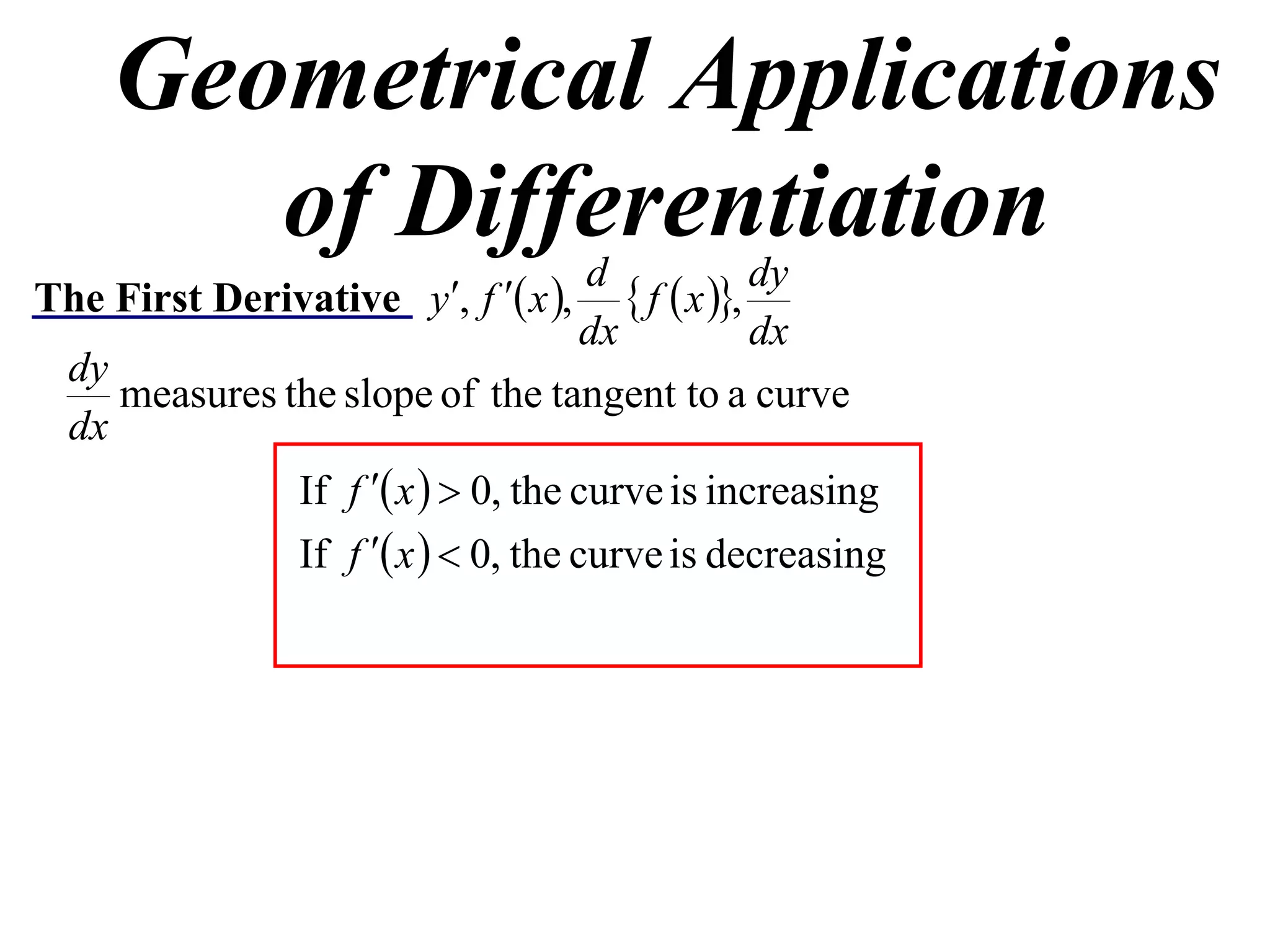
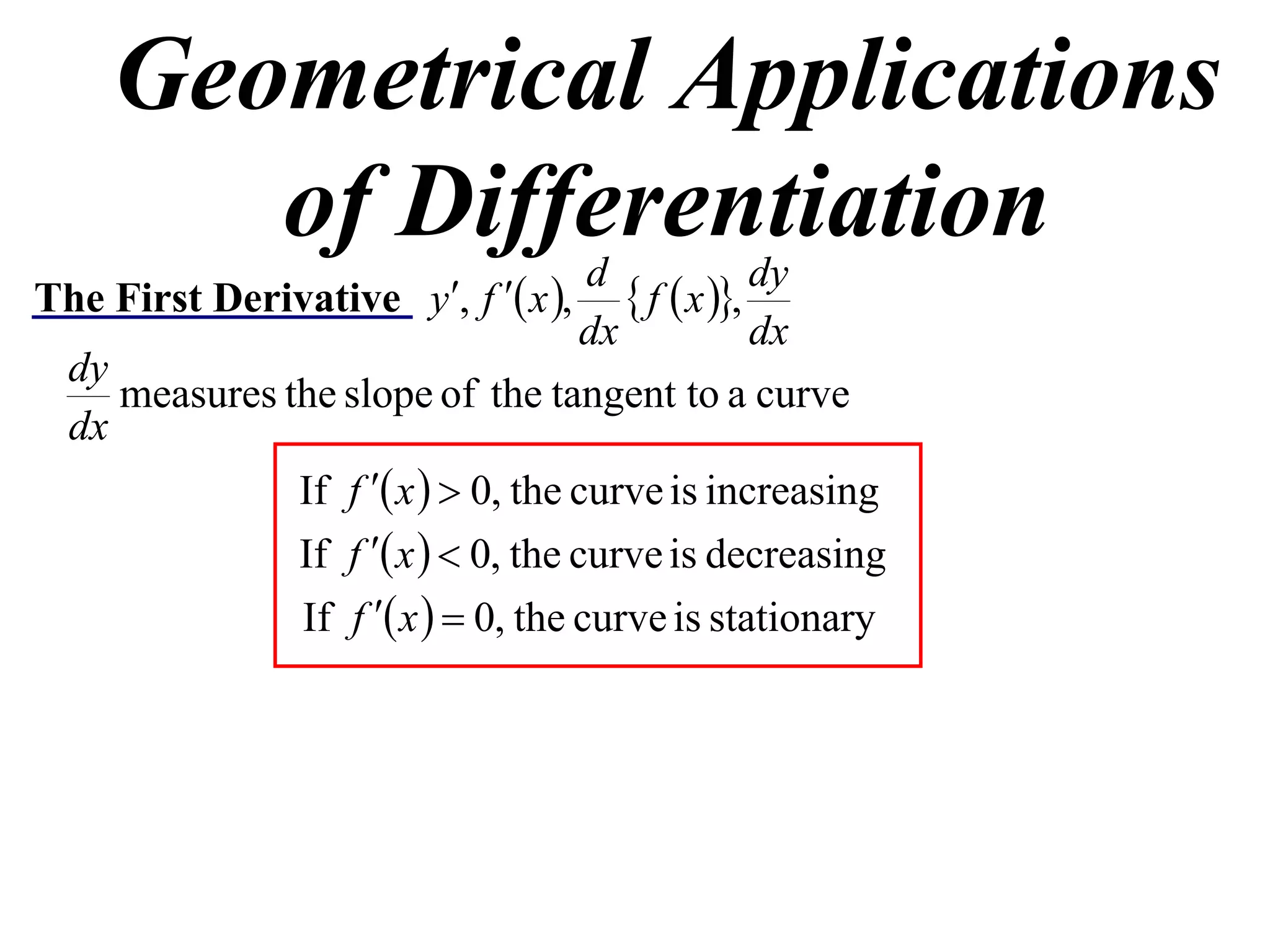
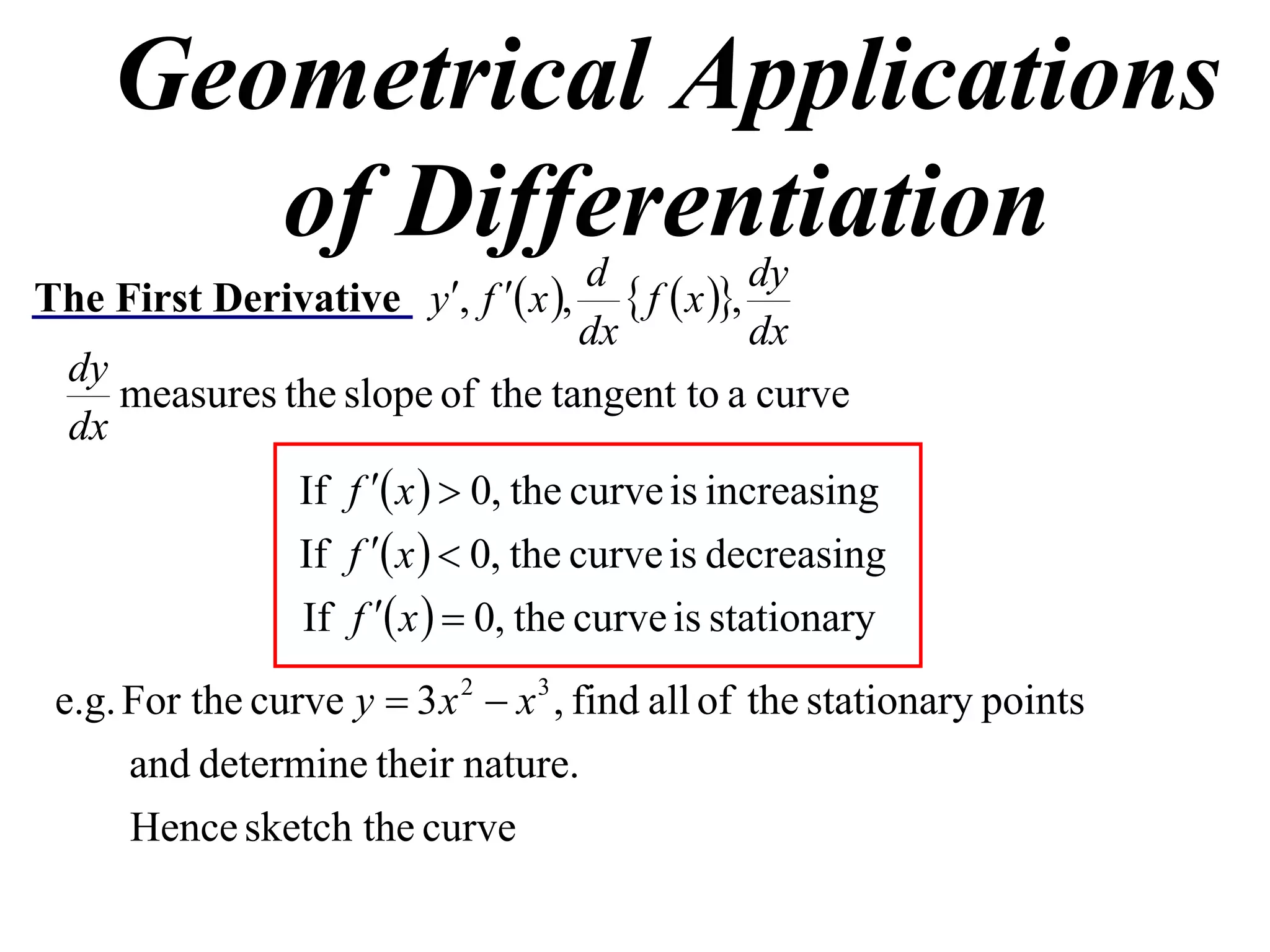
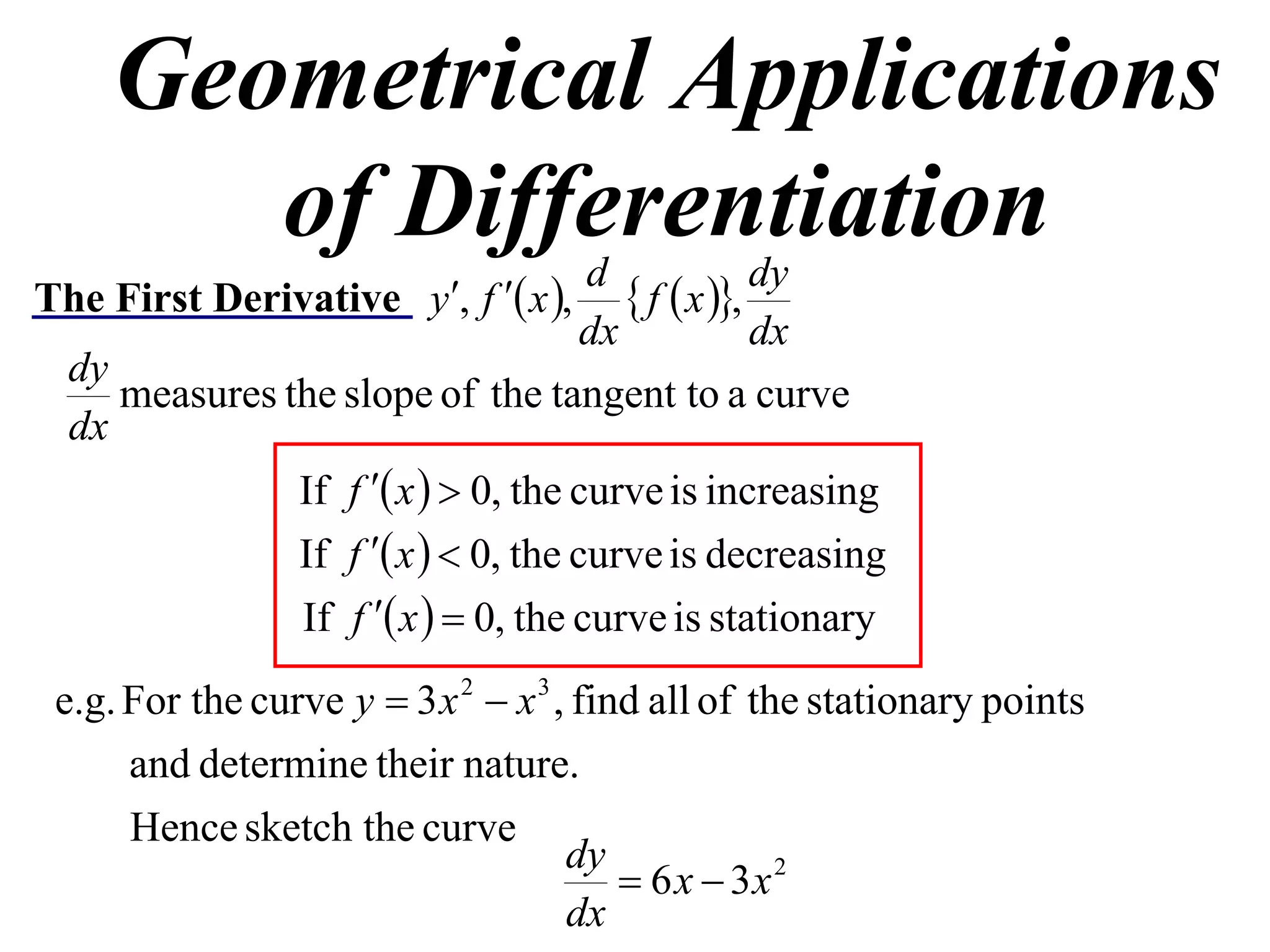
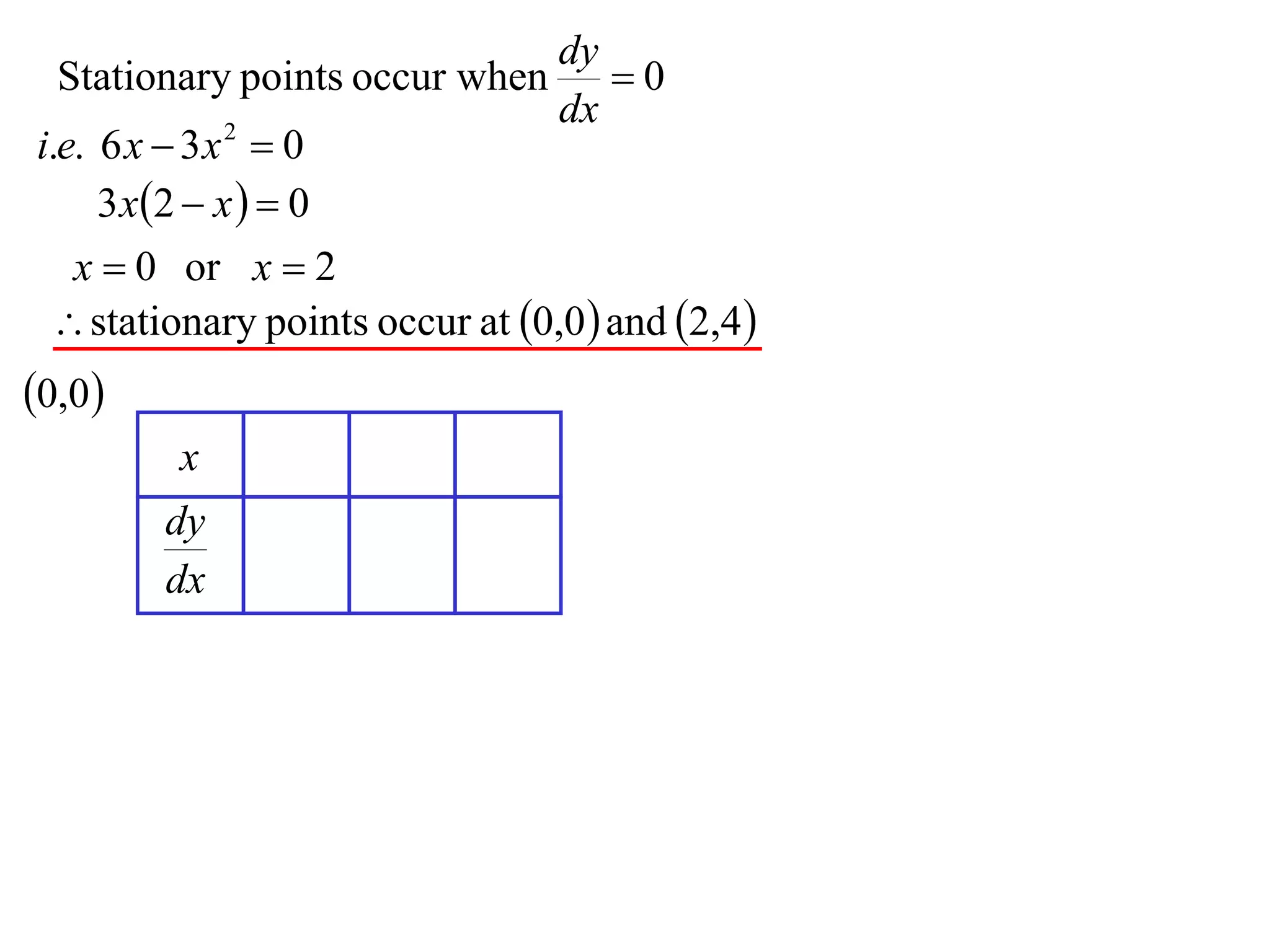
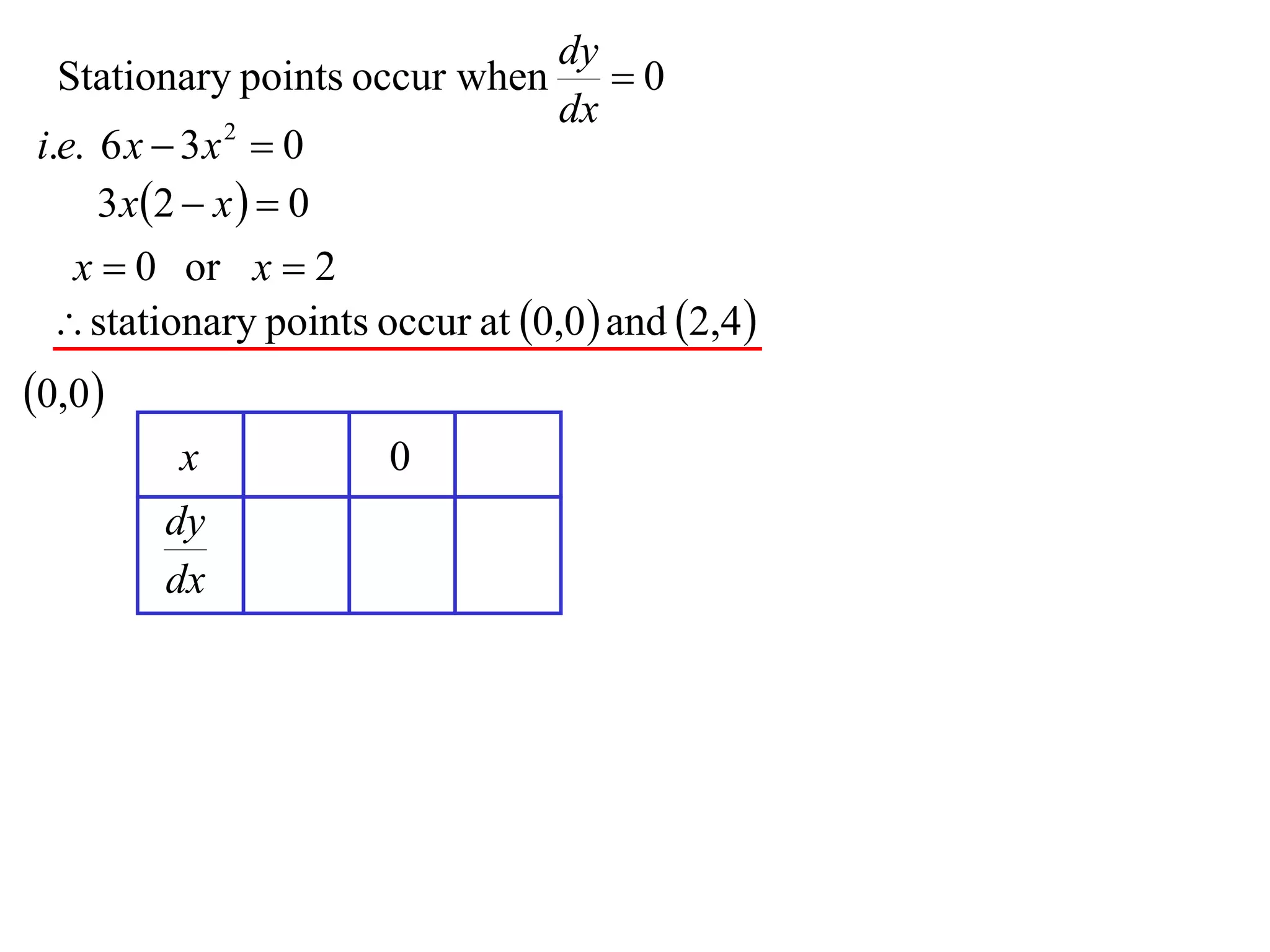
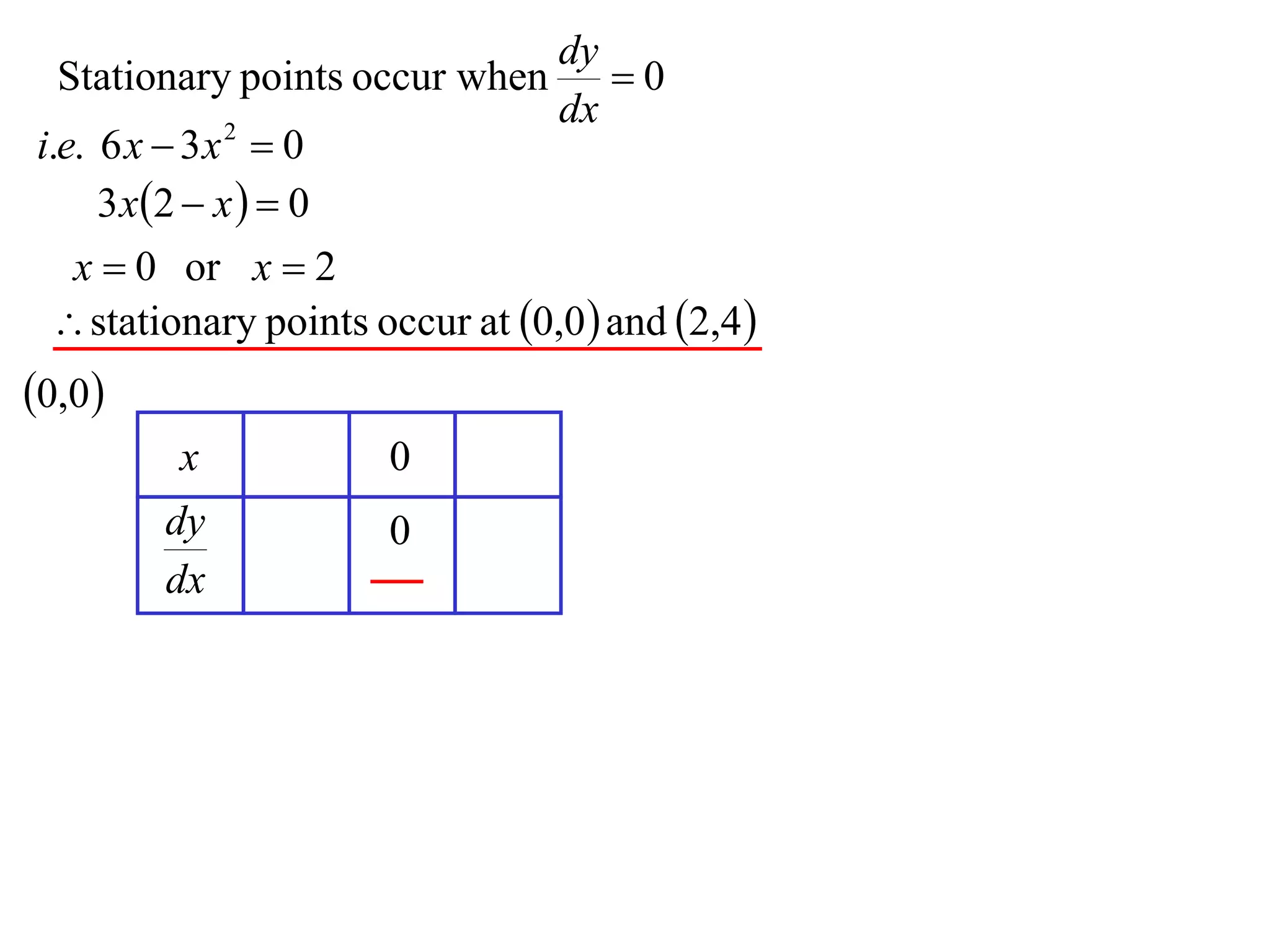
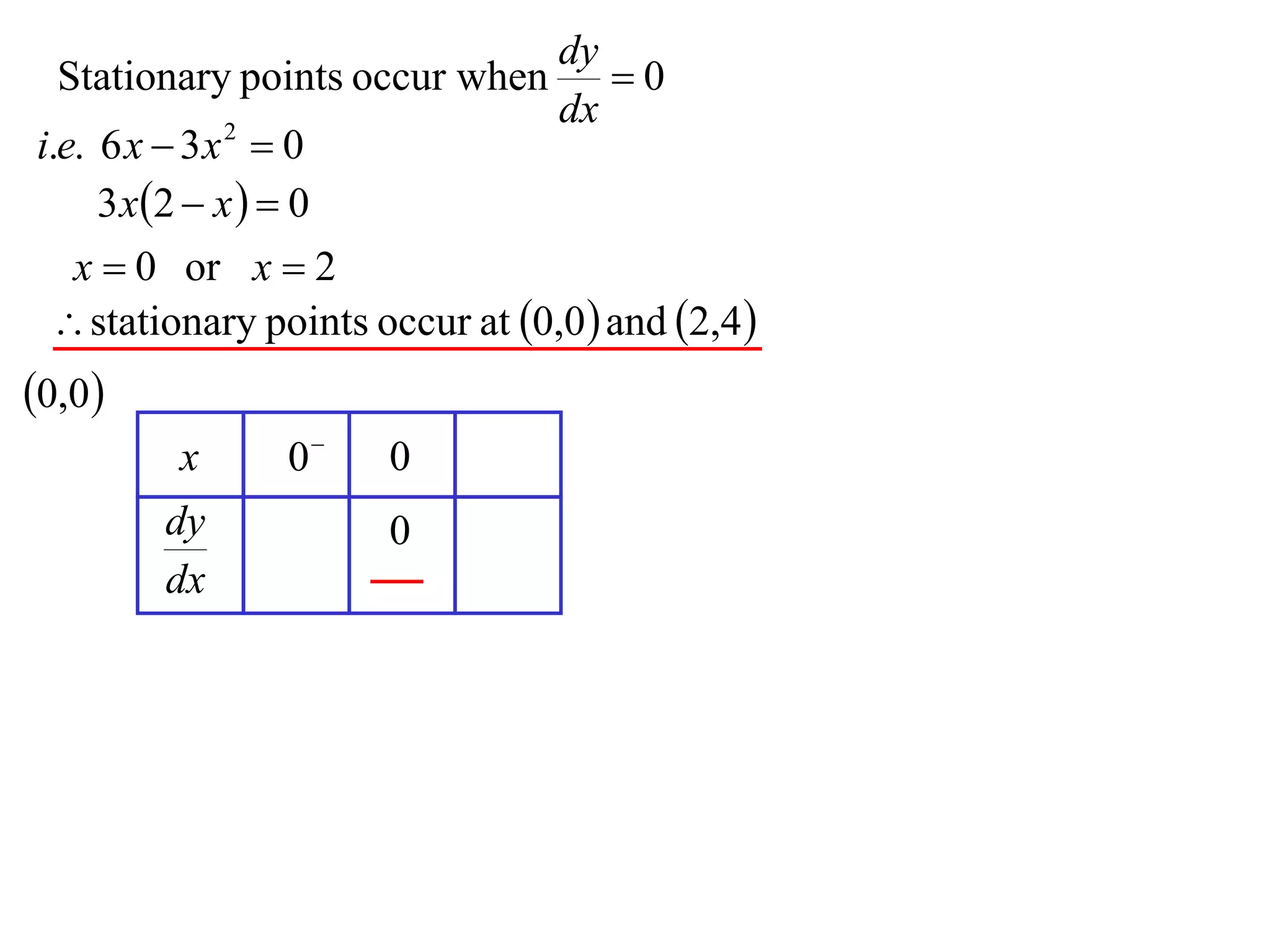
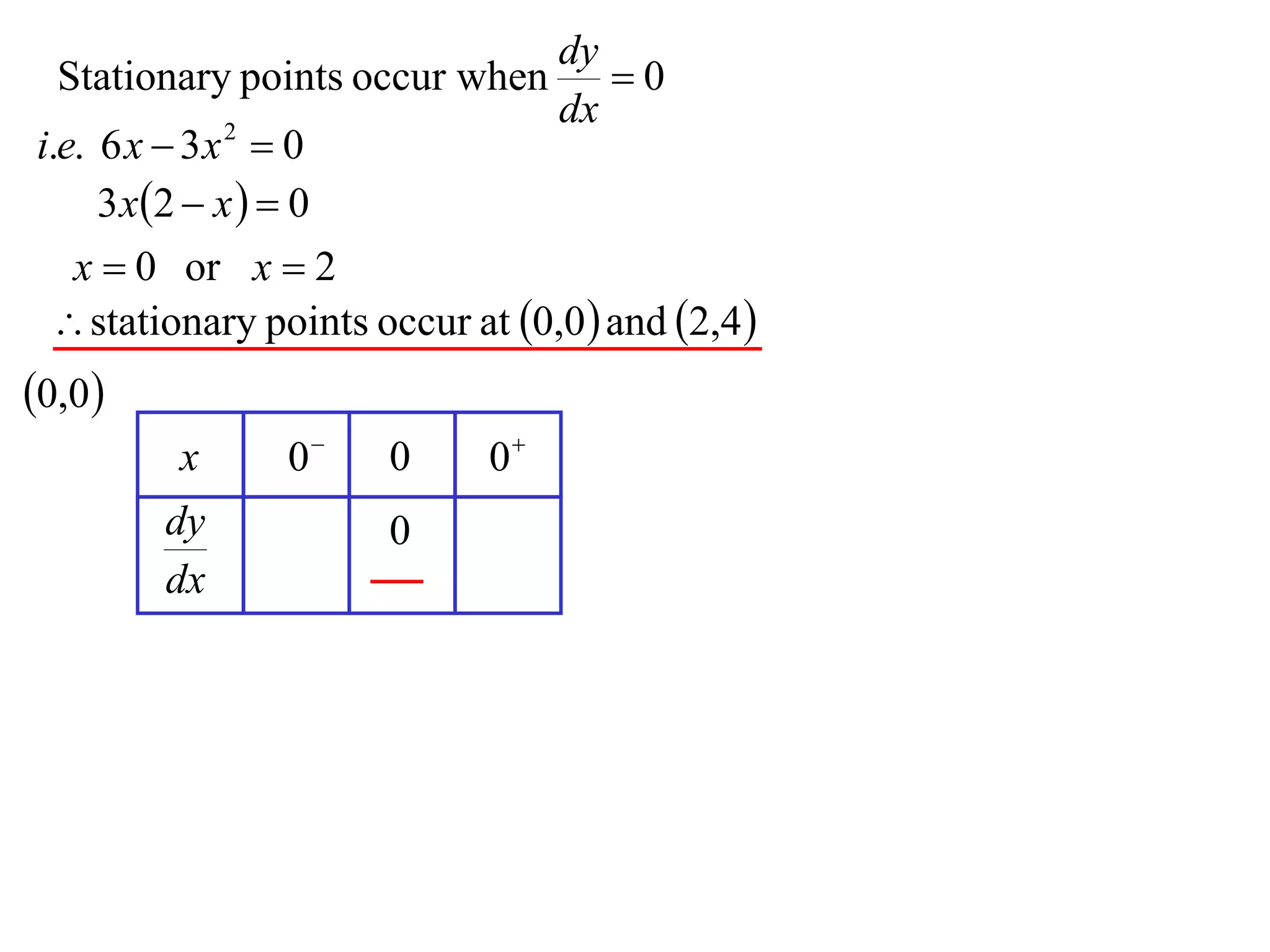
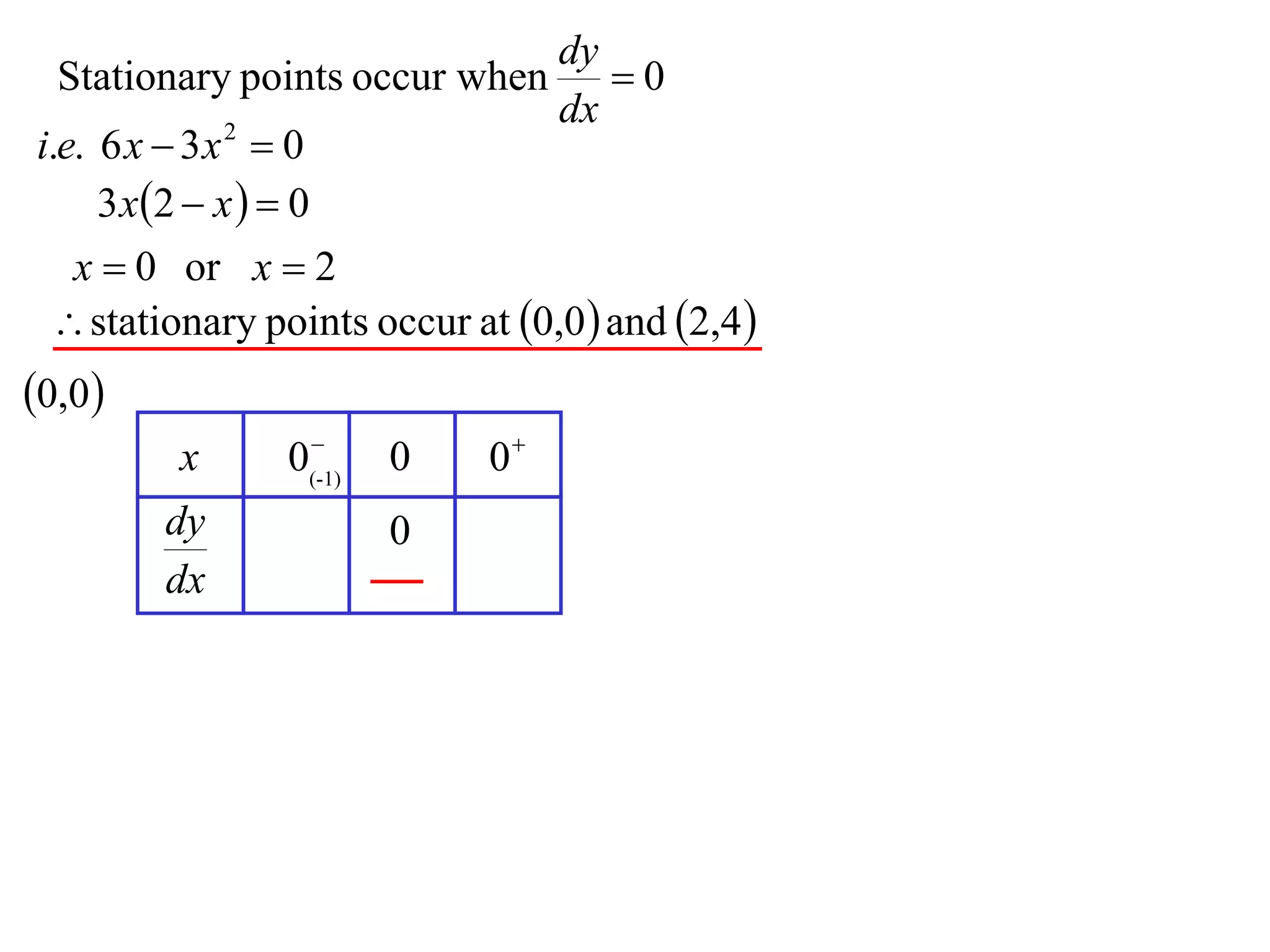
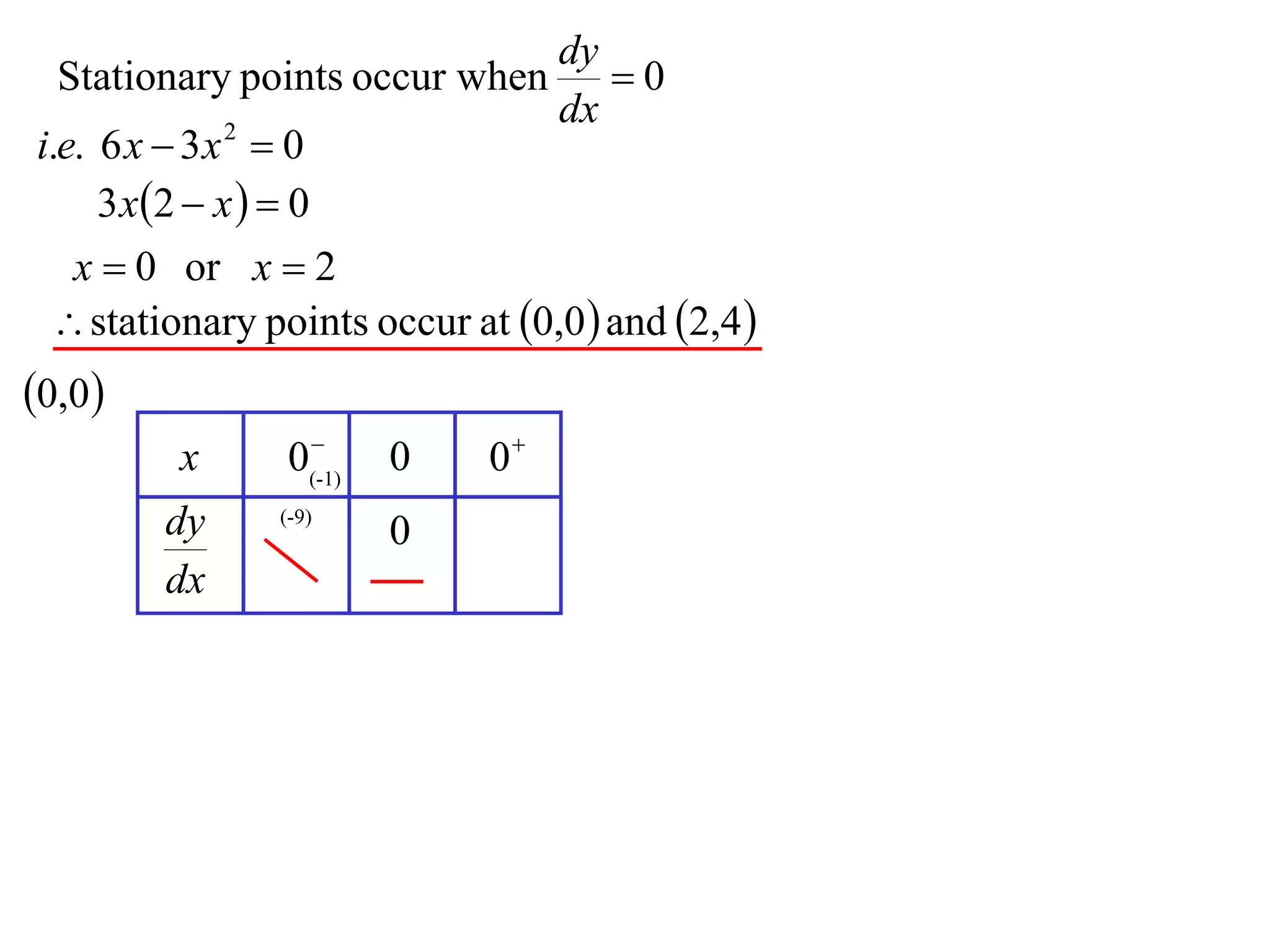
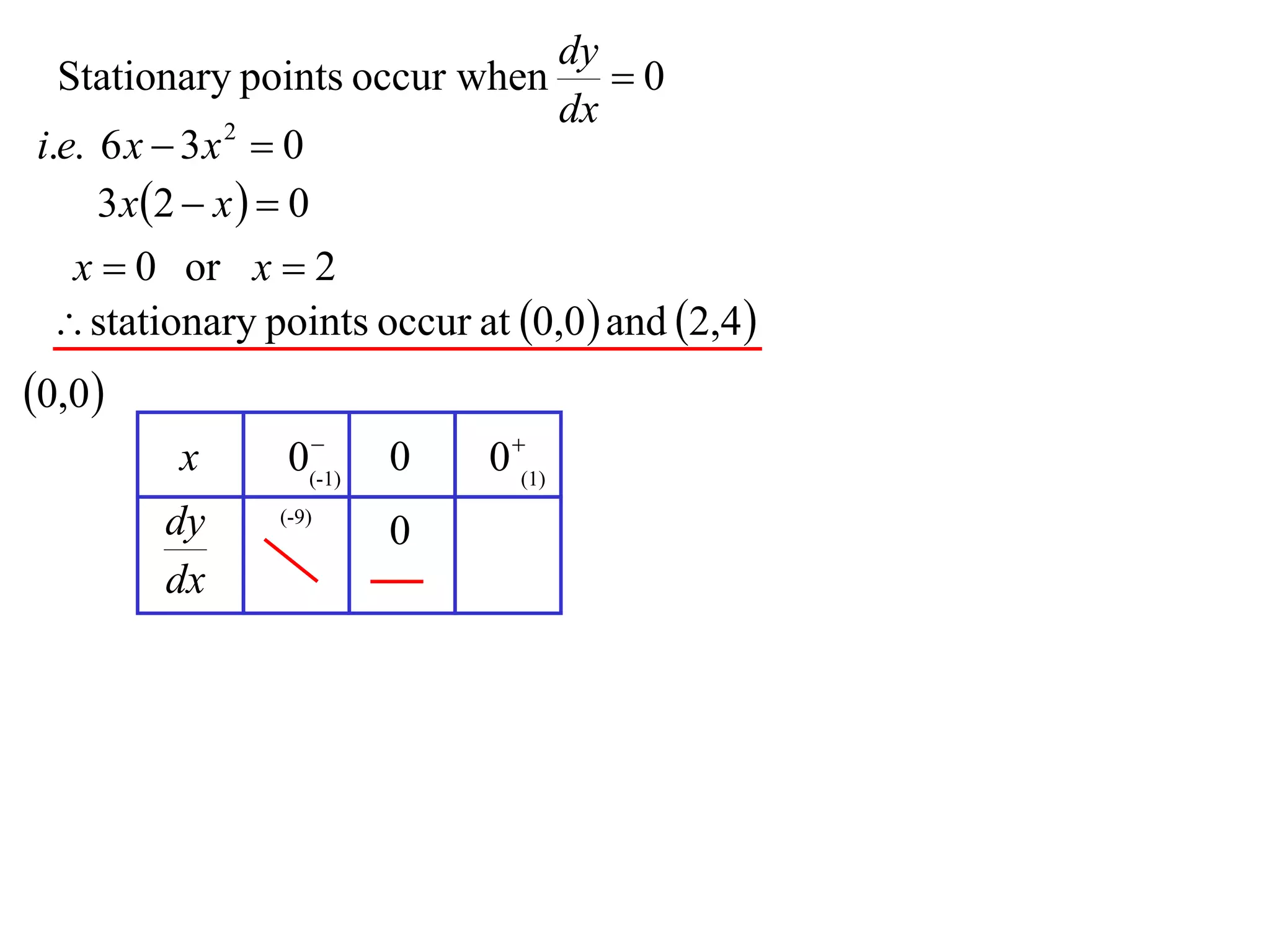
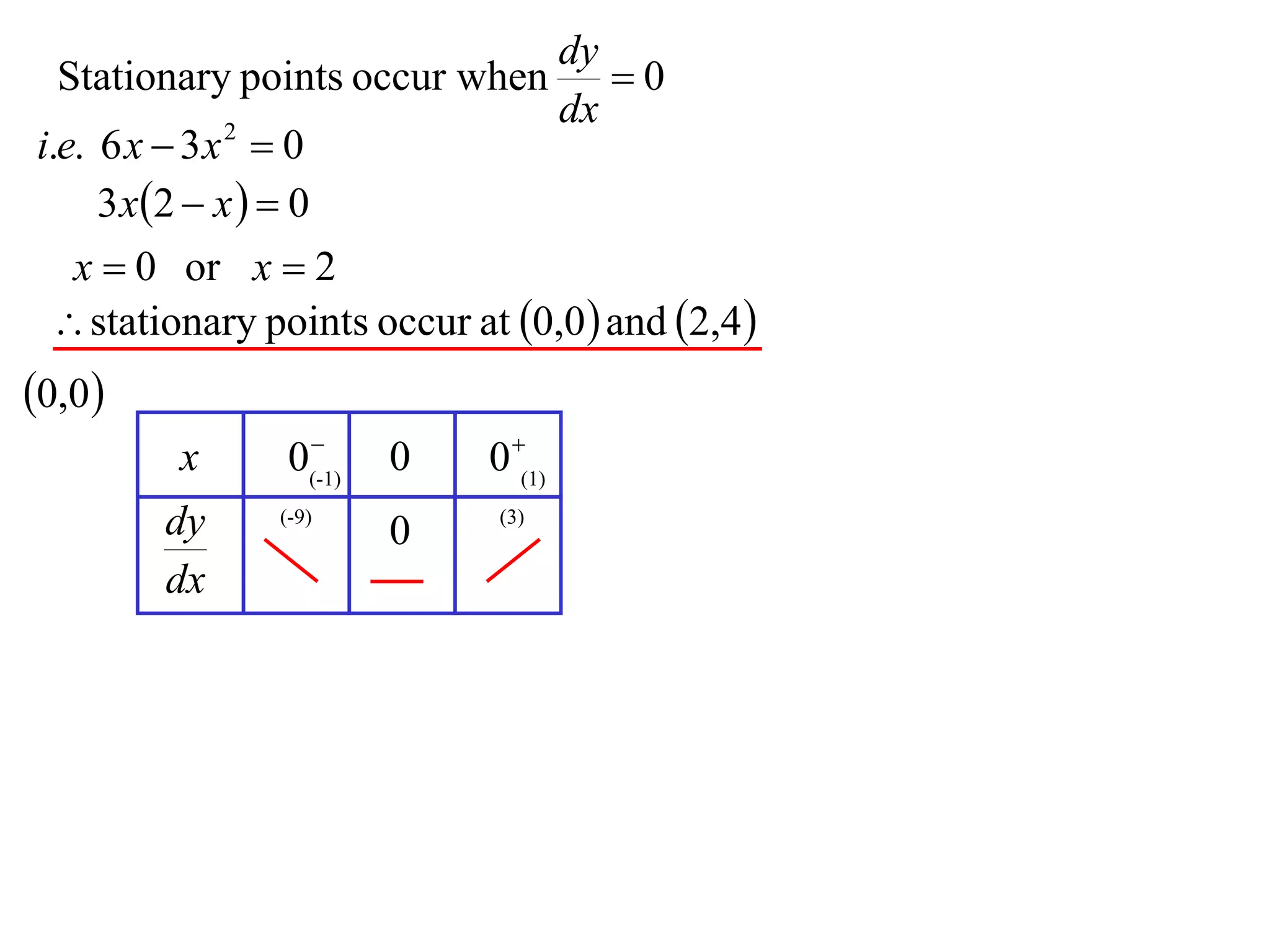
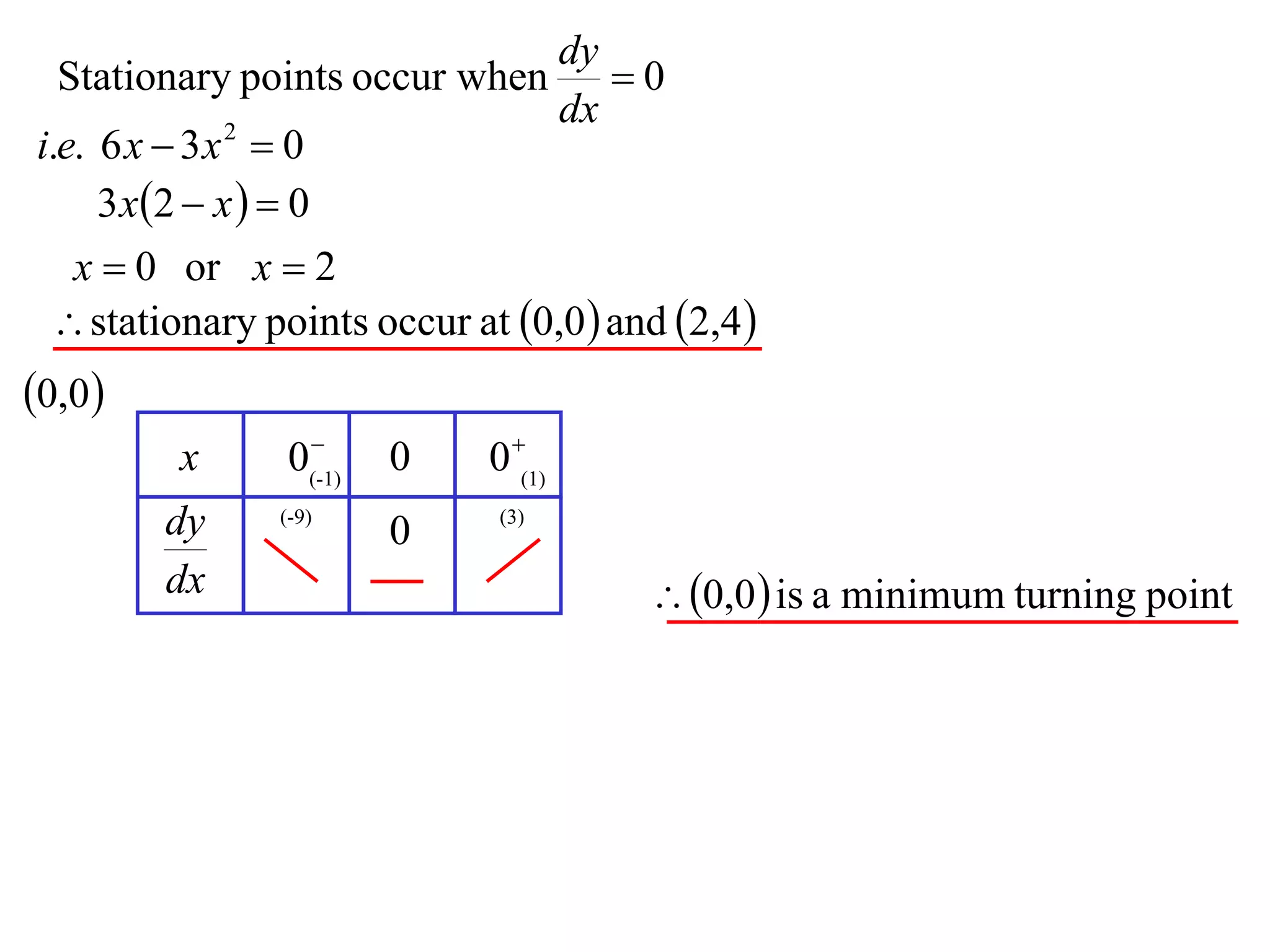
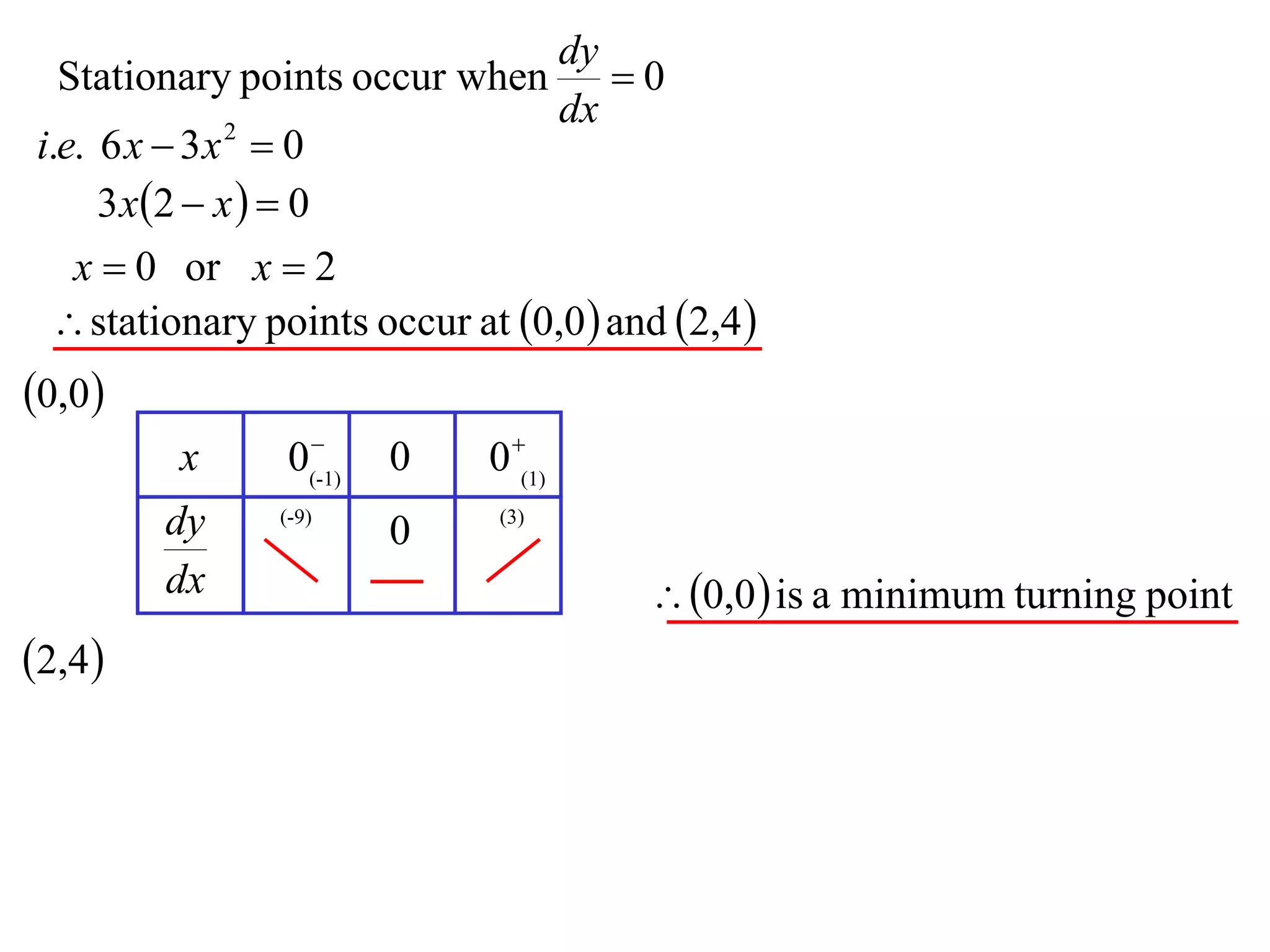
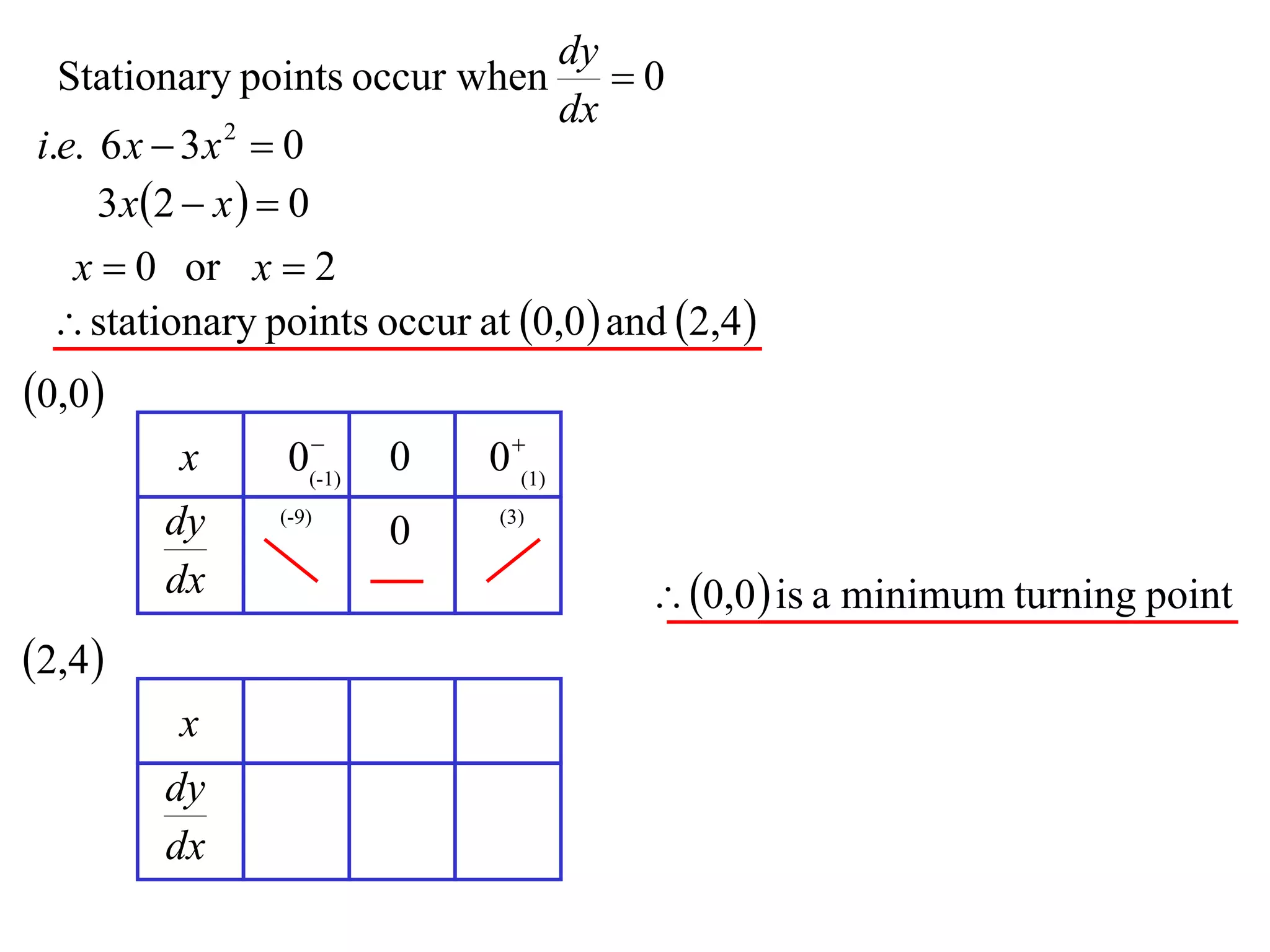
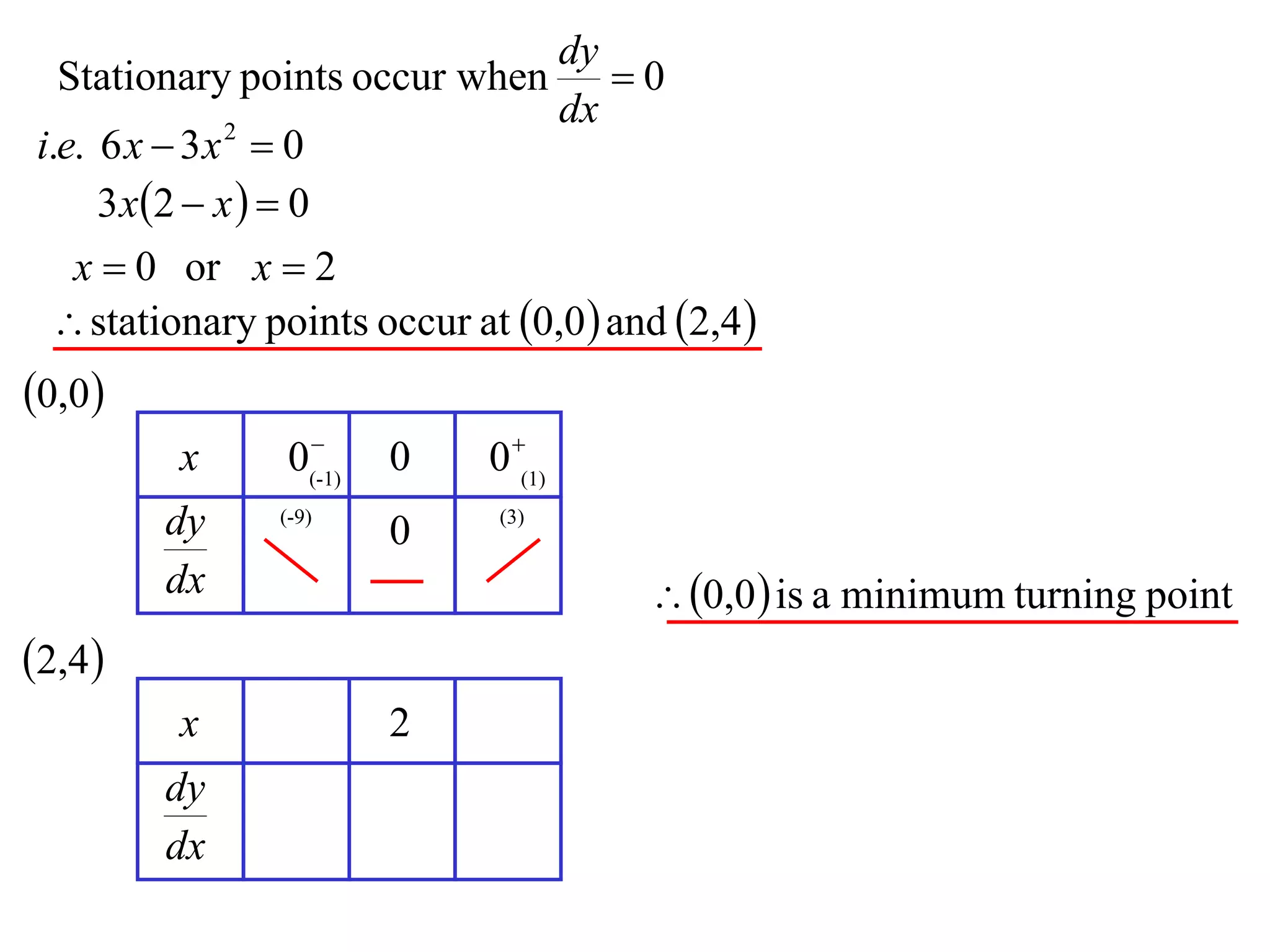
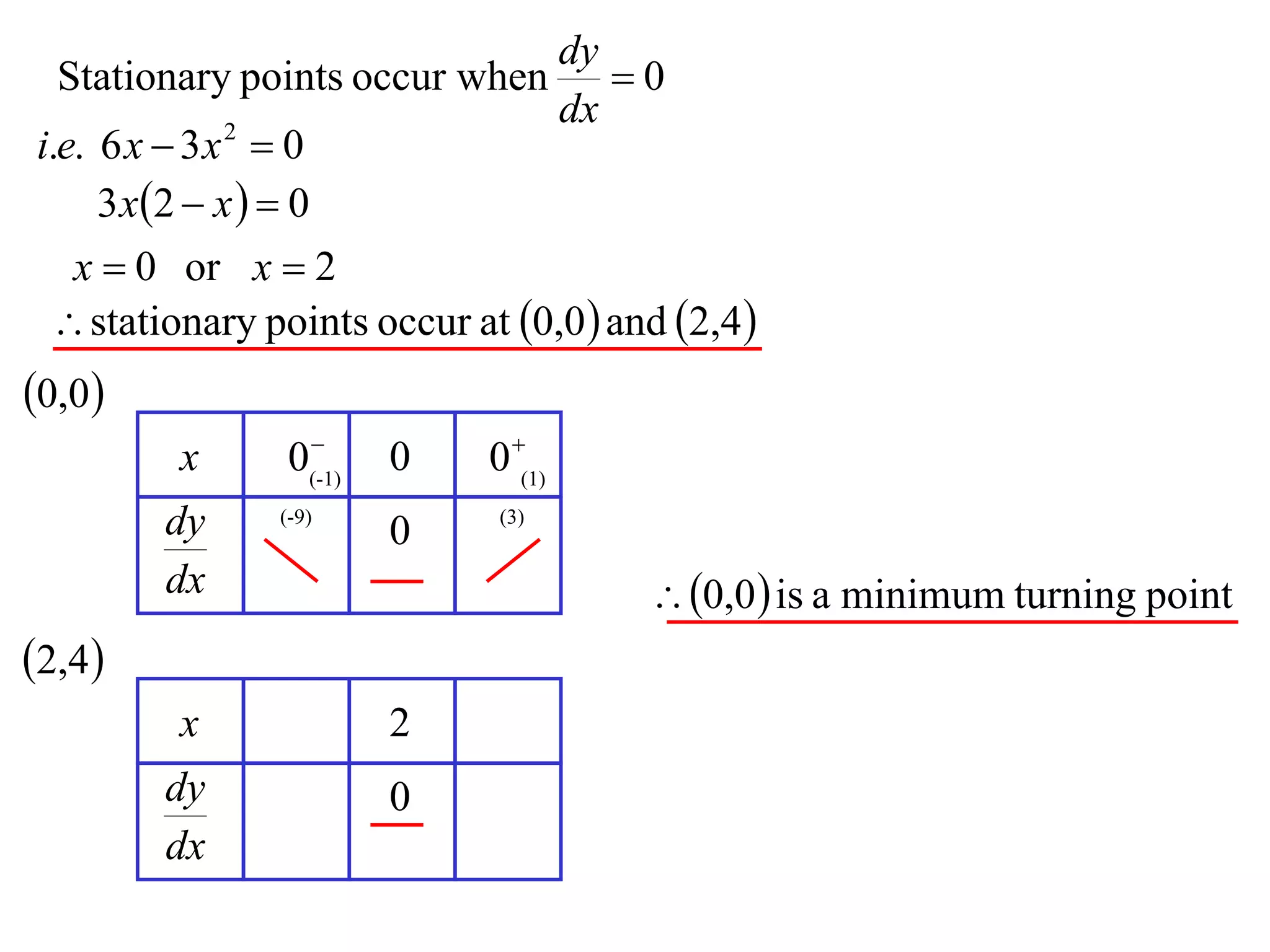
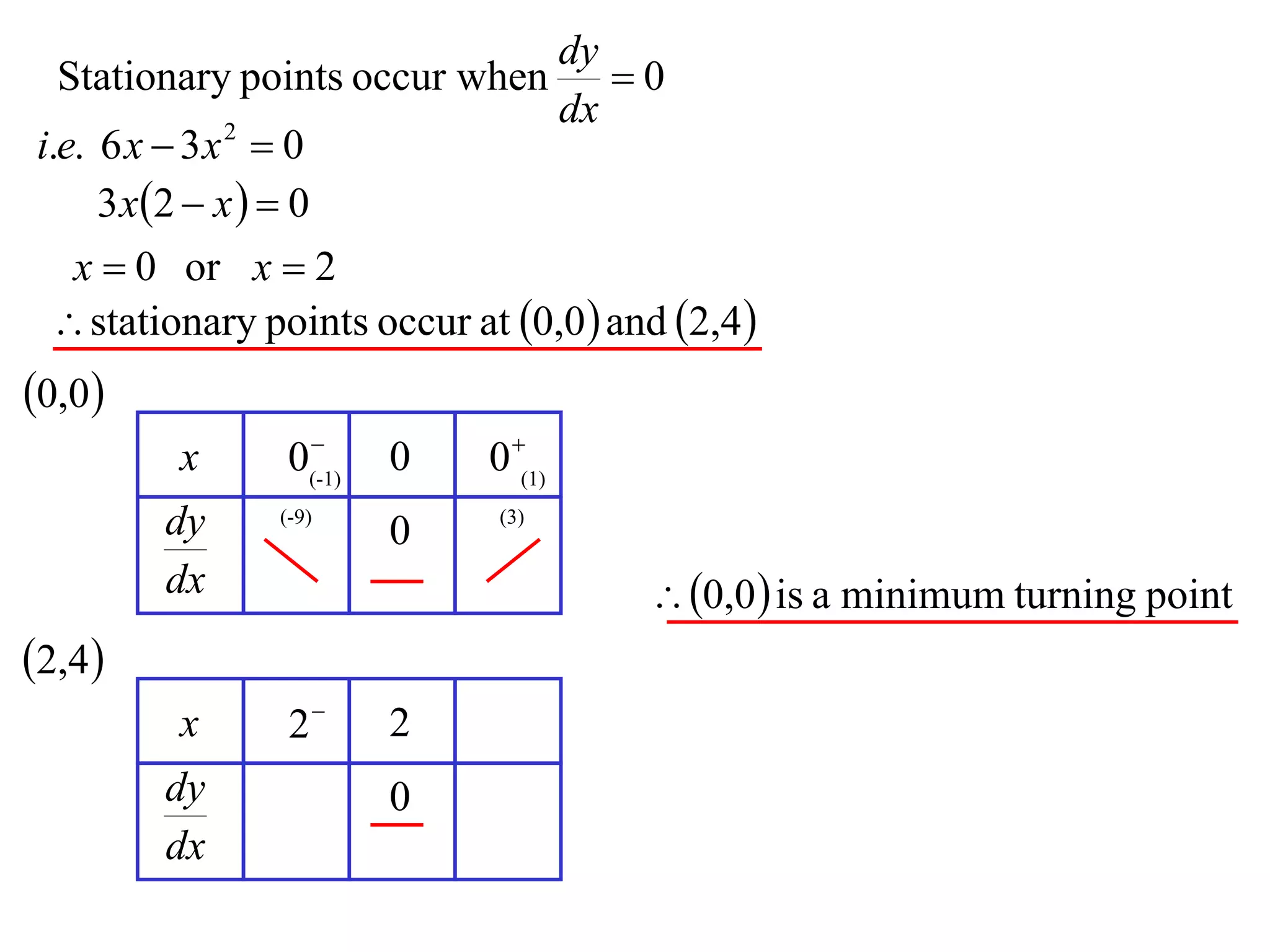
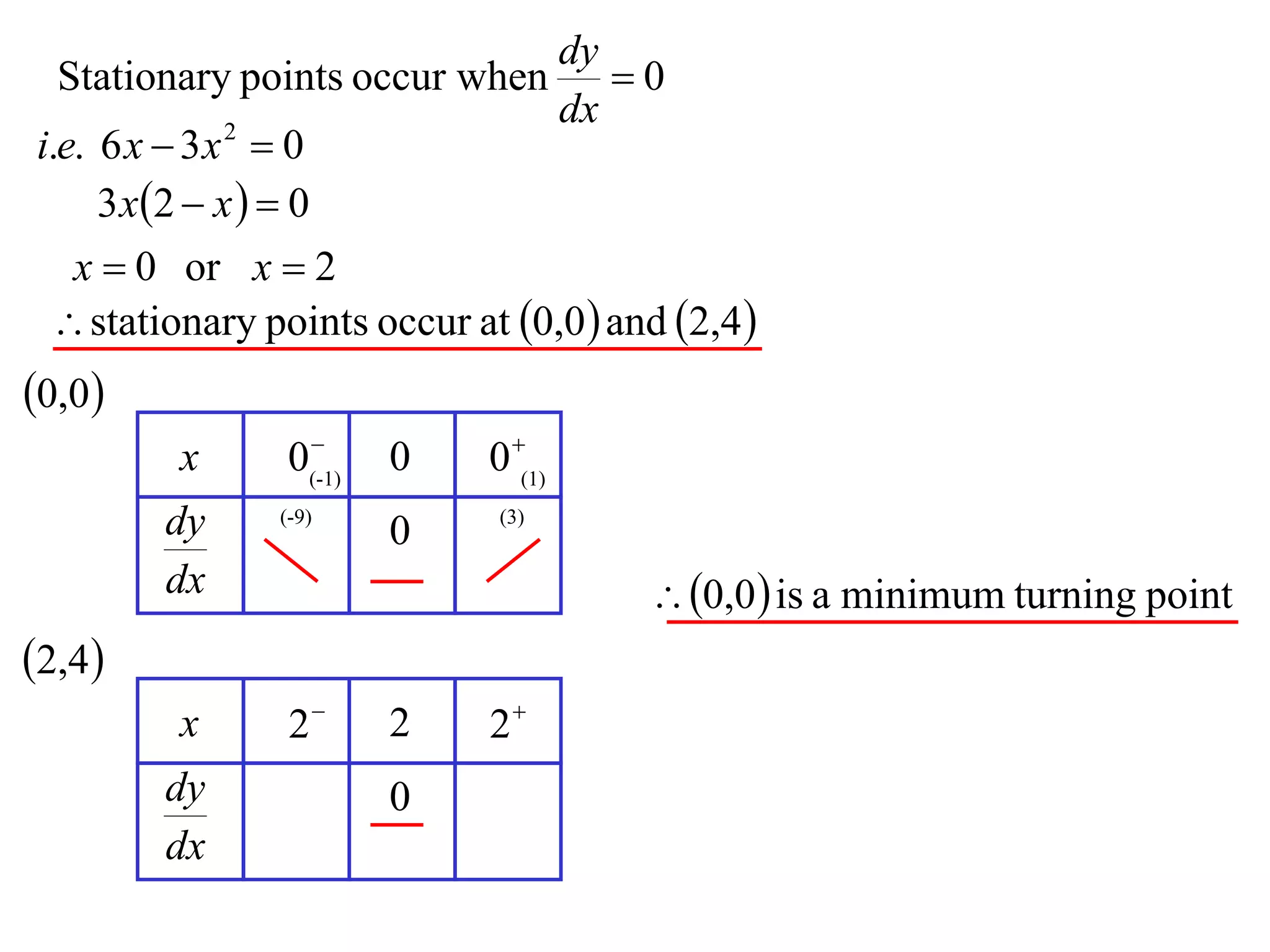
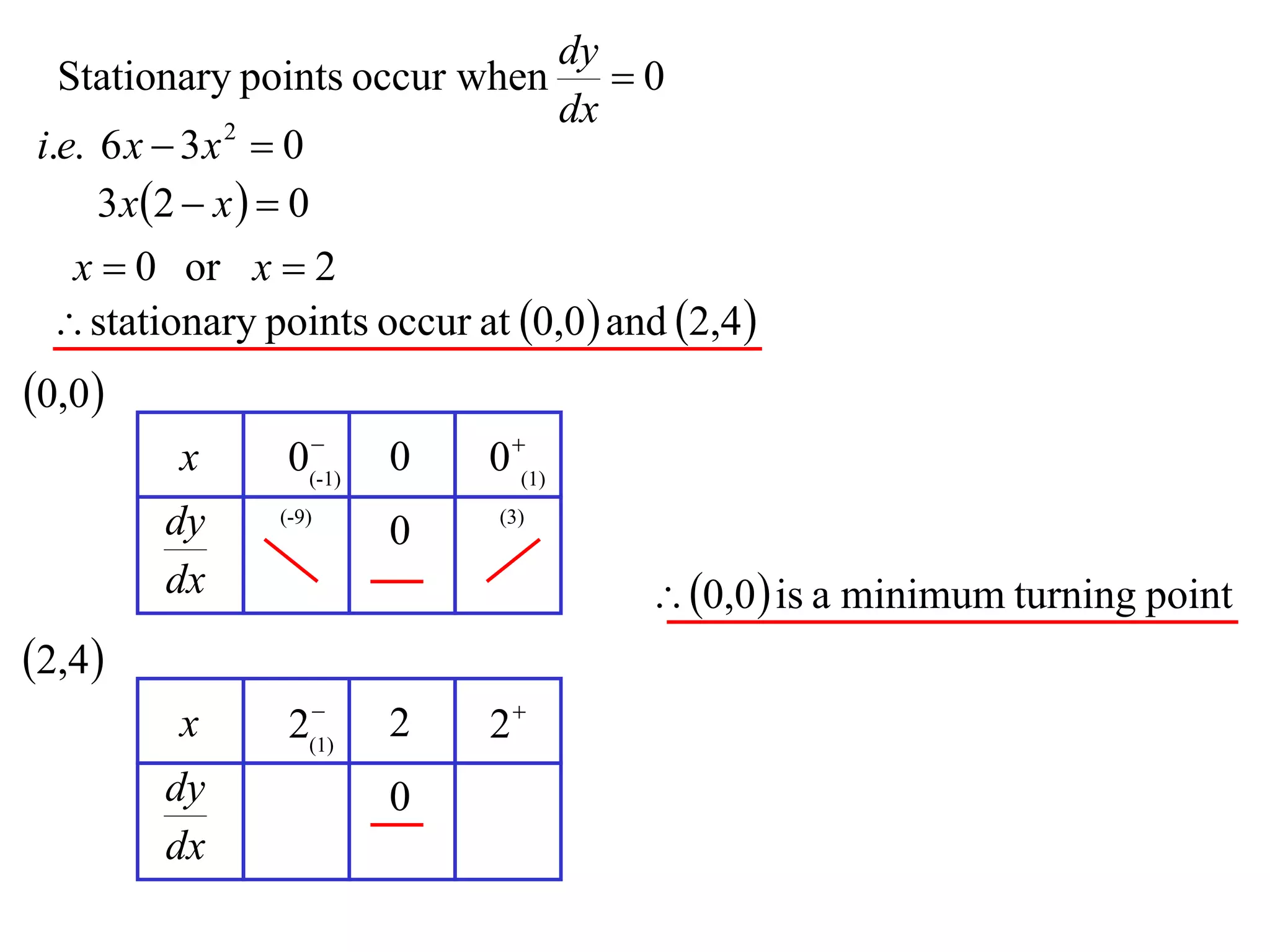
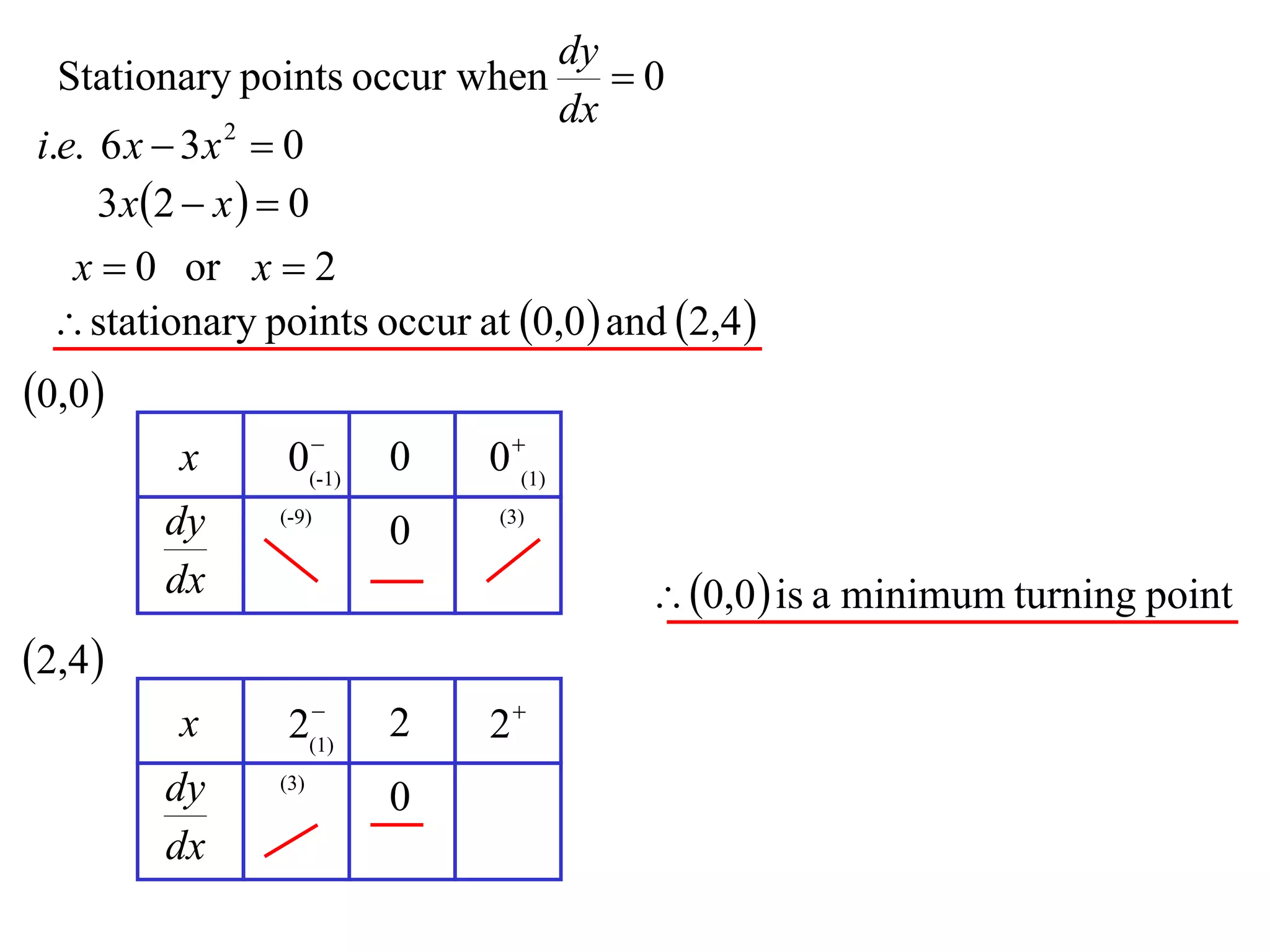
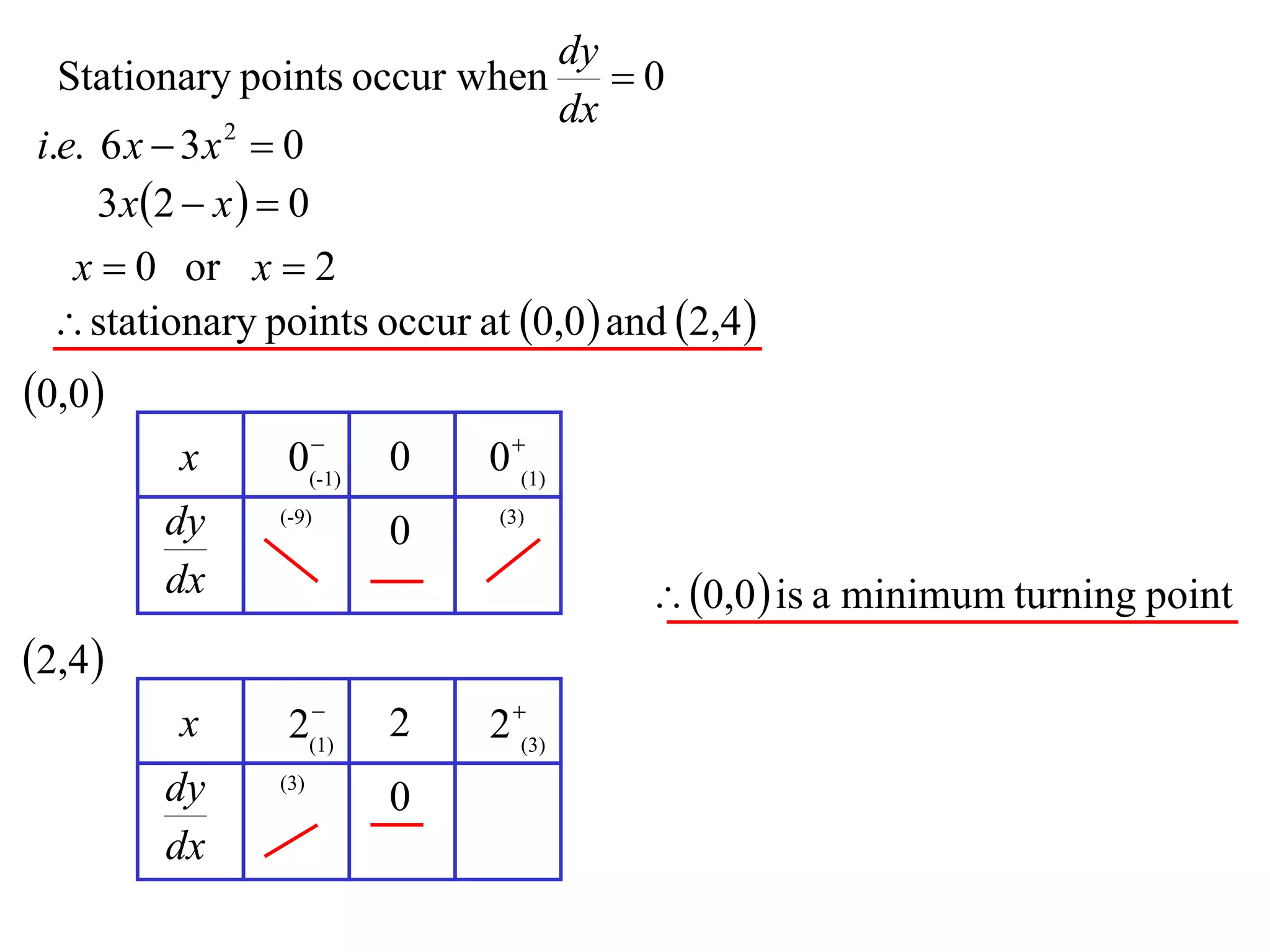
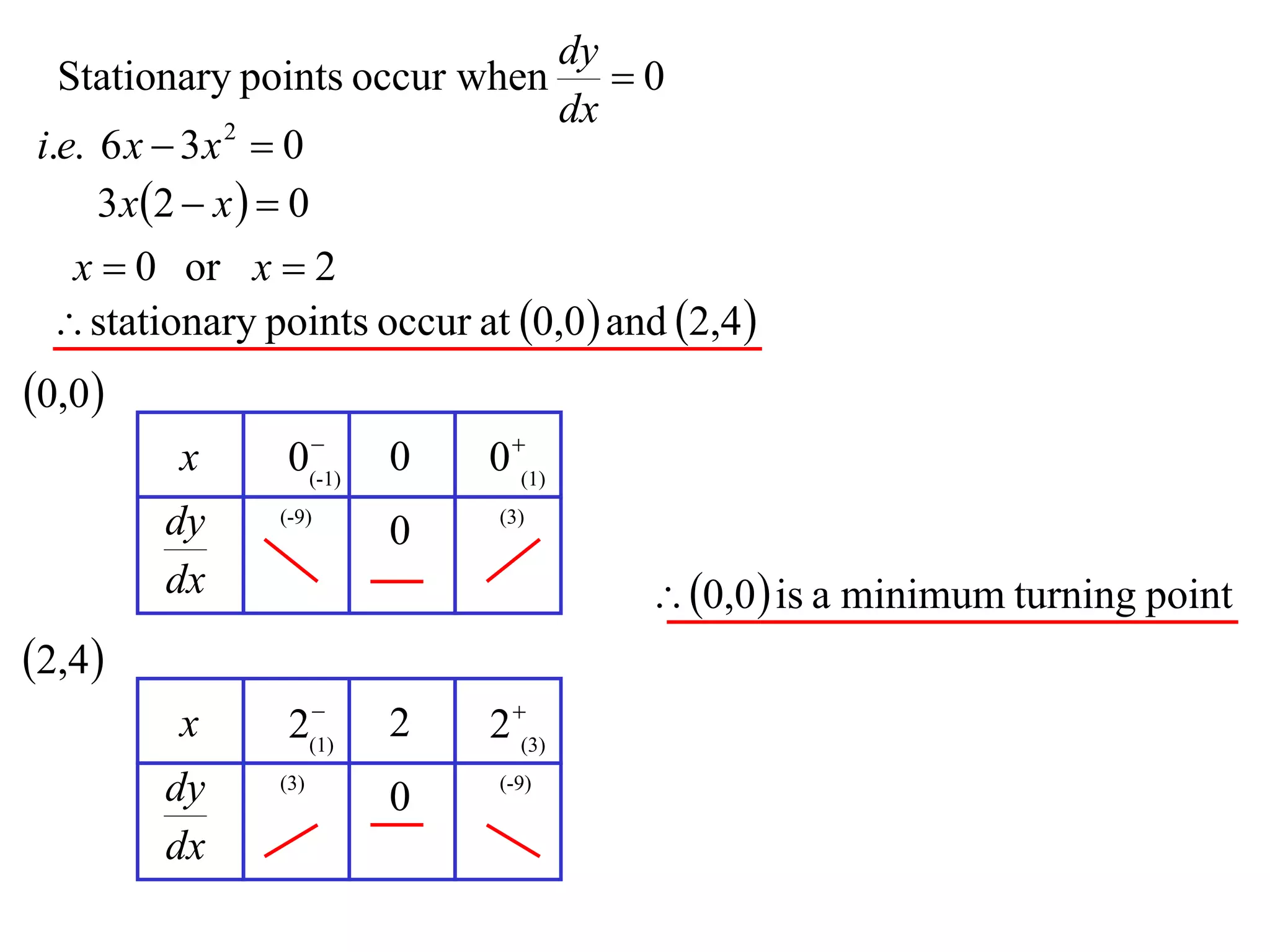
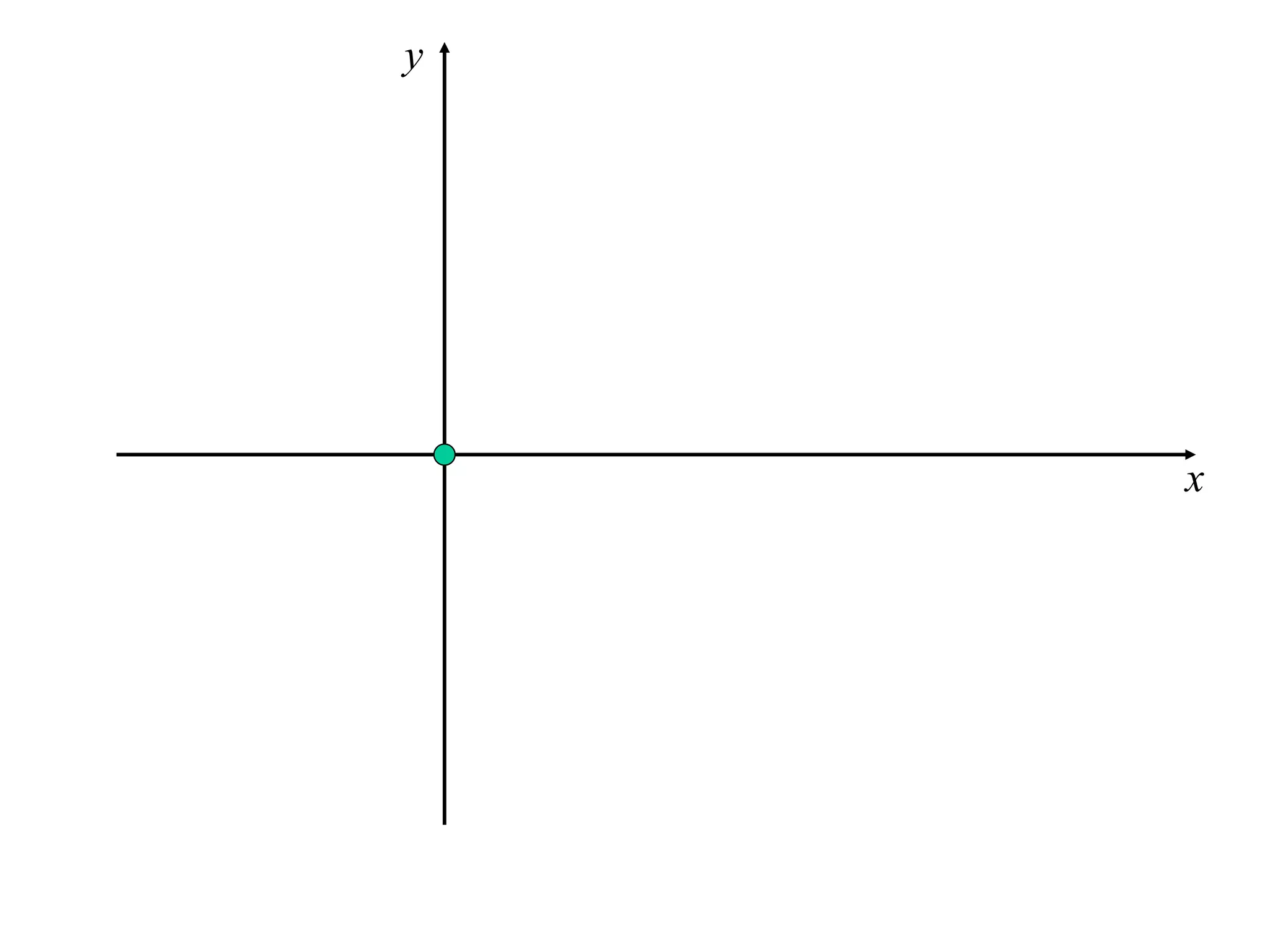
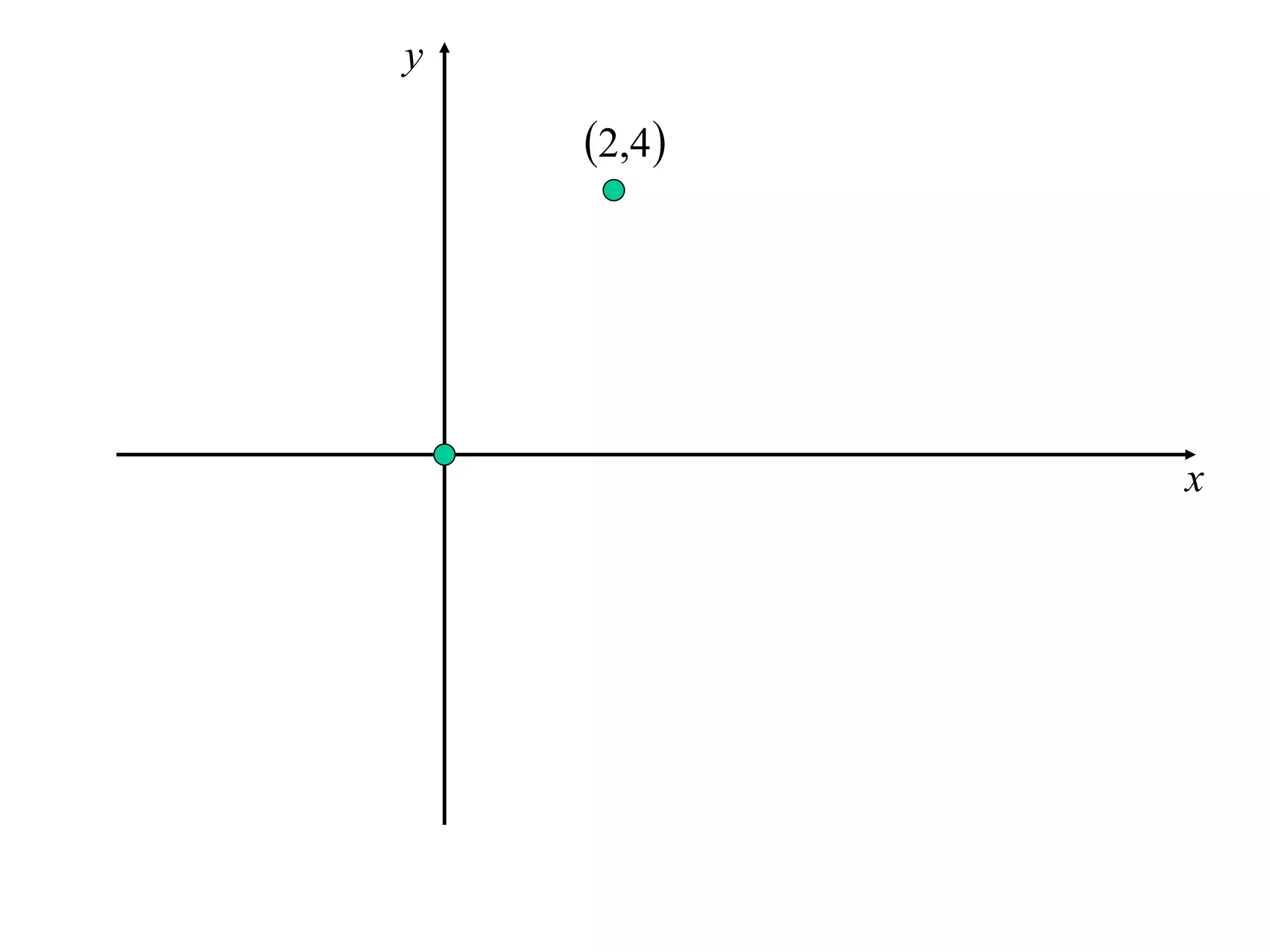
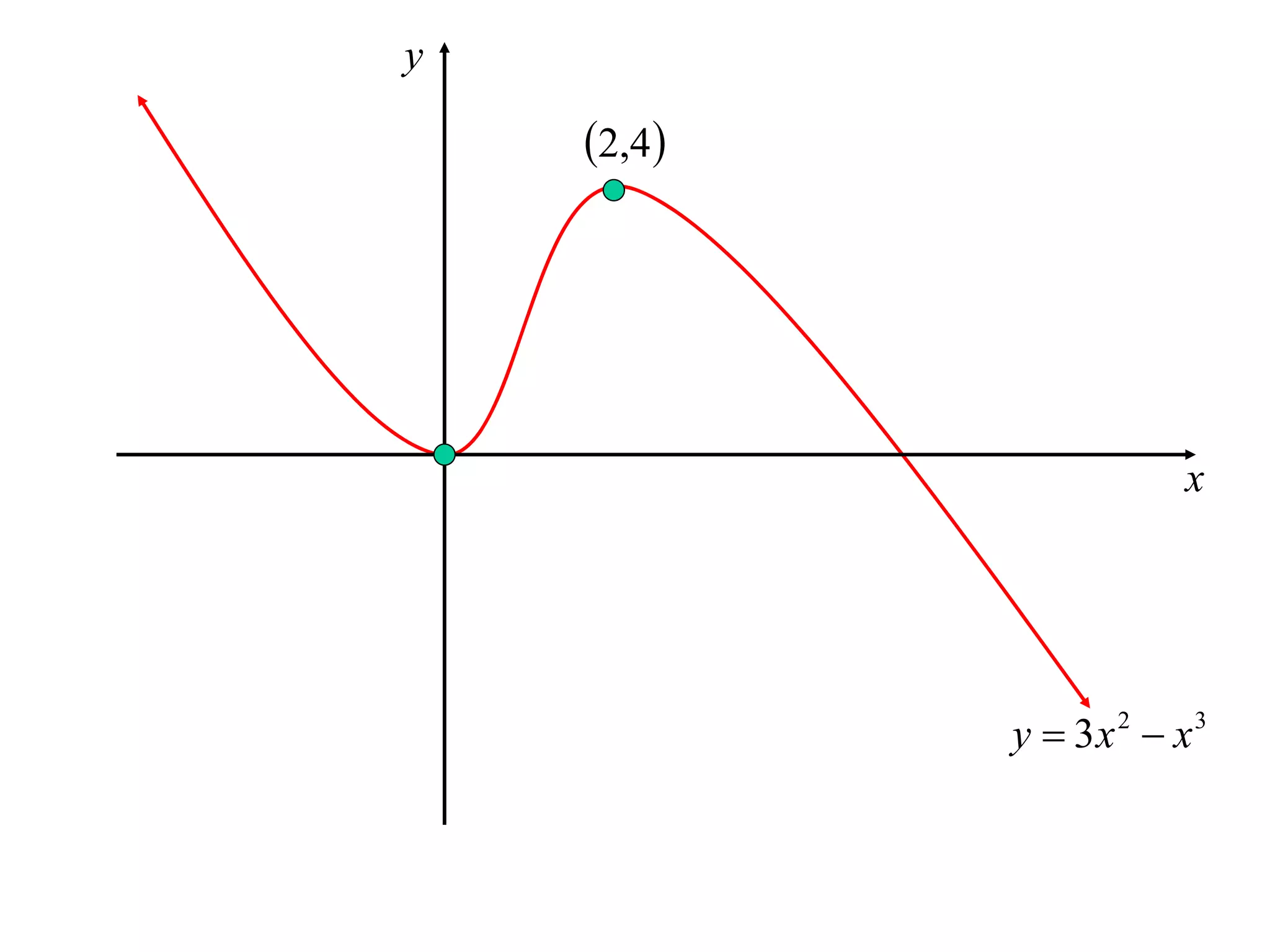
The document discusses the use of derivatives to analyze curves geometrically. It states that the derivative measures the slope of the tangent line to a curve. If the derivative is positive, the curve is increasing; if negative, decreasing; if zero, the curve is stationary. For the example curve y = 3x^2 - x^3, it finds the stationary points at (0,0) and (2,4) by setting the derivative equal to zero. It determines that (0,0) is a minimum turning point and (2,4) is a stationary point.