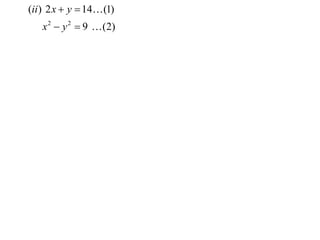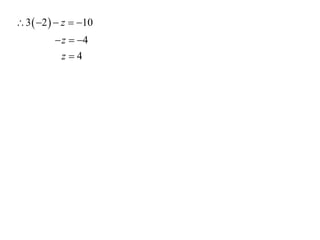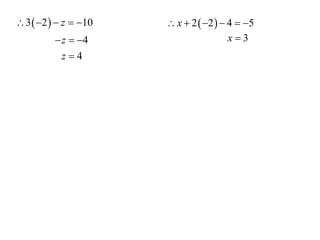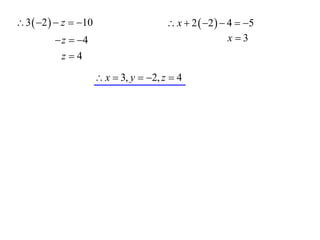The document describes how to solve simultaneous equations using three steps: 1) eliminate a variable from the equations, 2) solve for the remaining variable, and 3) substitute back to find the eliminated variable. It provides an example showing these steps to solve two simultaneous equations for x and y. It then shows another example involving eliminating variables to create two new equations that can be solved simultaneously for y and z. The key points are eliminating variables to reduce the equations, then solving the reduced equations to find the values of the variables.