11. brochongenic ca
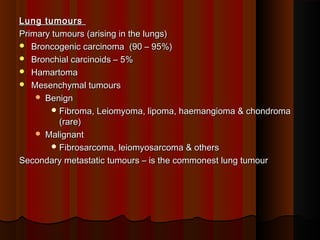
- 1. Lung tumoursLung tumours Primary tumours (arising in the lungs)Primary tumours (arising in the lungs) Broncogenic carcinoma (90 – 95%)Broncogenic carcinoma (90 – 95%) Bronchial carcinoids – 5%Bronchial carcinoids – 5% HamartomaHamartoma Mesenchymal tumoursMesenchymal tumours BenignBenign Fibroma, Leiomyoma, lipoma, haemangioma & chondromaFibroma, Leiomyoma, lipoma, haemangioma & chondroma (rare)(rare) MalignantMalignant Fibrosarcoma, leiomyosarcoma & othersFibrosarcoma, leiomyosarcoma & others Secondary metastatic tumours – is the commonest lung tumourSecondary metastatic tumours – is the commonest lung tumour
- 2. Bronchogenic carcinomaBronchogenic carcinoma Bronchogenic carcinoma is a malignant neoplasm of the lung arisingBronchogenic carcinoma is a malignant neoplasm of the lung arising from the epithelium of the bronchus or bronchiole.from the epithelium of the bronchus or bronchiole. Lung cancer is the most frequent cause of cancer death andLung cancer is the most frequent cause of cancer death and accounts for 14% of all cancer diagnoses and 28% of all canceraccounts for 14% of all cancer diagnoses and 28% of all cancer deaths.deaths.
- 3. Etiology & PathogenesisEtiology & Pathogenesis Risks of developing lung ca areRisks of developing lung ca are 1. Cigarette smoking1. Cigarette smoking • Most important & common etiological factor in theMost important & common etiological factor in the development of lung cancer.development of lung cancer. • Evidences are Statistical, clinical & experimentalEvidences are Statistical, clinical & experimental • Statistical - Smokers have 10 fold greater risk than nonStatistical - Smokers have 10 fold greater risk than non smokers & heavy smokers 20 fold greater risksmokers & heavy smokers 20 fold greater risk • Clinical – histological changes like hyperplasia,Clinical – histological changes like hyperplasia, squamous metaplasia & dysplasia can be seen insquamous metaplasia & dysplasia can be seen in smokerssmokers
- 4. CarcinogensCarcinogens Cigarette smoke contains a number of proven carcinogensCigarette smoke contains a number of proven carcinogens in both the particulate and gaseous phase including:in both the particulate and gaseous phase including: -Aromatic Hydrocarbons-Aromatic Hydrocarbons -Nitrosamines, Nitrosonornicotine-Nitrosamines, Nitrosonornicotine -Polonium-Polonium
- 5. 2. Industrial Exposure2. Industrial Exposure Radiations of all typeRadiations of all type Workers withWorkers with -Asbestos-Asbestos -Coal-Coal -Nickel-Nickel -Chromates-Chromates -Mustard Gas-Mustard Gas -Iron-Iron - Arsenic- Arsenic 3. Air Pollution – carcinogens in pollutant air3. Air Pollution – carcinogens in pollutant air
- 6. 4. Genetic factors4. Genetic factors It is suggested that there is genetic predisposition to lungIt is suggested that there is genetic predisposition to lung cancercancer 5. Scarring5. Scarring Some lung cancer arise in the vicinity of pulmonary scarsSome lung cancer arise in the vicinity of pulmonary scars (Infarct & TB) & are termed scar cancer(Infarct & TB) & are termed scar cancer
- 7. Clinical featuresClinical features Cough, sputum production, weight loss, anorexia, fatigue,Cough, sputum production, weight loss, anorexia, fatigue, dyspnea, hemoptysis, and chest paindyspnea, hemoptysis, and chest pain Obstruction may produce focal emphysema, atelectasis,Obstruction may produce focal emphysema, atelectasis, bronchiectasis, or pneumoniabronchiectasis, or pneumonia
- 8. MorphologyMorphology They arise in the lining epithelium of major bronchi usually close toThey arise in the lining epithelium of major bronchi usually close to hilus of lungshilus of lungs Starts as small mucosal lesion & then mayStarts as small mucosal lesion & then may Form intraluminal massForm intraluminal mass Invade the bronchial mucosaInvade the bronchial mucosa Form large bulky massesForm large bulky masses Bulky tumours may show focal areas of Hg, necrosis, softening &Bulky tumours may show focal areas of Hg, necrosis, softening & cavitaioncavitaion
- 9. A progression of histologic changes in the lung occurs from smokingA progression of histologic changes in the lung occurs from smoking fromfrom (1) proliferation of basal cells,(1) proliferation of basal cells, (2) to development of atypical nuclei with prominent nucleoli,(2) to development of atypical nuclei with prominent nucleoli, (3) to stratification,(3) to stratification, (4) to development of squamous metaplasia and(4) to development of squamous metaplasia and (5) carcinoma in situ, to(5) carcinoma in situ, to (6) invasive carcinoma.(6) invasive carcinoma.
- 10. Classification of Bronchogenic CarcinomaClassification of Bronchogenic Carcinoma According to morphology WHO has classified lung cancer as follow:According to morphology WHO has classified lung cancer as follow: 1.1. Squamous cell carcinoma (25-40%)Squamous cell carcinoma (25-40%) 2.2. Adenocarcinoma (25-40%)Adenocarcinoma (25-40%) a.a. bronchial derivedbronchial derived b.b. bronchioloalveolar carcinomabronchioloalveolar carcinoma 3.3. Small cell carcinoma (20-25%)Small cell carcinoma (20-25%) 4.4. Large cell carcinoma (10-15%)Large cell carcinoma (10-15%)
- 11. Squamous cell CarcinomaSquamous cell Carcinoma It is commonly found in menIt is commonly found in men Closely related with smoking.Closely related with smoking. Approximately 2/3Approximately 2/3rdrd of these tumors are centrally located and tend toof these tumors are centrally located and tend to expand against the bronchus, causing extrinsic compression.expand against the bronchus, causing extrinsic compression. These tumors are prone to undergo central necrosis and cavitation.These tumors are prone to undergo central necrosis and cavitation. SCCA tends to metastasize later than does ACA.SCCA tends to metastasize later than does ACA. SCCA may be more readily detected on sputum cytology than ACA.SCCA may be more readily detected on sputum cytology than ACA.
- 12. MicroscopicallyMicroscopically Well differebtiated to anaplasticWell differebtiated to anaplastic keratinization i.e. production of keratin pearls, stratification, andkeratinization i.e. production of keratin pearls, stratification, and intercellular bridge formation are exhibited.intercellular bridge formation are exhibited.
- 13. This isThis is anotheranother sqamoussqamous cellcell carcinomacarcinoma that extendsthat extends from hilumfrom hilum to pleura.to pleura. The blackThe black areasareas representrepresent anthracoticanthracotic pigmentpigment trapped intrapped in the tumor.the tumor.
- 14. This is a squamous cellThis is a squamous cell carcinoma of the lungcarcinoma of the lung that is arising centrallythat is arising centrally in the lung (as mostin the lung (as most squamous cellsquamous cell carcinomas do). It iscarcinomas do). It is obstructing the rightobstructing the right main bronchus. Themain bronchus. The neoplasm is very firmneoplasm is very firm and has a pale white toand has a pale white to tan cut surface.tan cut surface.
- 15. This is a largerThis is a larger squamous cellsquamous cell carcinoma in which acarcinoma in which a portion of the tumorportion of the tumor demonstrates centraldemonstrates central cavitation, probablycavitation, probably because the tumorbecause the tumor outgrew its bloodoutgrew its blood supply.supply.
- 16. This is the microscopic appearance of squamous cellThis is the microscopic appearance of squamous cell carcinoma with nests of polygonal cells with pink cytoplasmcarcinoma with nests of polygonal cells with pink cytoplasm and distinct cell borders. The nuclei are hyperchromatic .and distinct cell borders. The nuclei are hyperchromatic .
- 17. In this squamous cell carcinoma at the upper left is a keratin pearl. AtIn this squamous cell carcinoma at the upper left is a keratin pearl. At the right, the tumor is less differentiatedthe right, the tumor is less differentiated
- 18. Adenocarcinoma (ACA)Adenocarcinoma (ACA) It is derived from the mucus-producing cells of the bronchial epitheliumIt is derived from the mucus-producing cells of the bronchial epithelium in the terminal bronchioles or alveolar walls .in the terminal bronchioles or alveolar walls . It is the most common type of lung cancer in women and in non-It is the most common type of lung cancer in women and in non- smokers.smokers. Male female ratio is equalMale female ratio is equal Most of ACA tumors (75%) are peripherally located.Most of ACA tumors (75%) are peripherally located. It tends to metastasize earlier than squamous cell carcinoma (SCCA)It tends to metastasize earlier than squamous cell carcinoma (SCCA)
- 19. Microscopic featuresMicroscopic features Gland formation with mucin productionGland formation with mucin production Consist of cuboidal to columnar cells with adequate to abundant pinkConsist of cuboidal to columnar cells with adequate to abundant pink or vacuolated cytoplasmor vacuolated cytoplasm
- 20. Slide 16.48
- 21. moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma - peripheral lung cancers that have not metastasized can be easily resected
- 22. Microscopically, the bronchioloalveolar carcinoma is composed of columnar cellsMicroscopically, the bronchioloalveolar carcinoma is composed of columnar cells that proliferate along the framework of alveolar septae. The cells are well-that proliferate along the framework of alveolar septae. The cells are well- differentiated. These neoplasms in general have a better prognosis than mostdifferentiated. These neoplasms in general have a better prognosis than most other primary lung cancersother primary lung cancers
- 23. This is a peripheralThis is a peripheral adenocarcinoma of the lung.adenocarcinoma of the lung. Adenocarcinomas and large cellAdenocarcinomas and large cell anaplastic carcinomas tend toanaplastic carcinomas tend to occur more peripherally in lung.occur more peripherally in lung. Adenocarcinoma is the one cellAdenocarcinoma is the one cell type of primary lung tumor thattype of primary lung tumor that occurs more often in non-occurs more often in non- smokers and in smokers whosmokers and in smokers who have quit.have quit. If this neoplasm were confined toIf this neoplasm were confined to the lung (a lower stage), thenthe lung (a lower stage), then resection would have a greaterresection would have a greater chance for cure.chance for cure. The solitary appearance of thisThe solitary appearance of this neoplasm suggests that the tumorneoplasm suggests that the tumor is primary rather than metastatic.is primary rather than metastatic.
- 24. Small cell lung cancerSmall cell lung cancer About 80% are centrally located.About 80% are centrally located. The disease is characterized by a very aggressive tendency toThe disease is characterized by a very aggressive tendency to metastasize.metastasize. It is highly malignant .It is highly malignant . It is strongly associated with smoking (99%).It is strongly associated with smoking (99%). It spreads very early to mediastinal lymph nodes and distantIt spreads very early to mediastinal lymph nodes and distant sites, especially bone marrow and brain.sites, especially bone marrow and brain. Usually produce paraneoplstic syndromeUsually produce paraneoplstic syndrome
- 25. Arising centrally in this lung andArising centrally in this lung and spreading extensively is a smallspreading extensively is a small cell anaplastic (oat cell)cell anaplastic (oat cell) carcinoma.carcinoma. The cut surface of this tumor hasThe cut surface of this tumor has a soft, lobulated, white to tana soft, lobulated, white to tan appearance.appearance. The tumor seen here has causedThe tumor seen here has caused obstruction of the main bronchusobstruction of the main bronchus to left lung so that the distal lungto left lung so that the distal lung is collapsed.is collapsed. Oat cell carcinomas are veryOat cell carcinomas are very aggressive and oftenaggressive and often metastasize widely before themetastasize widely before the primary tumor mass in the lungprimary tumor mass in the lung reaches a large size.reaches a large size.
- 26. MicroscopicallyMicroscopically Sheets or clusters of cells with dark nuclei and very little round orSheets or clusters of cells with dark nuclei and very little round or oval cytoplasm.oval cytoplasm. This "oatlike" appearance under the microscope provides the termThis "oatlike" appearance under the microscope provides the term oat cell carcinoma to this disease.oat cell carcinoma to this disease. Few cells are spindle or polygonal shape too.Few cells are spindle or polygonal shape too.
- 27. Large cell carcinomaLarge cell carcinoma It is undifferentiated (anaplastic) carcinomaIt is undifferentiated (anaplastic) carcinoma These tumors tend to occur peripherally and may metastasizeThese tumors tend to occur peripherally and may metastasize relatively early.relatively early. MicroscopicallyMicroscopically ,, Anaplastic, pleomorphic cells with vesicular or hyperchromaticAnaplastic, pleomorphic cells with vesicular or hyperchromatic nuclei and abundant cytoplasm.nuclei and abundant cytoplasm. There are a large number of multinucleated giant cells.There are a large number of multinucleated giant cells.
- 28. Paraneoplastic syndromes in bronchogenic Ca.Paraneoplastic syndromes in bronchogenic Ca. ACTH- Cushings syndromeACTH- Cushings syndrome Serotonin – Carcinoid syndromeSerotonin – Carcinoid syndrome Gonadotropins – GynaecomastiaGonadotropins – Gynaecomastia ADH – HyponatraemiaADH – Hyponatraemia Parathormone – HypercalcaemiaParathormone – Hypercalcaemia Calcitonin – hypocalcaemiaCalcitonin – hypocalcaemia
- 29. SpreadSpread Invasion or local spreadInvasion or local spread May infiltrate the peribronchial tissue, mediastinum, pleural cavity orMay infiltrate the peribronchial tissue, mediastinum, pleural cavity or into peritoneuminto peritoneum MetastasisMetastasis Lymphatic spread – trachea, bronchial & mediastinal nodesLymphatic spread – trachea, bronchial & mediastinal nodes Blood spread – Liver, brain, bones & adrenal are common. No organBlood spread – Liver, brain, bones & adrenal are common. No organ or tissue is sapredor tissue is sapred
- 30. Secondary Pathology associated with lung cancerSecondary Pathology associated with lung cancer Bronchial ObstructionBronchial Obstruction Partial obstruction- EmphysemaPartial obstruction- Emphysema Total obstruction- AtelectasisTotal obstruction- Atelectasis Severe suppurative or ulcerative bronchitis or bronchiectasisSevere suppurative or ulcerative bronchitis or bronchiectasis Pulmonary abscessPulmonary abscess Superior venacava syndromeSuperior venacava syndrome Pericarditis and pleuritisPericarditis and pleuritis Systemic- Paraneoplastic syndromeSystemic- Paraneoplastic syndrome
- 31. Secondary metastatic tumours of lungsSecondary metastatic tumours of lungs Both carcinomas & sarcomas of any site in the body frequentlyBoth carcinomas & sarcomas of any site in the body frequently spread to the lungsspread to the lungs Via lymphatics or blood or direct continuity (oesophageal,Via lymphatics or blood or direct continuity (oesophageal, mediastinal)mediastinal) Usually multiple discrete nodules are scattered throughout the lungsUsually multiple discrete nodules are scattered throughout the lungs
- 32. Commonly suggested investigations for diagnosis of theCommonly suggested investigations for diagnosis of the diseasedisease - Sputum for cytologySputum for cytology - Chest X-rayChest X-ray - FNAC/biopsy of tumor mass or secondary lymph nodesFNAC/biopsy of tumor mass or secondary lymph nodes - BronchoscopyBronchoscopy - CT scan/MRICT scan/MRI
- 37. Classify the lung tumoursClassify the lung tumours Give the etiopathogenesis of Bronchogenic carcinomaGive the etiopathogenesis of Bronchogenic carcinoma Classify bronchogenic carcinomaClassify bronchogenic carcinoma Give the morphology of bronchogenic squamous cellGive the morphology of bronchogenic squamous cell carcinomacarcinoma
