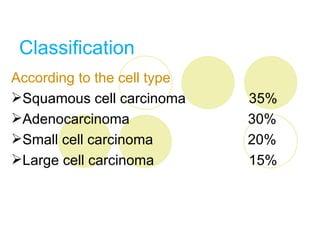
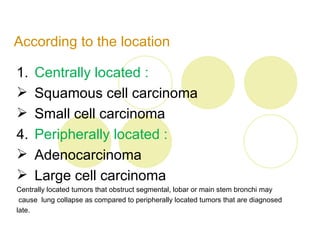
Lung cancer, characterized by uncontrolled growth of malignant cells in the lungs, is primarily caused by factors such as smoking and environmental exposure. It has various types, with clinical symptoms including persistent cough, hemoptysis, and dyspnea; treatment options vary based on stage and include surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy. The prognosis is generally poor, particularly with advanced stages, underscoring the importance of smoking cessation and ongoing research for better screening and treatment methods.







![Small cell lung cancer
Small cell lung cancer also called oat cell
because SCLC cells have oat grain
appearance.
It arises from endocrine cells [kulchitisky
cells] where many hormones are secreted.
Spreads to lymph nodes and other organs
more quickly than NSCLC.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lungcancer-ppt-120504085445-phpapp02/85/Lung-cancer-14-320.jpg)