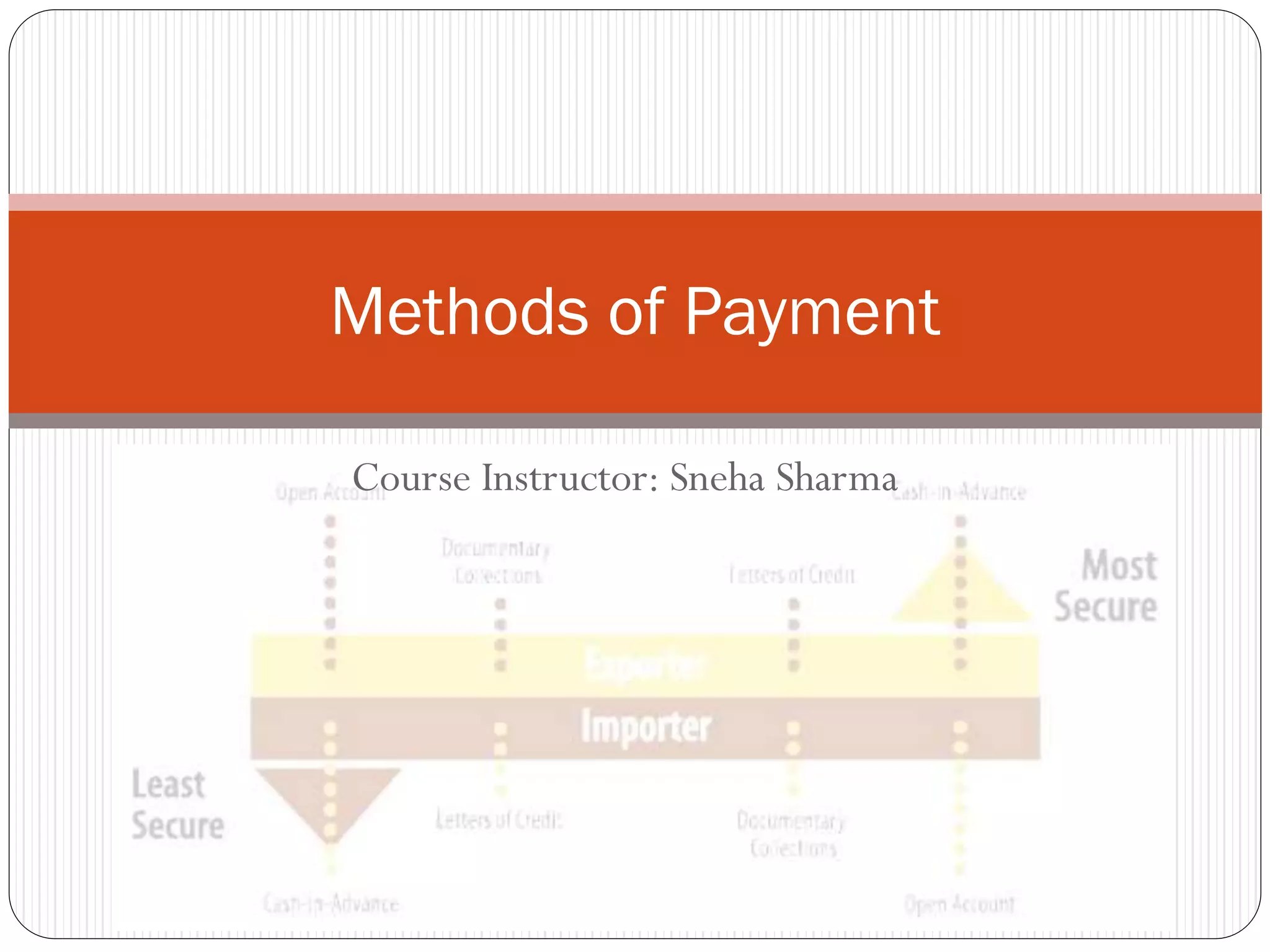
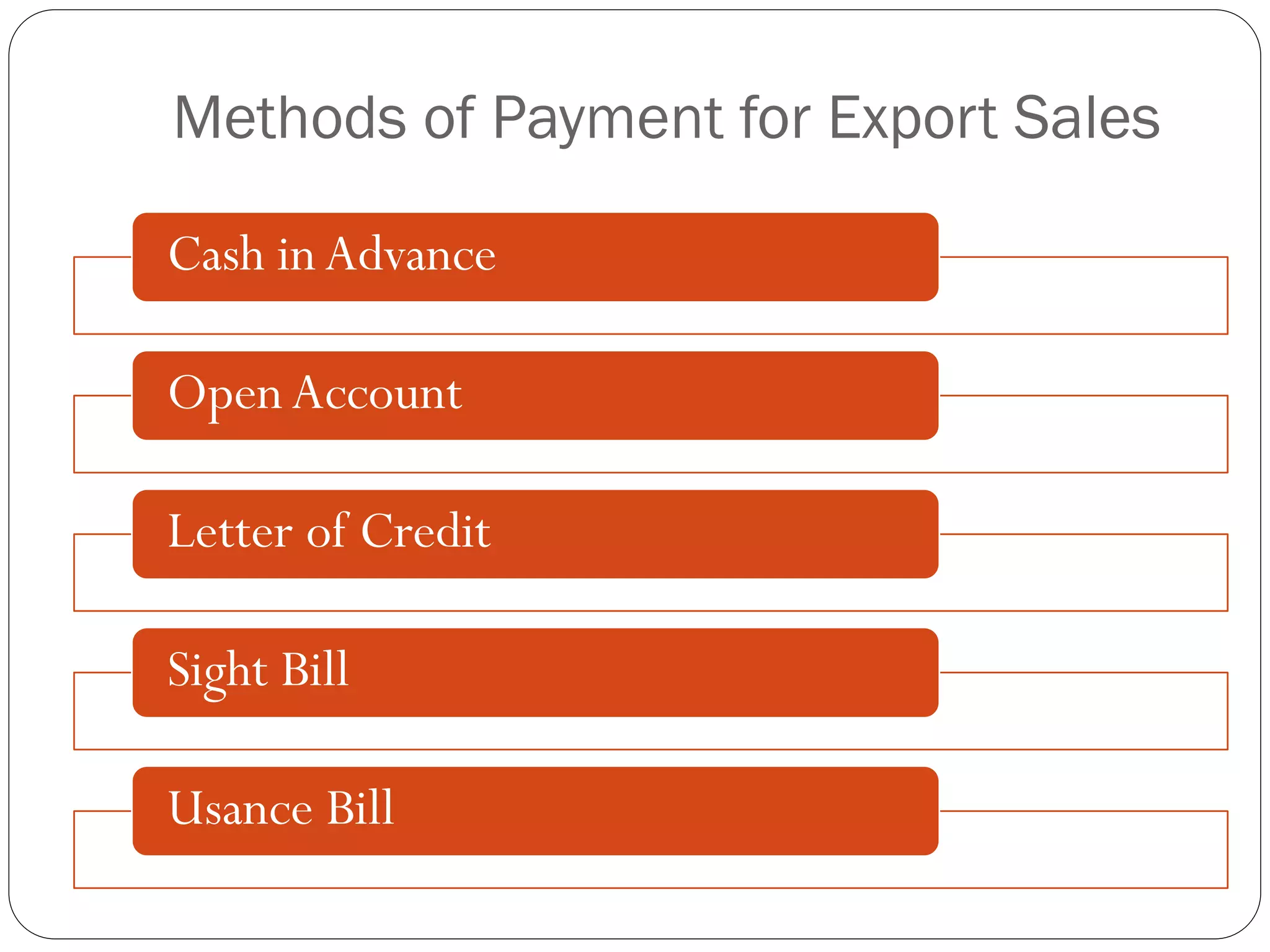
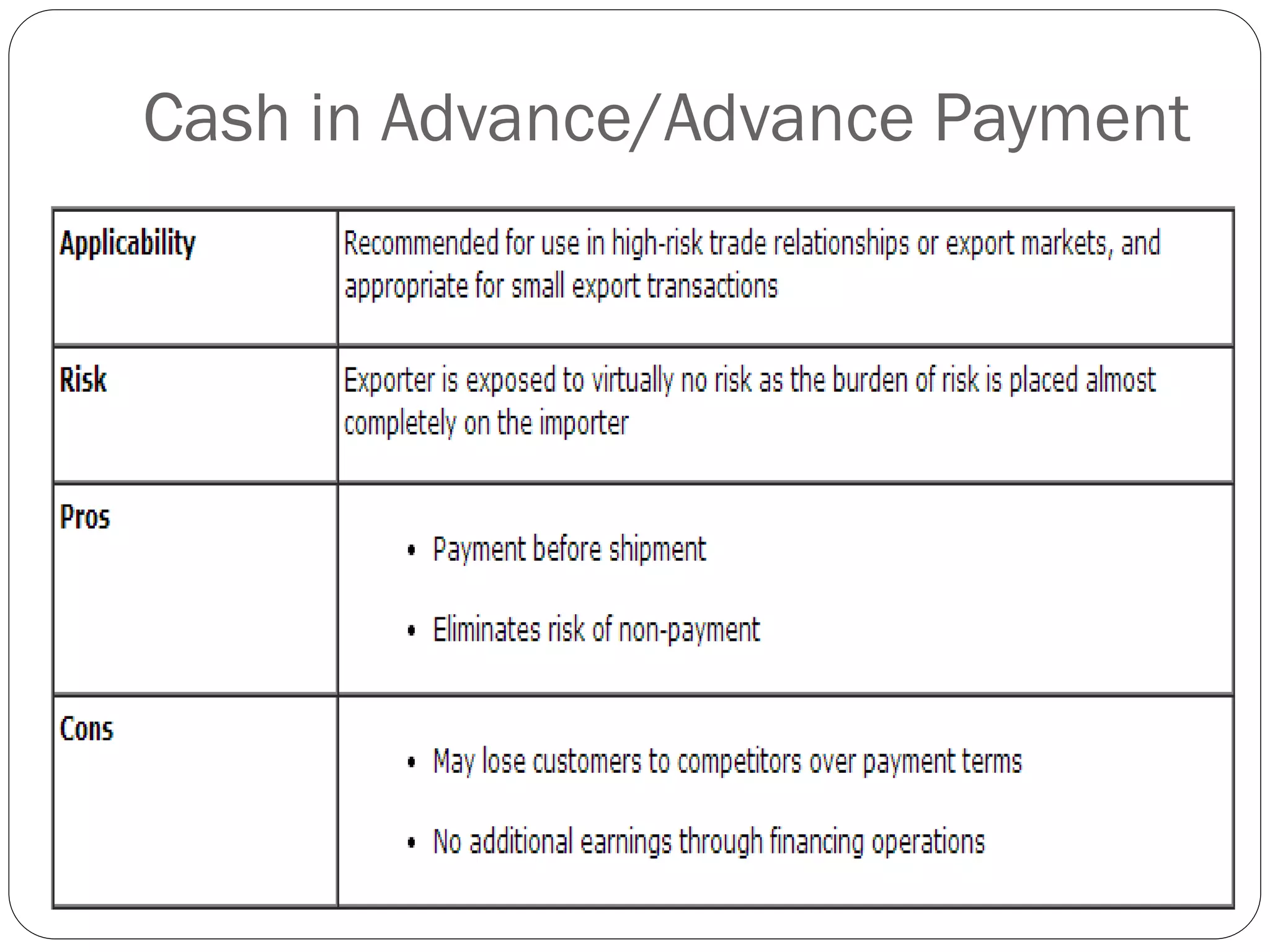
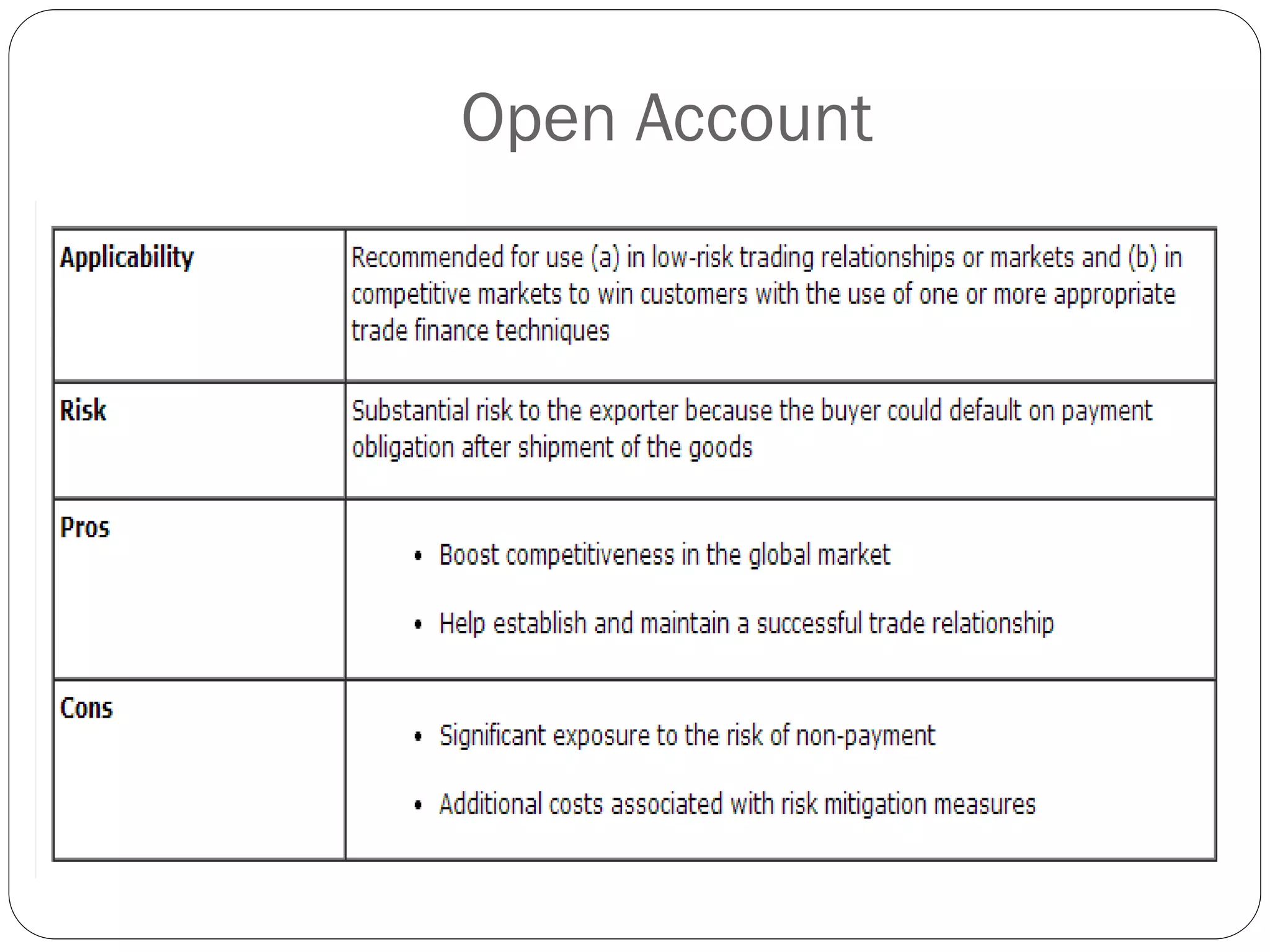
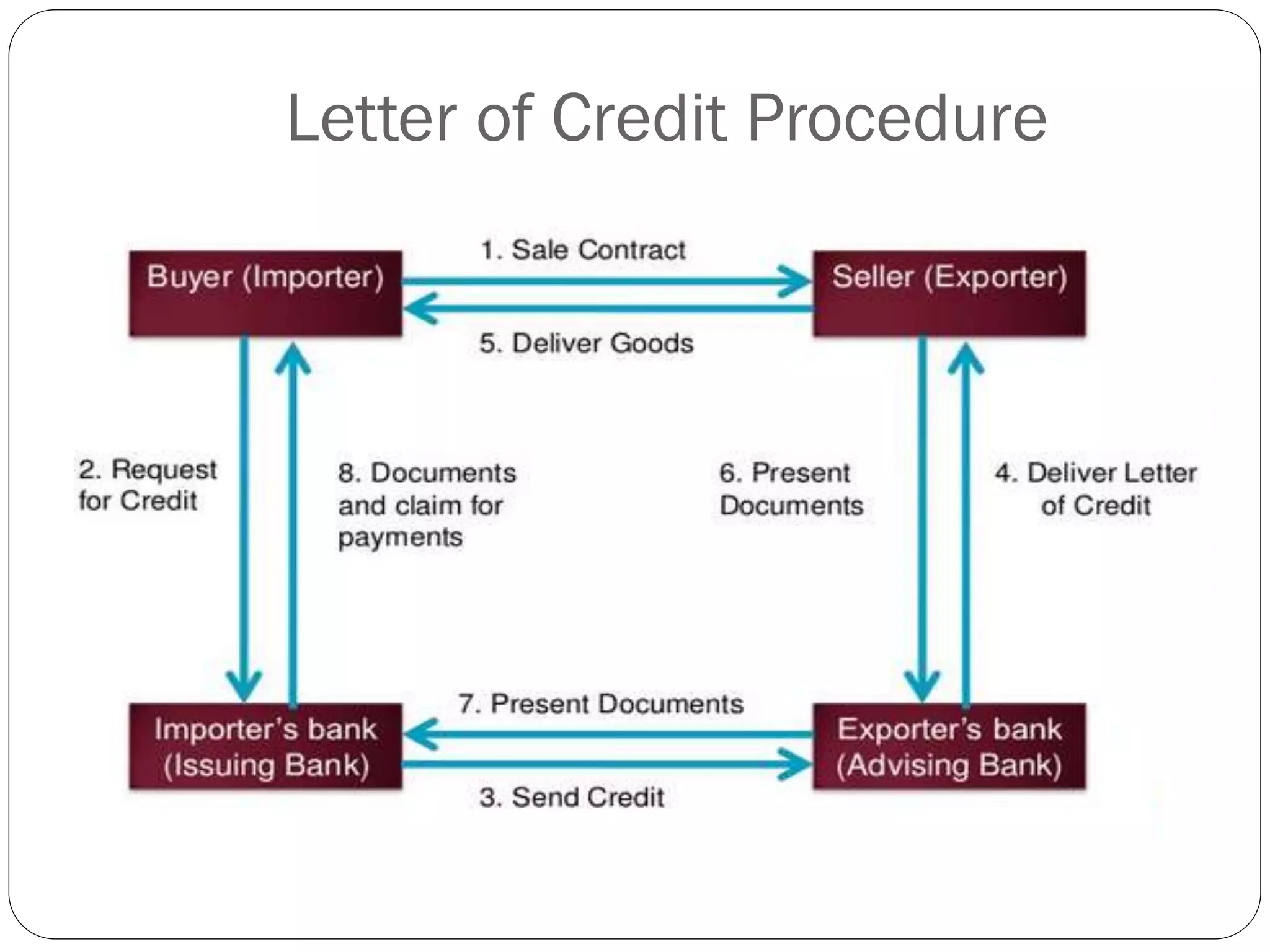
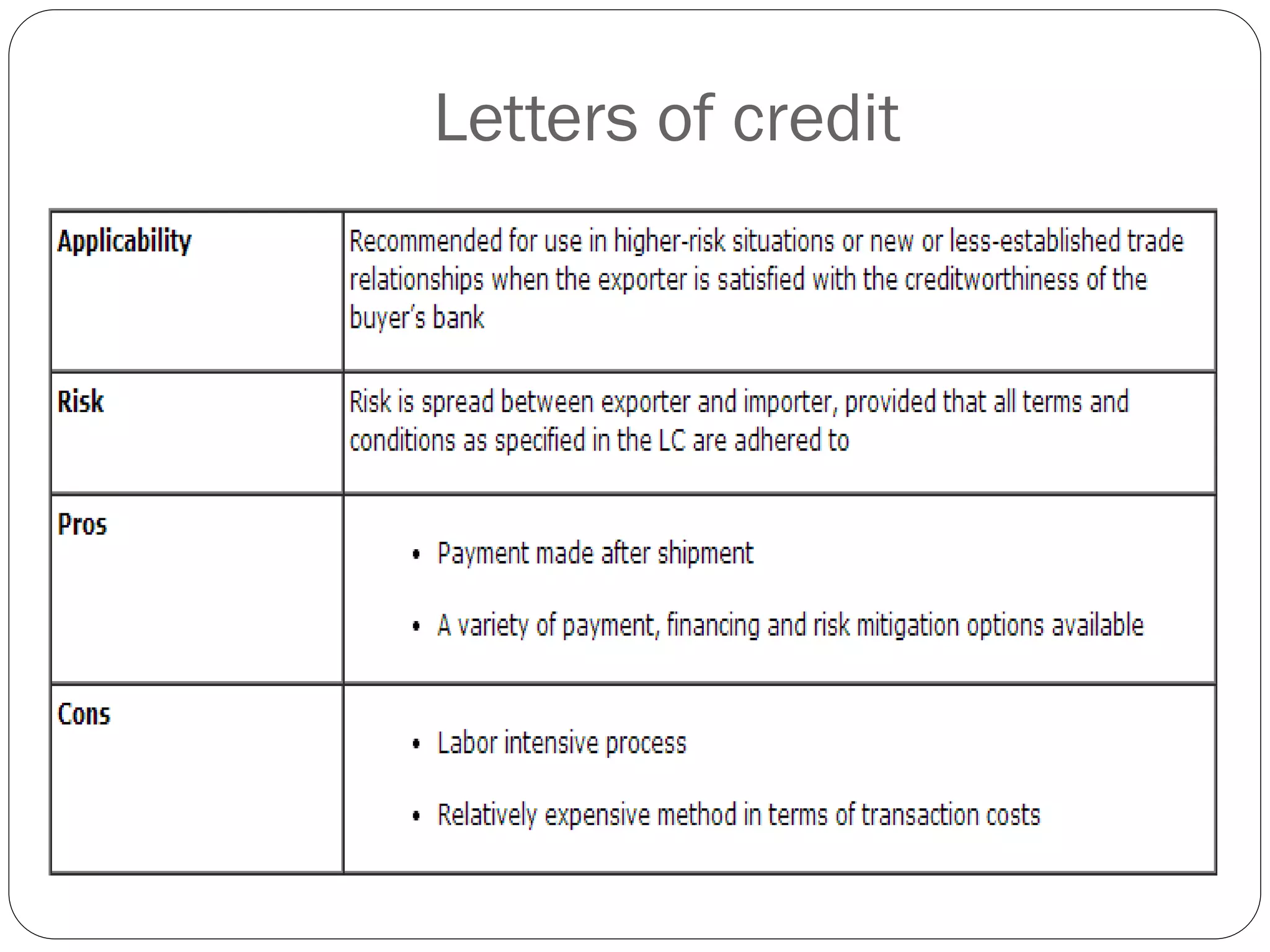
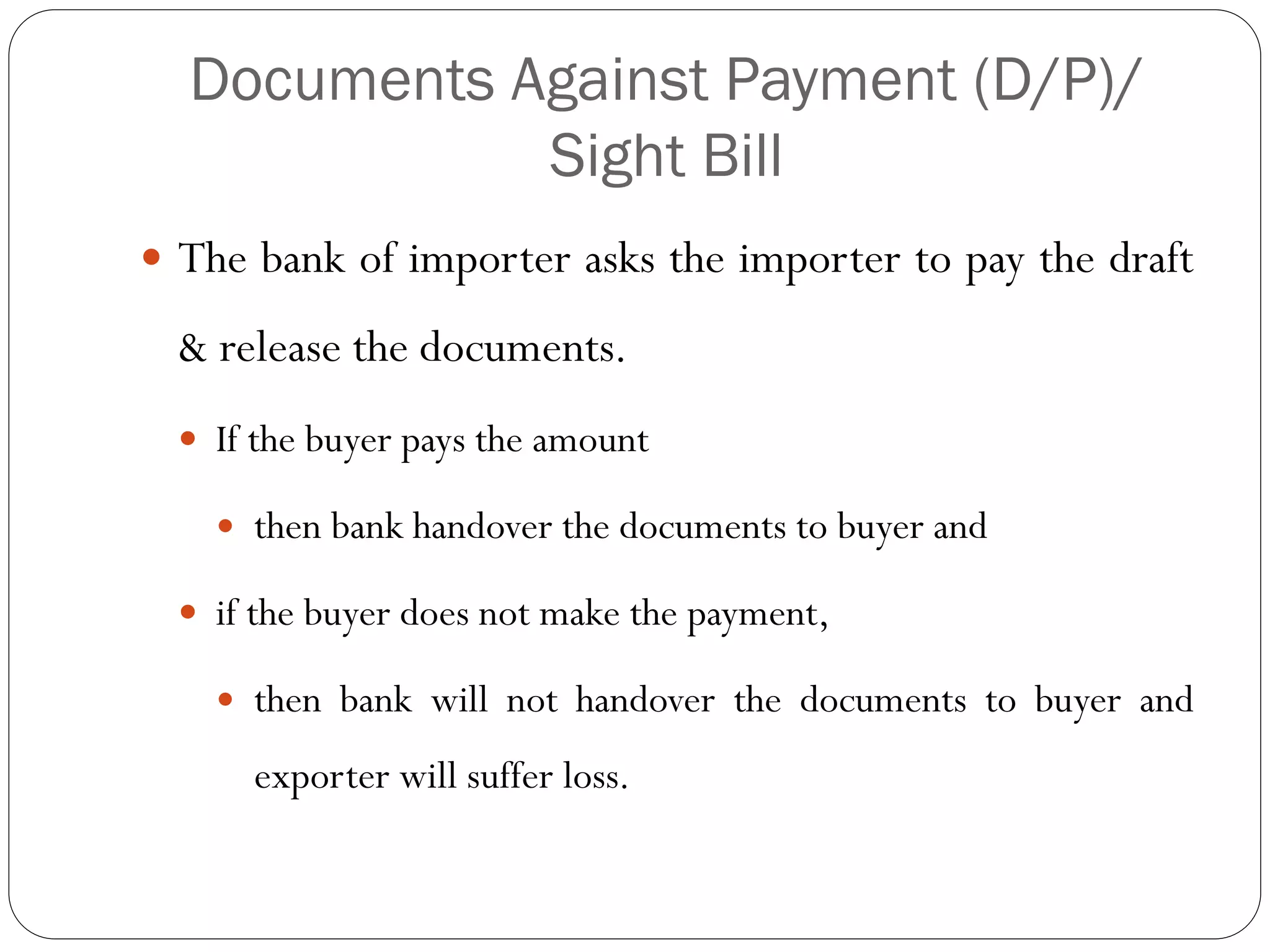
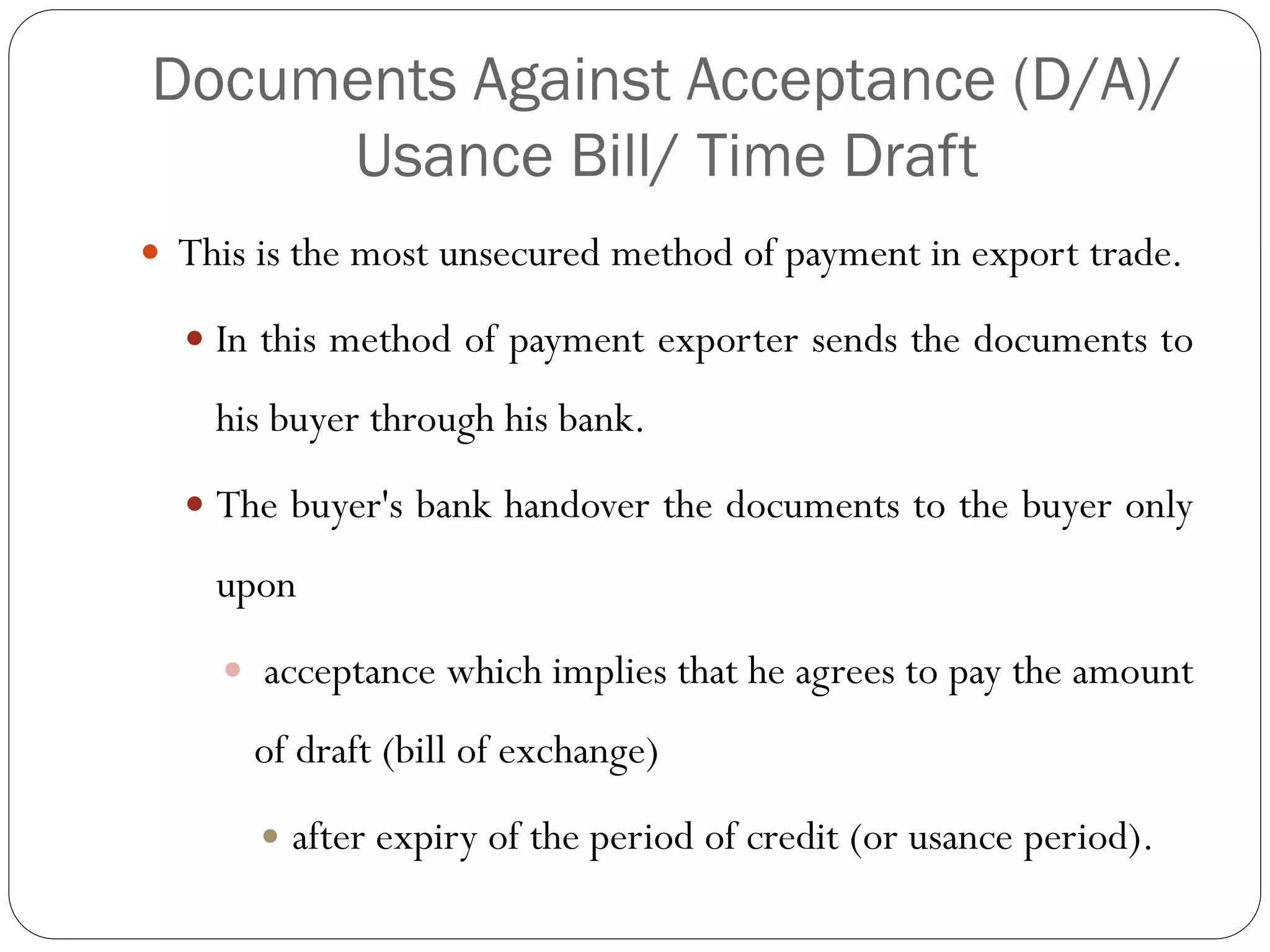
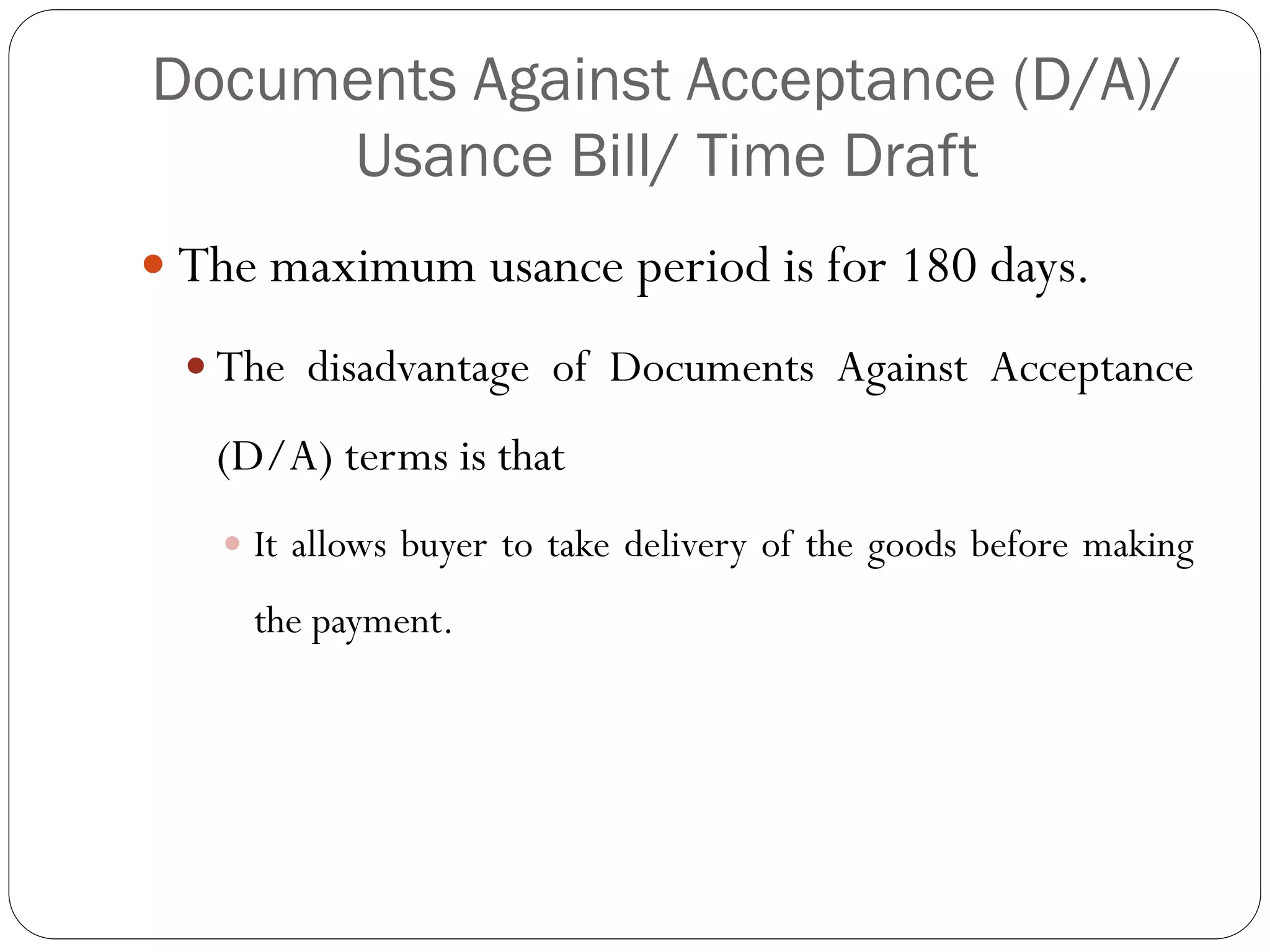
This document discusses various methods of payment for export sales, including cash in advance, open account, letters of credit, sight bills, and usance bills. Cash in advance requires upfront payment before goods are shipped. Open account allows goods to be shipped before payment is due, usually within 30-90 days, but carries the highest risk for exporters. Letters of credit provide a bank guarantee of payment if terms are met. Sight bills require payment on delivery of documents, while usance bills allow acceptance of payment within an agreed credit period after delivery.