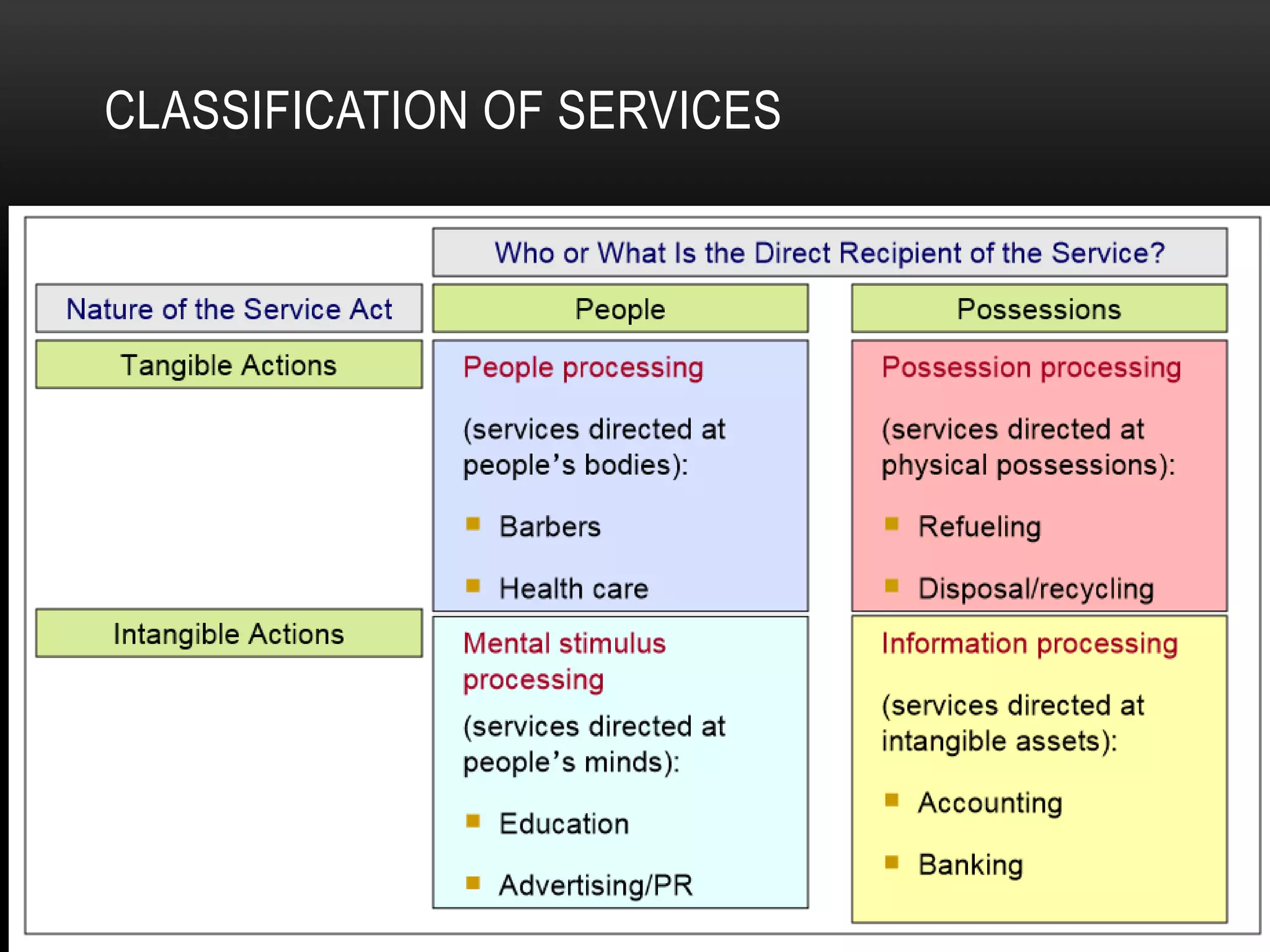
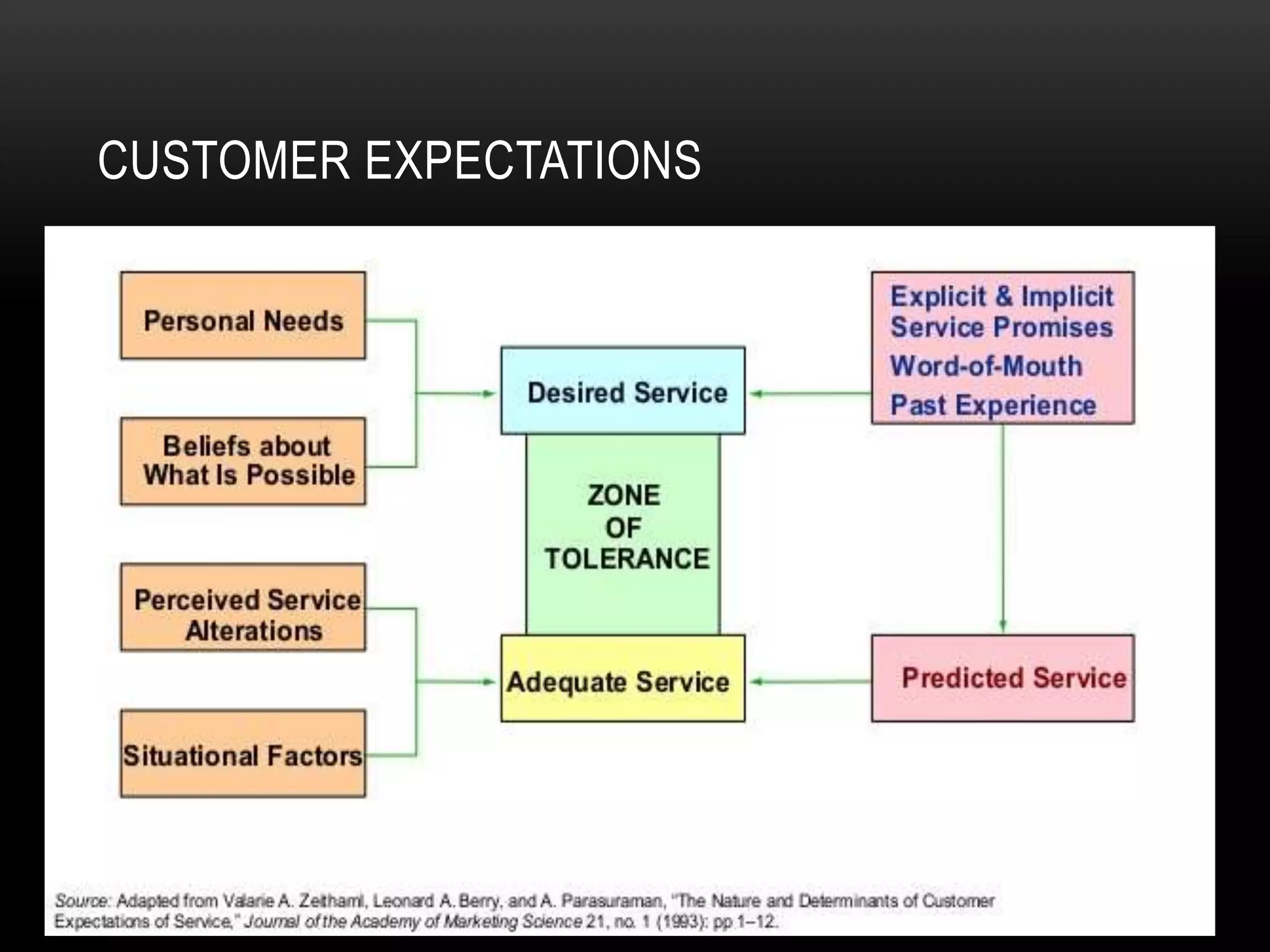
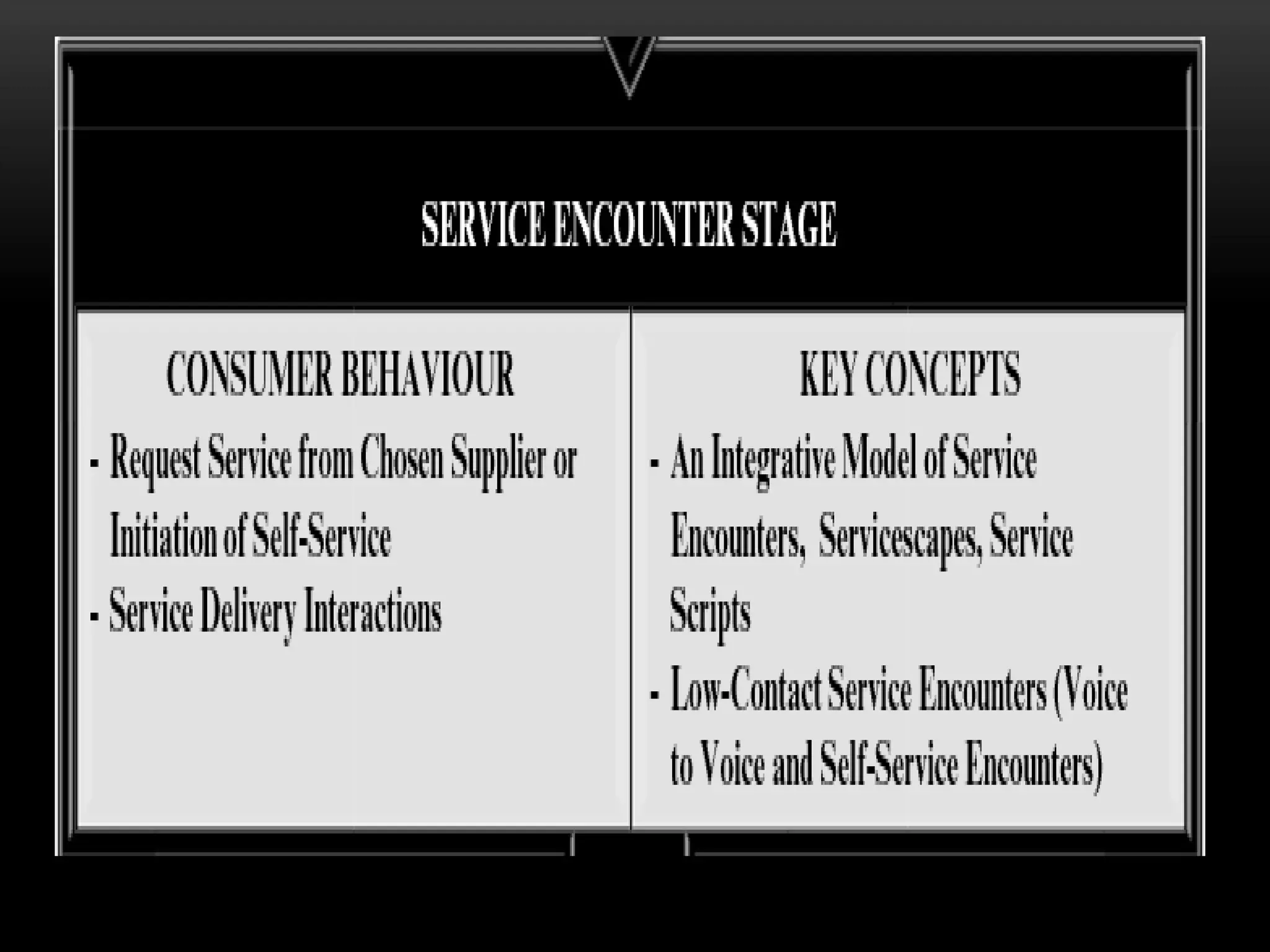
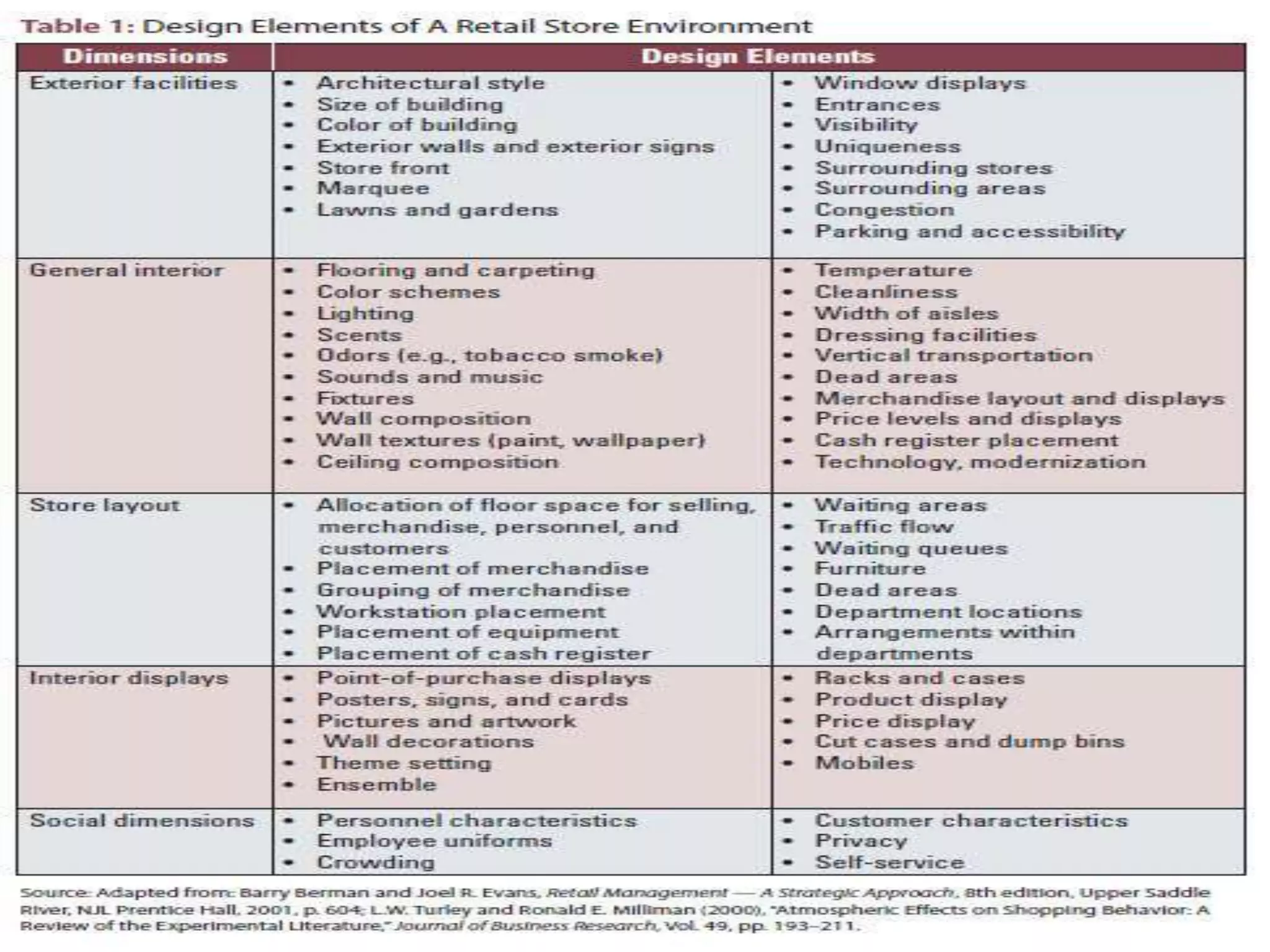
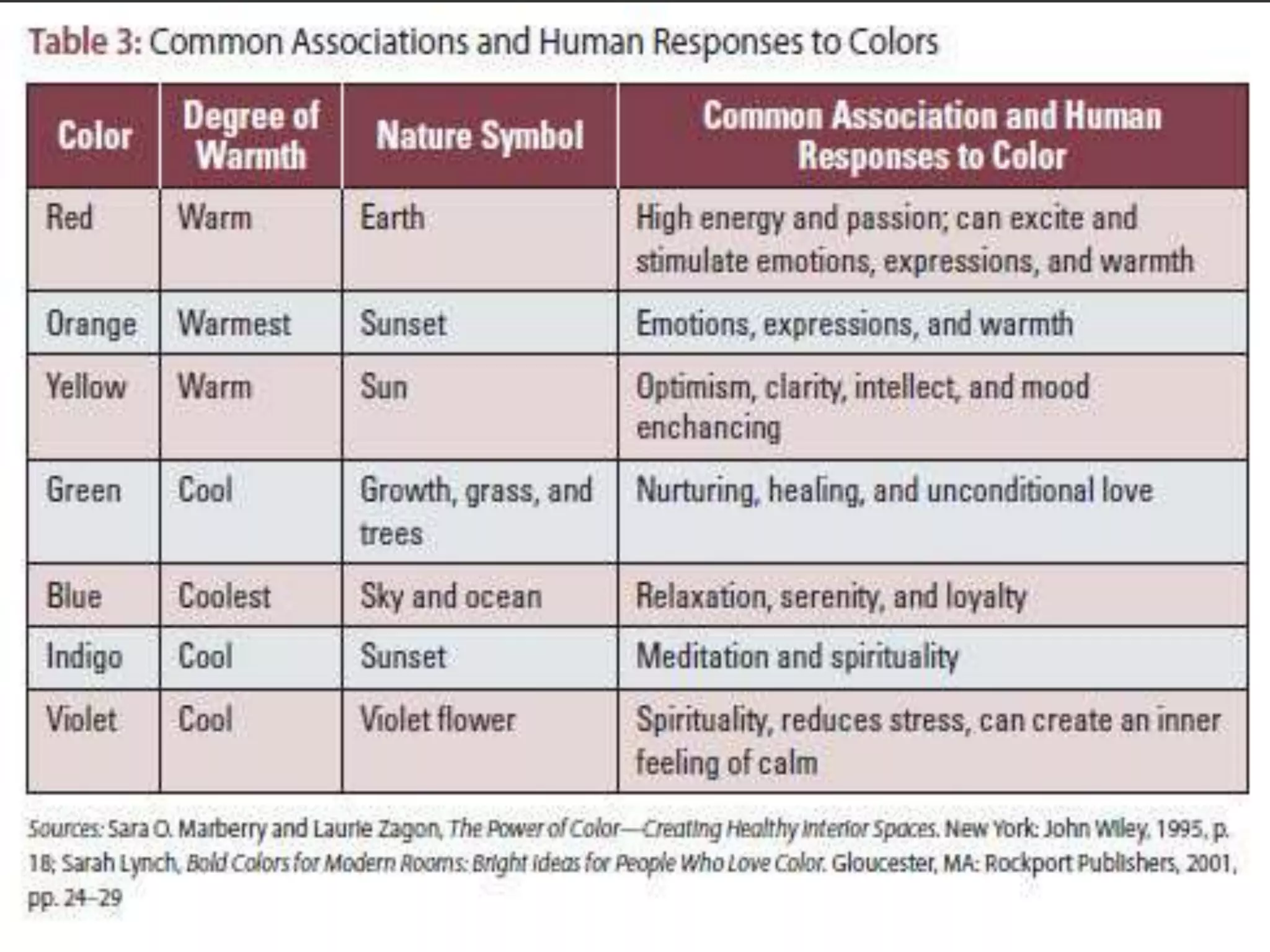
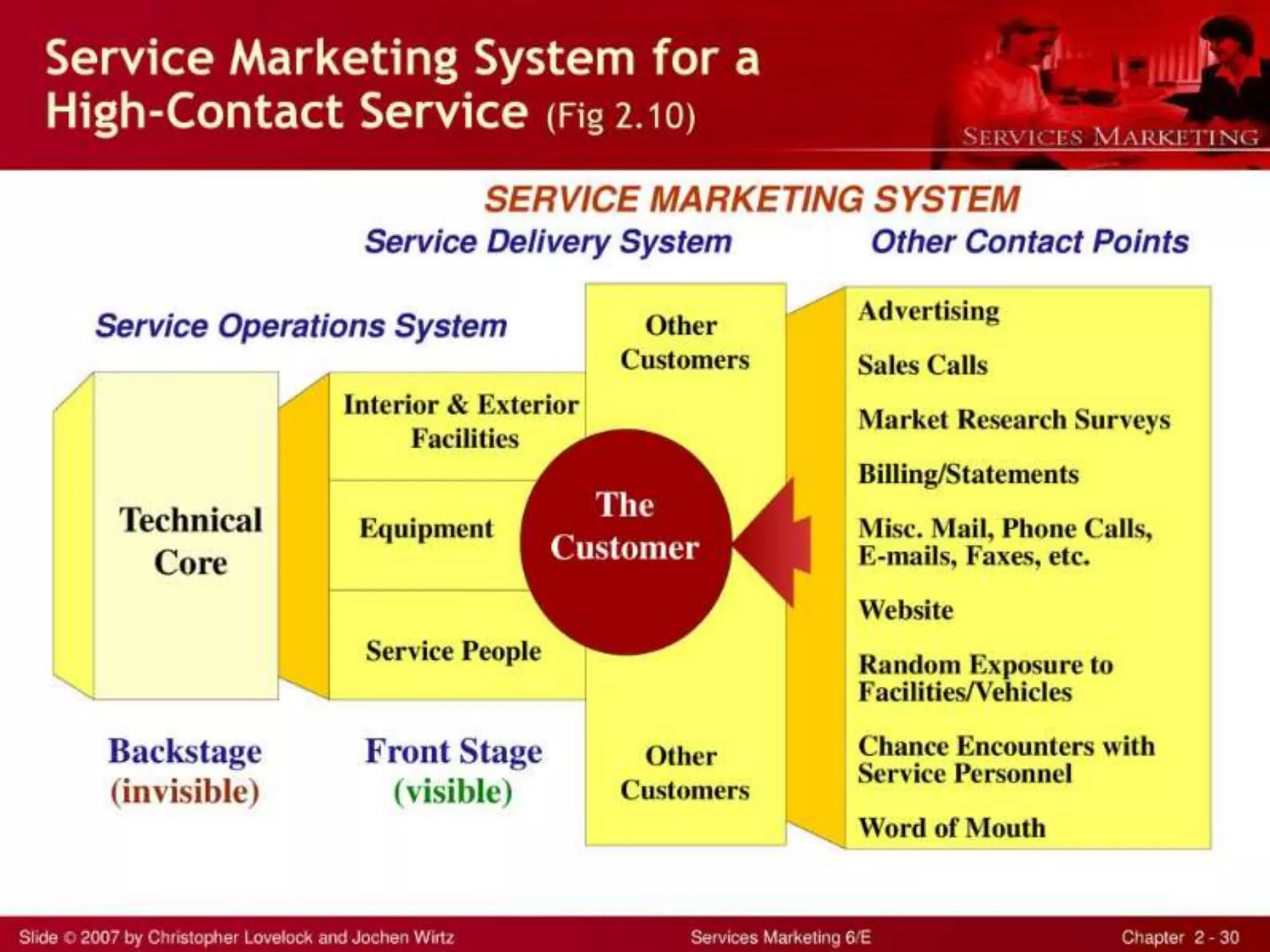
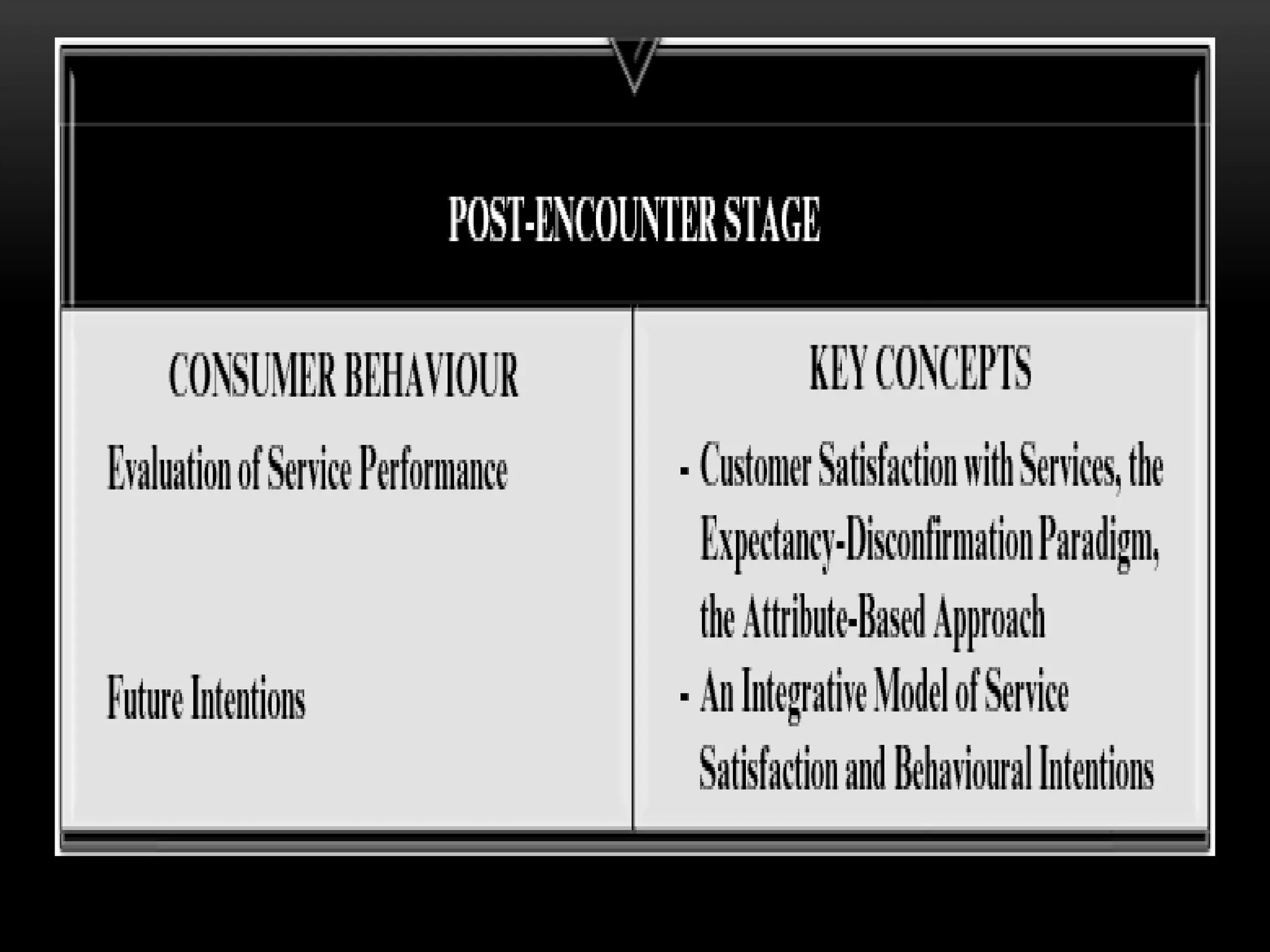
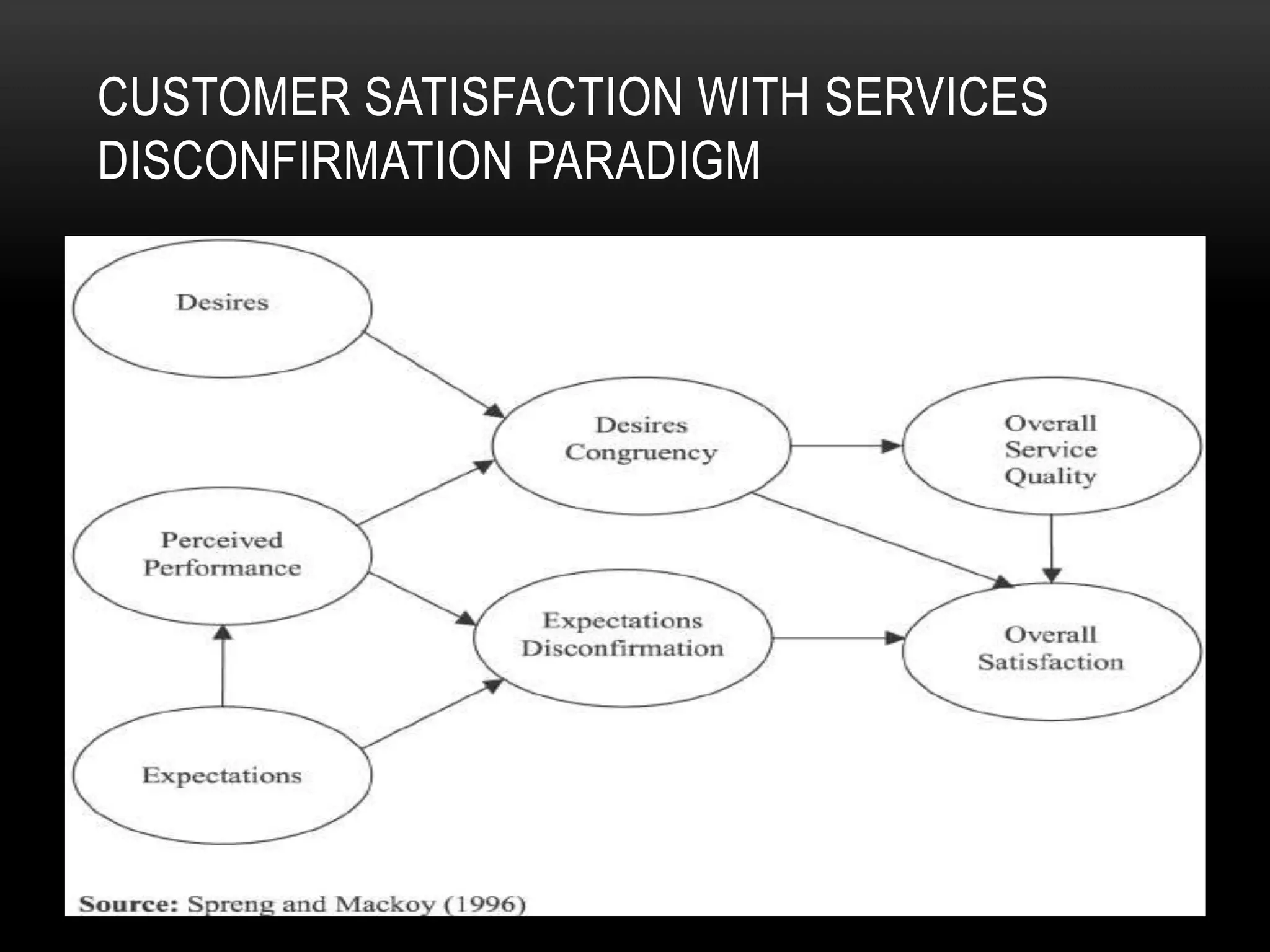
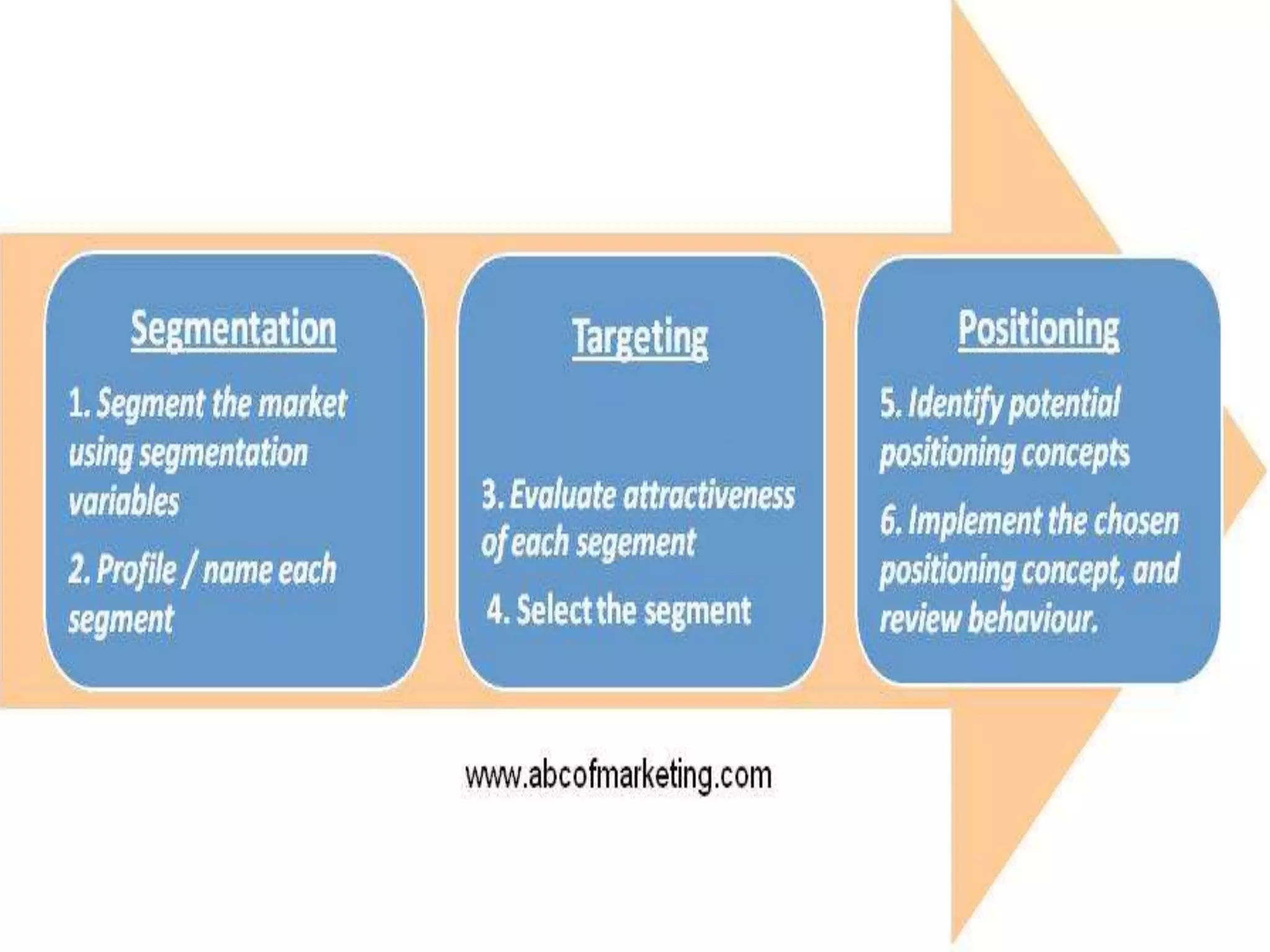
The document discusses the assessment of service market potential, including factors like market size, growth, competition, and profitability, specifically in the context of launching a Chinese cuisine restaurant. It covers classifications of services based on various criteria such as market segment, degree of tangibility, skills of the service provider, and customer contact, along with the expanded marketing mix known as the 7 P's. Additionally, it touches on market segmentation, targeting, and positioning to optimize marketing efforts.