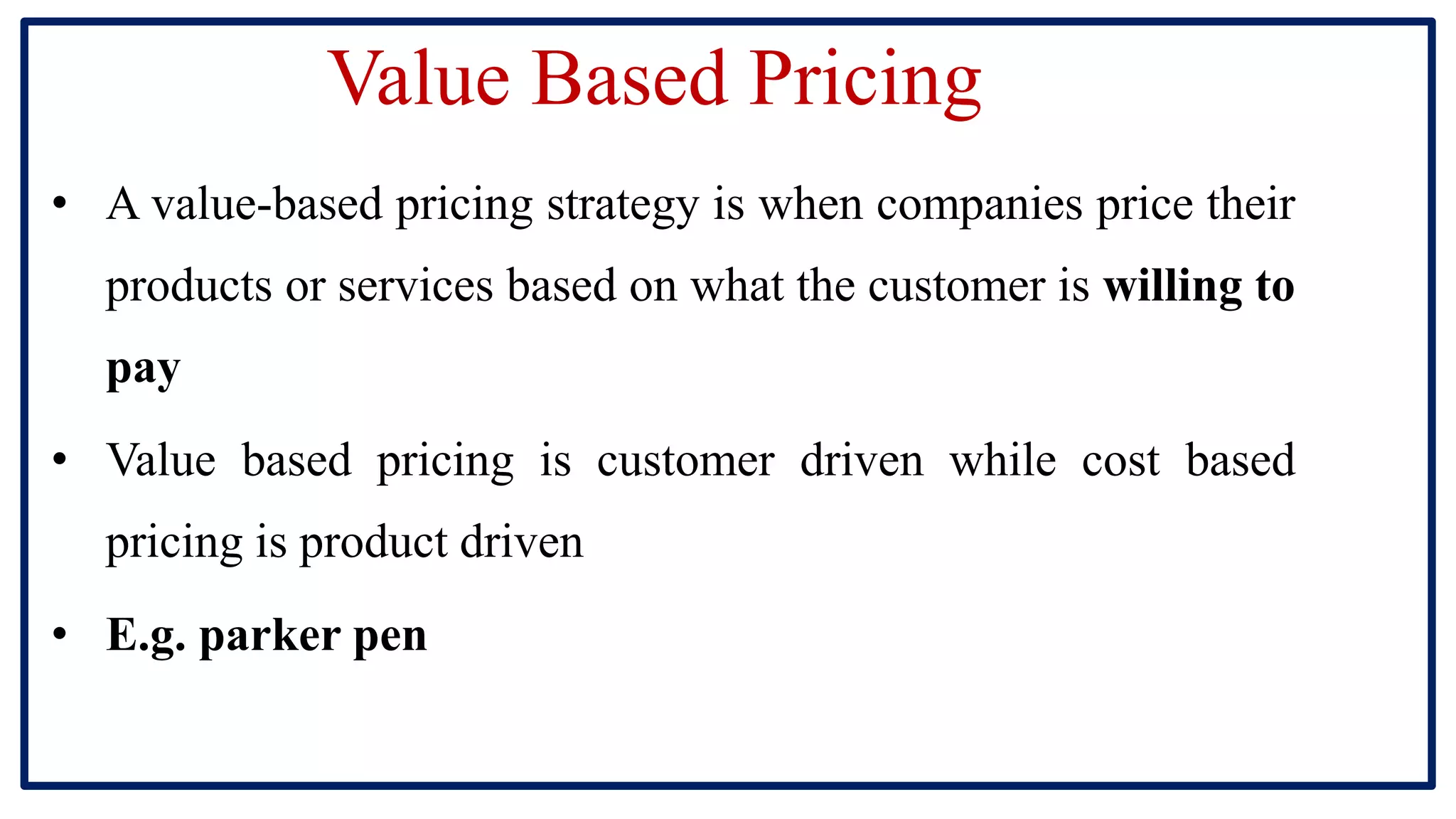
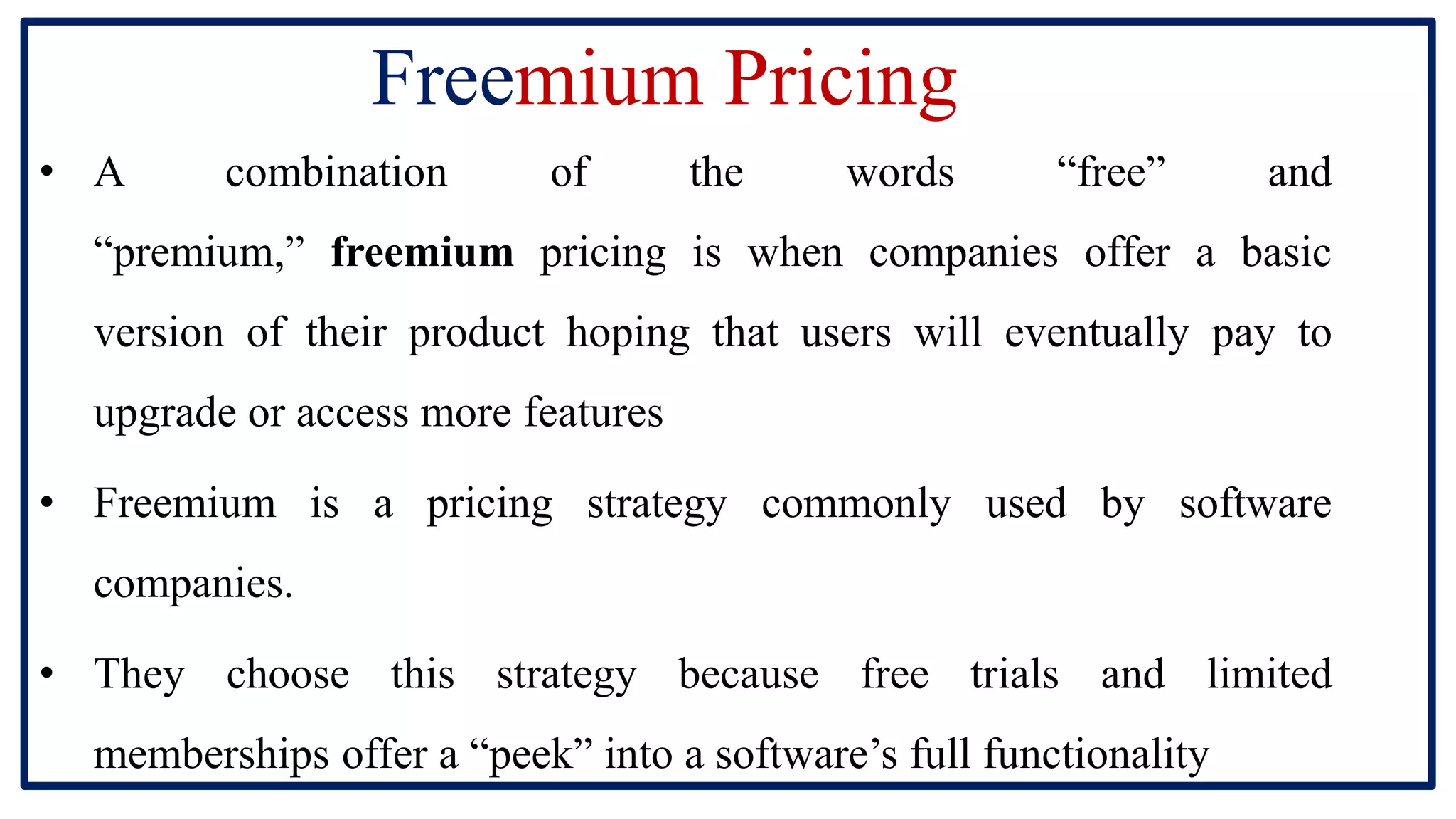
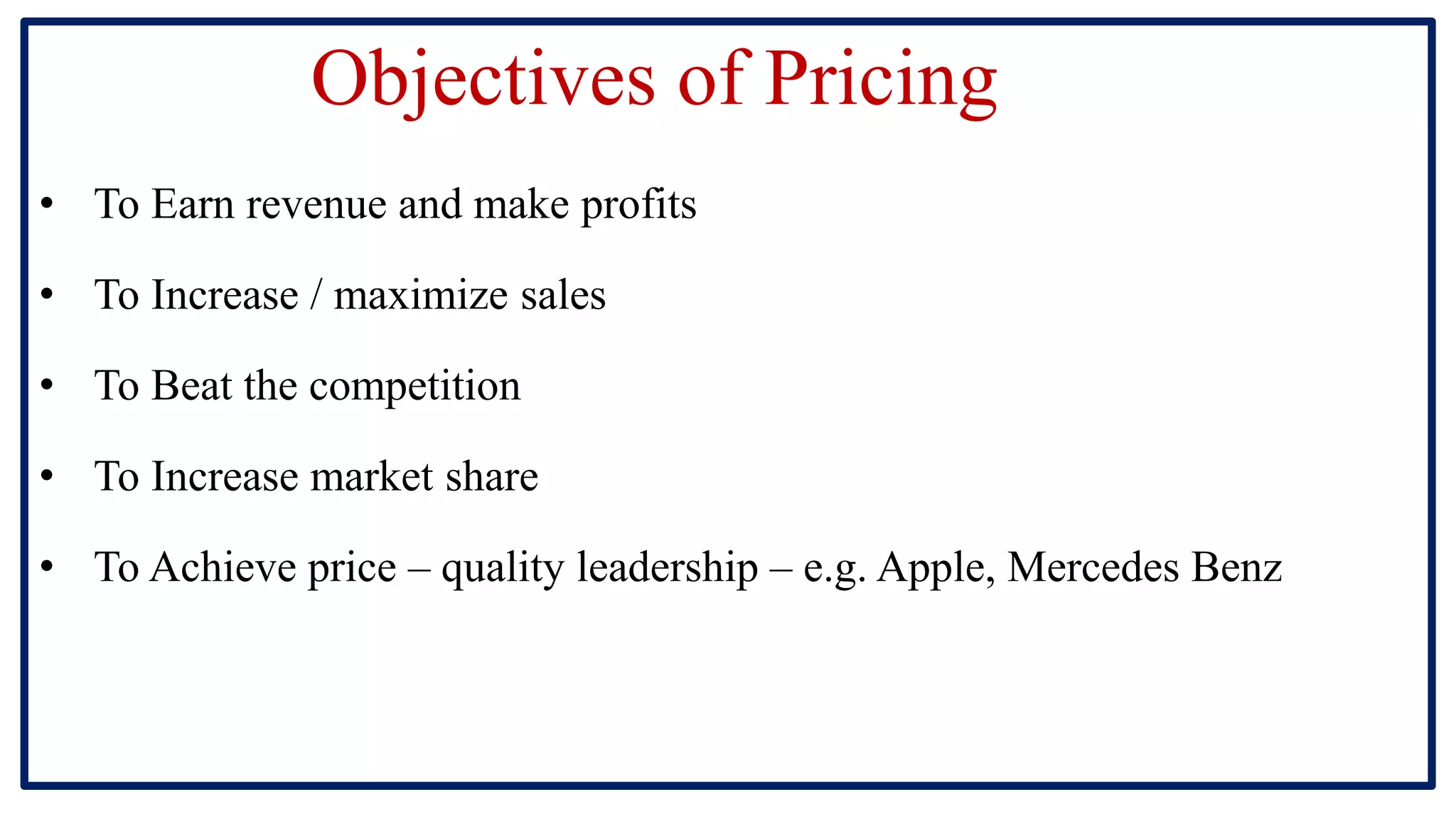
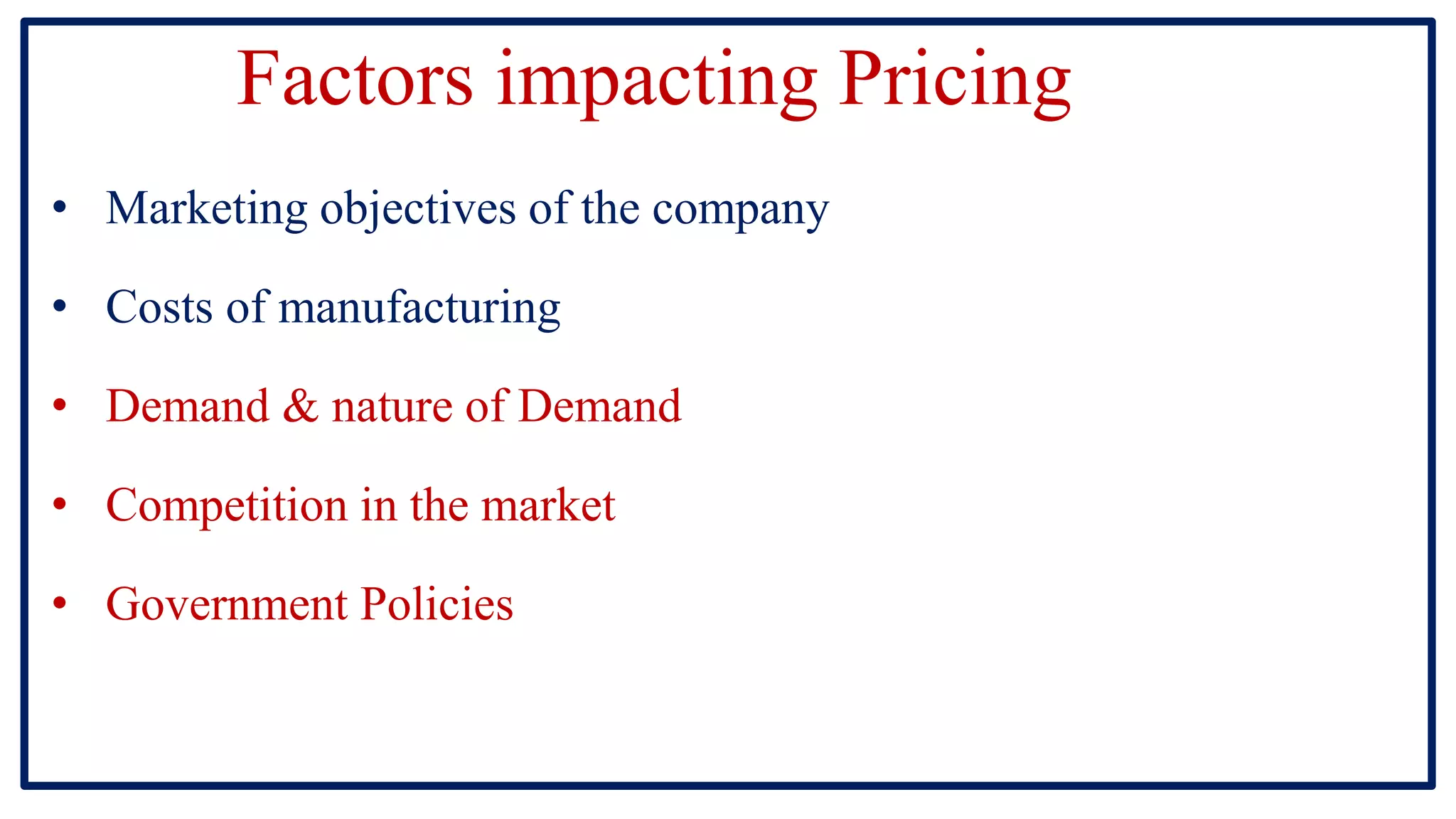
The document discusses pricing and pricing strategies. It defines pricing as the process of setting the price of a product or service. Setting prices can be challenging as prices that are too high will reduce sales and prices that are too low will not generate sufficient revenue. Pricing objectives include earning revenue, increasing sales, beating competition and gaining market share. Key factors that impact pricing are costs, demand, competition and government policies. Common methods for setting prices include cost-plus pricing, value-based pricing and competition-based pricing. Popular pricing strategies are skimming pricing, penetration pricing, dynamic pricing and bundle pricing.






![Cost Plus Pricing
• A cost-plus pricing is also called Mark Up pricing
• It’s also known as markup pricing since businesses who use
this strategy “mark up” their products based on how much
they’d like to profit.
• E.g. The shoes cost $25 to make, and the firm wants to make
a $25 profit on each sale. The company will set the price of
the shoes at $50 [at 100 percent Markup]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit6part1pricingandpricingstrategies-210416150300/75/Unit-6-part_1_pricing_and_pricing_strategies-9-2048.jpg)